| |||
|---|---|---|---|
The year 2013 in Archosaur paleontology was eventful. Archosaurs include the only living dinosaur group — birds — and the reptile crocodilians, plus all extinct dinosaurs, extinct crocodilian relatives, and pterosaurs. Archosaur palaeontology is the scientific study of those animals, especially as they existed before the Holocene Epoch began about 10,000 years ago. The year 2013 in paleontology included various significant developments regarding archosaurs.
This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that have been described during the year 2013, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that occurred in the year 2013.
Pseudosuchians
Research
- Mesoeucrocodylian fossils, which might be the first recorded Cenozoic fossils of atoposaurids, are described from the Eocene Kaninah Formation of Yemen by Stevens et al. (2013).[1]
New taxa
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sp. nov |
Valid[3] |
Puértolas-Pascual, Canudo & Moreno-Azanza |
Late Cretaceous (late Maastrichtian) |
A eusuchian crocodylomorph belonging to the family Allodaposuchidae. Originally described as a species of Allodaposuchus; Narváez et al. (2016) transferred it to the genus Agaresuchus.[4] |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Pol et al. |
Late Jurassic (Oxfordian) |
Sediments alternatively referred by different authors to the Cañadón Calcáreo Formation or to the Puesto Almada Member of the Cañadón Asfalto Formation[5] |
A non-crocodyliform crocodylomorph. The type species is Almadasuchus figarii. |
|||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Buscalioni et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A goniopholidid, a species of Anteophthalmosuchus. |
||||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Sues & Schoch |
Late Triassic (Norian) |
A non-crocodylomorph loricatan pseudosuchian, a new genus for "Halticosaurus" orbitoangulatus Huene (1932). |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Montefeltro et al. |
Late Jurassic |
A neosuchian crocodyliform related to Rugosuchus and Shamosuchus. The type species is Batrachomimus pastosbonensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Conrad et al. |
Miocene |
A new genus for "Crocodylus" pigotti. |
||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Bona & Carabajal |
Late Miocene |
A caiman. Originally described as a species of Caiman; transferred to the separate genus Paranasuchus by Bona et al. (2024).[11] |
||||
|
Sp. nov |
Fortier & Rincón |
Pleistocene |
A caiman, a species of Caiman. Considered to be a junior synonym of extant spectacled caiman (Caiman crocodilus) by Cidade et al. (2019).[13] |
|||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Hastings et al. |
Early or middle Miocene |
A caiman. The type species is Centenariosuchus gilmorei. |
||||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid[16] |
Martin et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
A pholidosaurid, a new genus for "Sunosuchus" thailandicus. |

| |||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Herrera, Gasparini & Fernández |
Late Jurassic (Tithonian) |
Neuquén Basin |
A metriorhynchid, a species of Cricosaurus. |
|||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Scheyer et al. |
Early Pliocene |
A species of Crocodylus. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Hastings et al. |
Probably early Miocene |
A caiman. The type species is Culebrasuchus mesoamericanus. |
||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Pinheiro et al. |
Itaboraí Basin |
A species of Eocaiman. |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Scheyer et al. |
Late Miocene |
A caiman. The type species is Globidentosuchus brachyrostris |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Marinho et al. |
Late Cretaceous |
A baurusuchid. The type species is Gondwanasuchus scabrosus. |
||||
|
Gen. et comb. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Buscalioni et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
A goniopholidid, a new genus for "Goniopholis" willetti Salisbury & Naish (2011); genus also contains a new species Hulkepholis plotos. |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Parrilla-Bel et al. |
Middle Jurassic (middle Callovian) |
A metriorhynchid. The type species is Maledictosuchus riclaensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Adams |
Early Cretaceous (late Aptian) |
A neosuchian crocodyliform. The type species is Paluxysuchus newmani. |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Small & Martz |
Late Triassic |
An aetosaur. The type species is Stenomyti huangae. |
||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Young et al. |
Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) |
A metriorhynchid, a species of Torvoneustes. |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid[26] |
Young et al. |
Middle Jurassic |
A metriorhynchid. The type species is Tyrannoneustes lythrodectikos. |

|
Newly named basal dinosauromorphs
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Martínez et al. |
Late Triassic (late Carnian) |
A silesaurid. The type species is Ignotosaurus fragilis. |
| |||
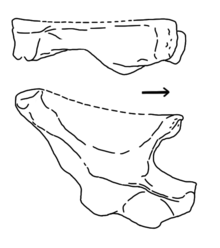
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Peecook et al. |
Middle Triassic (Anisian) |
A silesaurid. The type species is Lutungutali sitwensis. |

|
Non-avian dinosaurs
Research
- A new Troodontid Tooth is reported from Kallamedu Formation of India.[29]
- A study on the reproductive strategies of dinosaurs is published by Werner & Griebeler (2013).[30]
- A re-analysis of prior studies on the dinosaur growth rates is published by Myhrvold (2013).[31]
- A study on an assemblage of specimens of Aniksosaurus darwini from the Upper Cretaceous Bajo Barreal Formation (Argentina) evaluating whether the assemblage is truly monospecific and whether or not all the individuals died at the same time based on taphonomic data, is published by Ibiricu et al. (2013).[32]
- Redescription of Lusotitan atalaiensis and a study on the phylogenetic relationships of basal titanosauriform sauropods is published by Mannion et al. (2013).[33]
- A review of all fossil specimens referred to Euoplocephalus tutus, as well as specimens that were previously referred to Euoplocephalus but subsequently were assigned to different genera, is published by Arbour & Currie (2013).[34]
New taxa
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Evans, Larson & Currie |
Late Cretaceous (latest Maastrichtian) |
A dromaeosaurid. The type species is Acheroraptor temertyorum. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Evans et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Santonian) |
A pachycephalosaurid. The type species is Acrotholus audeti. |

| |||
|
Nom. nov |
Valid |
Easter |
Late Cretaceous |
A member of Oviraptoridae; a replacement name for Ingenia Barsbold (1981). Funston et al. (2018) considered this genus to be a junior synonym of the genus Heyuannia.[38] |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Brown et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Campanian) |
A relative of Orodromeus, Oryctodromeus and Zephyrosaurus. The type species is Albertadromeus syntarsus. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid[41] |
Choiniere et al. |
Middle or Late Jurassic (Callovian/Oxfordian boundary, more likely Callovian) |
A coelurosaur theropod, more closely related to ornithomimosaurs and maniraptorans than to tyrannosauroids. The type species is Aorun zhaoi. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Godefroit et al. |
Middle or Late Jurassic |
A basal member of Avialae[42] or a troodontid.[43] The type species is Aurornis xui. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov. |
Valid |
Machado et al. |
Late Cretaceous |
A titanosaur. The type species is Brasilotitan nemophagus. | ||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wick & Lehman |
Late Cretaceous (early Maastrichtian) |
A chasmosaurine ceratopsian. The type species is Bravoceratops polyphemus. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Prieto-Márquez et al. |
Late Cretaceous (late Maastrichtian) |
A lambeosaurine hadrosaurid related to Aralosaurus. The type species is Canardia garonnensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Farke & Sertich |
Late Cretaceous (Turonian) |
An abelisauroid theropod. The type species is Dahalokely tokana. |
| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Chen et al. |
Cretaceous (Albian or Cenomanian) |
A nodosaurid. The type species is Dongyangopelta yangyanensis. |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Godefroit et al. |
Middle or Late Jurassic |
A member of Paraves. The type species is Eosinopteryx brevipenna. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Kirkland et al. |
Early Cretaceous (early Albian) |
A nodosaurid. The type species is Europelta carbonensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Lü et al. |
Late Cretaceous |
A sauropod, a member of Somphospondyli. The type species is Gannansaurus sinensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wang et al. |
Late Cretaceous |
An oviraptorid. The type species is Ganzhousaurus nankangensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Pu et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
A therizinosaur. The type species is Jianchangosaurus yixianensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wei et al. |
Late Cretaceous |
An oviraptorid theropod. The type species is Jiangxisaurus ganzhouensis. |
| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Longrich |
Late Cretaceous (middle Campanian) |
A chasmosaurine ceratopsian. The type species is Judiceratops tigris. |

| |||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Brusatte & Benson |
Late Jurassic (Tithonian) |
Kimmeridge Clay |
A basal tyrannosauroid, a new genus for "Stokesosaurus" langhami (Benson, 2008). |
|||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Ibiricu et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian or Turonian) |
A rebbachisaurid sauropod. The type species is Katepensaurus goicoecheai. |

| |||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Bell & Brink |
Late Cretaceous (Santonian) |
A lambeosaurine hadrosaurid, a new genus for "Procheneosaurus" convincens. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Longrich et al. |
Late Cretaceous (late Campanian) |
A caenagnathid oviraptorosaur. The type species is Leptorhynchos gaddisi.[60] Originally genus also contained "Ornithomimus" elegans Parks (1933),[59] but this species was subsequently transferred to the separate genus Citipes.[61] |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Loewen et al. |
Late Cretaceous (middle Campanian) |
A tyrannosaurine tyrannosaurid. The type species is Lythronax argestes. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Lü et al. |
Late Cretaceous |
An oviraptorosaur. The type species is Nankangia jiangxiensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov. |
Valid |
Sampson et al. |
Late Cretaceous (late Campanian) |
A centrosaurine ceratopsian. The type species is Nasutoceratops titusi. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Le Loeuff, Suteethorn & Buffetaut |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A basal member of Titanosauria. The type species is Normanniasaurus genceyi. |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Nesbitt et al. |
Middle Triassic (late Anisian) |
The oldest known dinosaur or the sister taxon of the Dinosauria. The type species is Nyasasaurus parringtoni. |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid[68] |
Penkalski |
Late Cretaceous (late Campanian) |
An ankylosaurine ankylosaurid. The type species is Oohkotokia horneri. The species was subsequently argued by Arbour and Currie (2013) to be a junior synonym of Scolosaurus cutleri.[34] |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Coria et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Campanian) |
A lithostrotian titanosaur related to Aeolosaurus. The type species is Overosaurus paradasorum. |

| |||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Prieto-Márquez & Wagner |
Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) |
Originally described as a species of Saurolophus; subsequently made the type species of a separate genus Augustynolophus by Prieto-Márquez et al. (2015).[71] |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Cau, Dalla Vecchia & Fabbri |
Cenomanian |
A carcharodontosaurid. The type species is Sauroniops pachytholus. Announced in 2012; the final version of the article naming it was published in 2013. | 
| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Zanno & Makovicky |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) |
A Neovenatorid theropod. The type species is Siats meekerorum. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Yang et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
Hekou Group |
A member of Polacanthinae. The type species is Taohelong jinchengensis |
|||
|
Gen. et sp. nov. |
Valid |
Fanti et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
A rebbachisaurid sauropod. The type species is Tataouinea hannibalis. |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Coria et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Campanian) |
An ornithopod dinosaur. The type species is Trinisaura santamartaensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Xu et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Campanian) |
An oviraptorid. The type species is Wulatelong gobiensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wu et al. |
Middle Jurassic |
A sauropod related to Mamenchisaurus. The type species is Xinjiangtitan shanshanesis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Lü et al. |
Late Cretaceous |
An oviraptorid theropod dinosaur. The type species is Yulong mini. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wang et al. |
Early Late Cretaceous |
A basal member of Hadrosauroidea. The type species is Yunganglong datongensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Lü et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
A titanosauriform sauropod. The type species is Yunmenglong ruyangensis. |
Birds
Research
- Eleutherornis is re-examined and classified as a member of Phorusrhacidae by Angst et al. (2013).[82]
New taxa
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Acrocephalidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Acrocephalidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
An Acrocephalidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
An Acrocephalidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Aegithalidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
An Aegithalidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid [85] |
Late Miocene |
|
An Alcidae. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid [85] |
|
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Pliocene |
A Psittacidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
An Alaudidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 13 |
A member of Anatidae. Originally described as a species of Anas;[87] Zelenkov (2016) transferred the species to the genus Aythya.[88] |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Motacillidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Motacillidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Late Pliocene |
Middle Villafranchian |
An Accipitridae. |
||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pleistocene |
|
A Strigidae, this is the type species of the new genus. |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov. |
Valid |
Benson & Erickson |
A member of the family Sulidae. The type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
An Alaudidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pleistocene |
Rio de la Plata Estuary |
A Falconidae. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Certhiidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
MN 13 |
A Cettiidae. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Cettiidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Djebel Chambi |
A basal Cuculidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
A basal Galliformes. The type species of the genus. |
||||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
A basal member of the Ornithuromorpha. The type species of the new genus. |

| |||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Cinclidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Cinclidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Late Holocene |
Cave deposits |
A Scolopacidae. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Cave deposits |
A Picidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Hirundinidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Hirundinidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Hirundinidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
A Charadriiformes related to the Alcidae. The type species of the new genus. |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Emberizidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Emberizidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
An Emberizidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Emberizidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
An Emberizidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Eocene |
|
An Apodiformes, basal Hemiprocni Karkhu, 1992, Eocypselidae Harrison, 1984. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
MN 15-16 |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Alaudidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Comb. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
MN 1-2 |
A Threskiornithidae, a new genus for "Ibis" pagana Milne-Edwards (1868), the type species of the new genus with which it creates a Comb. nov. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pleistocene |
|
A Strigidae. |

| |||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Cretaceous |
An Enantiornithes Walker, 1981, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
An Acrocephalidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Hirundinidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Hirundinidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Cretaceous |
A basal member of Ornithuromorpha. This is the type species of the new genus. |

| ||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Pliocene |
A Psittacidae. The type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
A Cracticidae. The type species of the new genus. |

| ||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Laniidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Laniidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Laniidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Laniidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
An Alaudidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Alaudidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Alaudidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Alaudidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
A Coraciidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Miocene |
A Tytonidae. The type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Motacillidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Motacillidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Not Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. The name is not valid because the "é" in the species name should be a plain "e". |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Oligocene |
A Coliidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Oligocene |
A Strigidormes, Protostrigidae Wetmore, 1933, possibly a species of Oligostrix Fischer, 1983. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
An Oriolidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle-Late Turolian, MN12-13 |
Originally classified as a member of Otididae.[106] Zelenkov, Boev & Lazaridis (2016) reinterpreted it as a member of Gruiformes belonging to the family Eogruidae and the subfamily Ergilornithinae; the authors considered it to be a possible member of the genus Amphipelargus of uncertain specific assignment.[107] |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
1790 ± 40 BP |
A Strigidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Middle Miocene |
A Phoenicopteriformes, Palaelodidae Stejneger, 1885. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Paridae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Paridae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Paridae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Passeridae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Passeridae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Passeridae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Comb. nov. |
Valid |
Early Pliocene |
A Rallidae; a new genus for "Crex" zazhigini Kurochkin (1980), creating a Comb. nov. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Picidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
An Ardeidae. This is the type species of the new genus. |

| |||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Calcariidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
An Apterygidae. The type species of the new genus. |

| ||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Prunellidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Prunellidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
||||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Yang Jian |
Middle Paleocene |
A bird of uncertain phylogenetic placement, but placed in a new family: Qianshanornithidae fam. nov. Mayr, Yang, De Bast, Li et Smith, 2013, most closely resembling Strigogyps Gaillard, 1908, Ameghinornithidae Mourer-Chauviré, 1981. The type species of the new genus. |

| |||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Late Pleistocene |
Underwater Cave |
A Rallidae. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Regulidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
A Passeriformes. The type species of the new genus. |

| |||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Hirundinidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Early Oligocene |
A Gruiformes, Parvigruidae Mayr, 2005. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Oligocene |
Early Chattian, |
An Anatidae, Romainvilliinae Lambrecht, 1933. The type species of the new genus. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Muscicapidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Eocene |
A Neognathae related to the Charadriiformes. The type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Sittidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Not Valid, Junior homonym |
Jenö Kessler |
MN 15-16 |
A Sittidae; the name is preoccupied, a junior homonym of the brown-headed nuthatch, Sitta pusilla Latham, 1790. In the article describing the taxon its name is spelled Sitta pusilla or Sitta pussila on different pages.[83] |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Sittidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Sturnidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Sturnidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Sturnidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Cretaceous |
An Enantiornithes Walker, 1981. The type species the new genus. |

| ||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Sylviidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Sylviidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Turdidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Turdidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Turdidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
MN 15-16 |
A Turdidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Turdidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
A Turdidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late early Eocene |
|
A possible relative of the Threskiornithidae. The type species of the new genus. |
||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Mary Walters |
Initially thought to be a stone-curlew (a member of Burhinidae); subsequently argued to be a member of Presbyornithidae by De Pietri et al. (2016).[122] The type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Cretaceous |
An early member of the Ornithothoraces of uncertain phylogenetic placement. The type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
An Ornithuromorphae Chiappe, Ji, Ji et Norell, 1999, Yanornithiformes Zhou et Zhang, 2001, Yanornithidae Zhou et Zhang, 2001 |
||||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
A basal member of the Ornithuromorpha. The type species of new genus Yumenornis . |

| |||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Possibly Jiufotang Formation |
A member of the Enantiornithes Walker, 1981. The type species of the new genus. |

|
Newly named pterosaurs
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Andres & Myers |
Late Cretaceous (early Coniacian) |
A non-pteranodontoid pteranodontian. The type species is Alamodactylus byrdi. |
||||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Bennett |
Late Jurassic |
A new genus for "Pterodactylus" longicollum von Meyer (1854). |

| |||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Rodrigues & Kellner |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
Cambridge Greensand |
A new genus for "Ornithocheirus" nasutus Seeley (1870); genus might also contain "Ornithocheirus" colorhinus Seeley (1870). Rodrigues & Kellner (2013) also considered it possible that "Pterodactylus" sedgwickii Owen (1859) belonged to the genus Camposipterus,[128] but subsequently it was made the type species of a separate genus Aerodraco.[129] |

| ||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Kellner |
Early Cretaceous |
A tapejarid. The type species is Caupedactylus ybaka. |

| |||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Rodrigues & Kellner |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian/Turonian) |
A new genus for "Pterodactylus" cuvieri Bowerbank (1851). |

| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Martill & Etches |
Kimmeridgian |
A basal monofenestratan. |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Vremir et al. |
Late Cretaceous (early Maastrichtian) |
An azhdarchid. The type species is Eurazhdarcho langendorfensis. |

| |||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Rodrigues & Kellner |
Cretaceous (Albian to Cenomanian/Turonian) |
Cambridge Greensand |
A new genus for "Pterodactylus" giganteus Bowerbank (1846); genus also contains "Ornithocheirus" machaerorhynchus Seeley (1870) and "Ornithocheirus" microdon Seeley (1870). |

| ||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Andres & Myers |
Early Cretaceous (late Aptian or early Albian) |
A non-azhdarchid azhdarchoid. The type species is Radiodactylus langstoni. |
||||
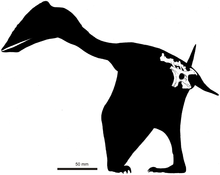
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Naish, Simpson & Dyke |
Early Cretaceous (probably early Aptian) |
An azhdarchoid. The type species is Vectidraco daisymorrisae. |
| |||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Codorniú & Gasparini |
Late Jurassic (Tithonian) |
A pterodactyloid pterosaur related to the clade Euctenochasmatia or Archaeopterodactyloidea. The type species is Wenupteryx uzi. |
References
- ^ Nancy J. Stevens; Robert V. Hill; Mohammed Al-Wosabi; Anne Schulp; Mustafa As-Saruri; Fuad Al-Nimey; Lea Ann Jolley; Yvonne Schulp-Stuip; Patrick O’Connor (2013). "A middle Eocene mesoeucrocodylian (Crocodyliformes) from the Kaninah Formation, Republic of Yemen". Geologos. 19 (3): 175–183. Bibcode:2013Geolg..19..175S. doi:10.2478/logos-2013-0010. S2CID 55179944.
- ^ E. Puértolas-Pascual; J. I. Canudo; M. Moreno-Azanza (2014). "The eusuchian crocodylomorph Allodaposuchus subjuniperus sp. nov., a new species from the latest Cretaceous (upper Maastrichtian) of Spain". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology. 26 (1): 91–109. doi:10.1080/08912963.2012.763034. S2CID 85004774.
- ^ "Puértolas, Eduardo, José I. Canudo & Miguel Moreno-Azanza. 2013. The eusuchian crocodylomorph Allodaposuchus subjuniperus sp. nov., a new species from the latest Cretaceous (upper Maastrichtian) of Spain". Archived from the original on 2019-09-08. Retrieved 2014-01-22.
- ^ I. Narváez; C.A. Brochu; F. Escaso; A. Pérez-García; F. Ortega (2016). "New Spanish Late Cretaceous eusuchian reveals the synchronic and sympatric presence of two allodaposuchids". Cretaceous Research. 65: 112–125. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2016.04.018.
- ^ a b Diego Pol; Oliver W. M. Rauhut; Agustina Lecuona; Juan M. Leardi; Xing Xu; James M. Clark (2013). "A new fossil from the Jurassic of Patagonia reveals the early basicranial evolution and the origins of Crocodyliformes". Biological Reviews. 88 (4): 862–872. doi:10.1111/brv.12030. hdl:11336/7536. PMID 23445256. S2CID 14648168.
- ^ a b Buscalioni, A.D.; Alcalá, L.; Espílez, E.; Mampel, L. (2013). "European Goniopholididae from the Early Albian Escucha Formation in Ariño (Teruel, Aragón, España)". Spanish Journal of Palaeontology. 28 (1): 103–122. doi:10.7203/sjp.28.1.17835. S2CID 73570030.
- ^ Hans-Dieter Sues; Rainer R. Schoch (2013). "Reassessment of cf. Halticosaurus orbitoangulatus from the Upper Triassic (Norian) of Germany – a pseudosuchian, not a dinosaur". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 168 (4): 859–872. doi:10.1111/zoj.12038. S2CID 83693894.
- ^ Felipe C. Montefeltro; Hans C. E. Larsson; Marco A. G. de França; Max C. Langer (2013). "A new neosuchian with Asian affinities from the Jurassic of northeastern Brazil". Naturwissenschaften. 100 (9): 835–841. Bibcode:2013NW....100..835M. doi:10.1007/s00114-013-1083-9. PMID 23893176. S2CID 11705304.
- ^ Jack L. Conrad; Kirsten Jenkins; Thomas Lehmann; Fredrick K. Manthi; Daniel J. Peppe; Sheila Nightingale; Adam Cossette; Holly M. Dunsworth; William E. H. Harcourt-Smithb; Kieran P. Mcnulty (2013). "New specimens of 'Crocodylus' pigotti (Crocodylidae) from Rusinga Island, Kenya, and generic reallocation of the species". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (3): 629–646. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.743404. S2CID 86141651.
- ^ Paula Bona; Ariana Paulina Carabajal (2013). "Caiman gasparinae sp. nov., a huge alligatorid (Caimaninae) from the late Miocene of Paraná, Argentina". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 37 (4): 462–473. doi:10.1080/03115518.2013.785335. hdl:11336/19850. S2CID 84672157.
- ^ Paula Bona; Francisco Barrios; Martín Daniel Ezcurra; María Victoria Fernandez Blanco; Giovanne Mendes Cidade (2024). "New taxa of giant caimans from the southernmost hyperdiverse wetlands of the South American late Miocene". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 22 (1). 2375027. doi:10.1080/14772019.2024.2375027.
- ^ Daniel Costa Fortier; Ascanio Daniel Rincón (2013). "Pleistocene crocodylians from Venezuela, and the description of a new species of Caiman". Quaternary International. 305: 141–148. Bibcode:2013QuInt.305..141F. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2012.03.018.
- ^ Giovanne M. Cidade; Daniel Fortier; Ascanio Daniel Rincón; Annie Schmaltz Hsiou (2019). "Taxonomic review of two fossil crocodylians from the Cenozoic of South America and its implications for the crocodylian fauna of the continent". Zootaxa. 4656 (3): 475–486. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4656.3.5. PMID 31716812. S2CID 202012442.
- ^ a b Alexander K. Hastings; Jonathan I. Bloch; Carlos A. Jaramillo; Aldo F. Rincon; Bruce J. Macfadden (2013). "Systematics and biogeography of crocodylians from the Miocene of Panama". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (2): 239–263. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.713814. S2CID 83972694.
- ^ Jeremy E. Martin; Komsorn Lauprasert; Eric Buffetaut; Romain Liard; Varavudh Suteethorn (2014). "A large pholidosaurid in the Phu Kradung Formation of north-eastern Thailand". Palaeontology. 57 (4): 757–769. doi:10.1111/pala.12086. S2CID 128482290.
- ^ "Martin, Jeremy E., Komsorn Lauprasert, Eric Buffetaut, Romain Liard & Varavudth Suteethorn. 2013. A large pholidosaurid in the Phu Kradung Formation of north-eastern Thailand". Archived from the original on 2019-08-20. Retrieved 2014-01-10.
- ^ Yanina Herrera; Zulma Gasparini; Marta S. Fernández (2013). "A new Patagonian species of Cricosaurus (Crocodyliformes, Thalattosuchia): first evidence of Cricosaurus in Middle–Upper Tithonian lithographic limestone from Gondwana". Palaeontology. 56 (3): 663–678. doi:10.1111/pala.12010. S2CID 131724027.
- ^ a b T. M. Scheyer; O. A. Aguilera; M. Delfino; D. C. Fortier; A. A. Carlini; R. Sánchez; J. D. Carrillo-Briceño; L. Quiroz; M. R. Sánchez-Villagra (2013). "Crocodylian diversity peak and extinction in the late Cenozoic of the northern Neotropics". Nature Communications. 4: Article number: 1907. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.1907S. doi:10.1038/ncomms2940. hdl:11336/13639. PMID 23695701.
- ^ André E.P. Pinheiro; Daniel C. Fortier; Diego Pol; Diógenes A. Campos; Lílian P. Bergqvist (2013). "A new Eocaiman (Alligatoridae, Crocodylia) from the Itaboraí Basin, Paleogene of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology. 25 (3): 327–337. doi:10.1080/08912963.2012.705838. hdl:11336/5404. S2CID 84897348.
- ^ Thiago da Silva Marinho; Fabiano Vidoi Iori; Ismar de Souza Carvalho; Felipe Mesquita de Vasconcellos (2013). "Gondwanasuchus scabrosus gen. et sp. nov., a new terrestrial predatory crocodyliform (Mesoeucrocodylia: Baurusuchidae) from the Late Cretaceous Bauru Basin of Brazil". Cretaceous Research. 44: 104–111. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2013.03.010.
- ^ Jara Parrilla-Bel; Mark T. Young; Miguel Moreno-Azanza; José Ignacio Canudo (2013). "The First Metriorhynchid Crocodylomorph from the Middle Jurassic of Spain, with Implications for Evolution of the Subclade Rhacheosaurini". PLOS ONE. 8 (1): e54275. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...854275P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054275. PMC 3553084. PMID 23372699.
- ^ Thomas L. Adams (2013). "A new neosuchian crocodyliform from the Lower Cretaceous (late Aptian) Twin Mountains Formation of North-Central Texas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (1): 85–101. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.713277. S2CID 140535823.
- ^ Bryan J. Small; Jeffrey W. Martz (2013). "A new aetosaur from the Upper Triassic Chinle Formation of the Eagle Basin, Colorado, USA". In S.J. Nesbitt; J.B. Desojo; R.B. Irmis (eds.). Anatomy, Phylogeny and Palaeobiology of Early Archosaurs and their Kin. Geological Society, London, Special Publications. Vol. 379. The Geological Society of London. pp. 393–412. doi:10.1144/SP379.18. S2CID 129503069.
- ^ Mark T. Young; Marco Brandalise De Andrade; Steve Etches; Brian L. Beatty (2013). "A new metriorhynchid crocodylomorph from the Lower Kimmeridge Clay Formation (Late Jurassic) of England, with implications for the evolution of dermatocranium ornamentation in Geosaurini". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 169 (4): 820–848. doi:10.1111/zoj.12082.
- ^ Mark T. Young; Marco Brandalise de Andrade; Stephen L. Brusatte; Manabu Sakamoto; Jeff Liston (2013). "The oldest known metriorhynchid super-predator: a new genus and species from the Middle Jurassic of England, with implications for serration and mandibular evolution in predacious clades". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 11 (4): 475–513. doi:10.1080/14772019.2012.704948. S2CID 85276836.
- ^ "Young, Mark T., Marco B. Andrade, Stephen L. Brusatte, Manabu Sakamoto & Jeff Liston. 2013. The oldest known metriorhynchid super-predator: a new genus and species from the Middle Jurassic of England, with implications for serration and mandibular evolution in predacious clades". Archived from the original on 2013-01-12. Retrieved 2014-01-10.
- ^ Ricardo N. Martínez; Cecilia Apaldetti; Oscar A. Alcober; Carina E. Colombi; Paul C. Sereno; Eliana Fernandez; Paula Santi Malnis; Gustavo A. Correa; Diego Abelin (2013). "Vertebrate succession in the Ischigualasto Formation". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. Memoir 12: Basal sauropodomorphs and the vertebrate fossil record of the Ischigualasto Formation (Late Triassic: Carnian-Norian) of Argentina: 10–30. Bibcode:2013JVPal..32S..10M. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.818546. hdl:11336/7771. S2CID 37918101.
- ^ Brandon R. Peecook; Christian A. Sidor; Sterling J. Nesbitt; Roger M. H. Smith; J. Sebastien Steyer; Kenneth D. Angielczyk (2013). "A new silesaurid from the upper Ntawere Formation of Zambia (Middle Triassic) demonstrates the rapid diversification of Silesauridae (Avemetatarsalia, Dinosauriformes)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (5): 1127–1137. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.755991. S2CID 140653951.
- ^ Goswami, A.; Prasad, G. V. R.; Verma, O.; Flynn, J. J.; Benson, R. B. J. (2013-04-16). "A troodontid dinosaur from the latest Cretaceous of India". Nature Communications. 4 (1): 1703. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.1703G. doi:10.1038/ncomms2716. ISSN 2041-1723.
- ^ Jan Werner; Eva Maria Griebeler (2013). "New insights into non-avian dinosaur reproduction and their evolutionary and ecological implications: linking fossil evidence to allometries of extant close relatives". PLOS ONE. 8 (8): e72862. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...872862W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072862. PMC 3749170. PMID 23991160.
- ^ Nathan P. Myhrvold (2013). "Revisiting the estimation of dinosaur growth rates". PLOS ONE. 8 (12): e81917. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...881917M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0081917. PMC 3864909. PMID 24358133.
- ^ Lucio M. Ibiricu; Rubén D. Martínez; Gabriel A. Casal; Ignacio A. Cerda (2013). "The behavioral implications of a multi-individual bonebed of a small theropod dinosaur". PLOS ONE. 8 (5): e64253. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...864253I. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064253. PMC 3655058. PMID 23691183.
- ^ Philip D. Mannion; Paul Upchurch; Rosie N. Barnes; Octávio Mateus (2013). "Osteology of the Late Jurassic Portuguese sauropod dinosaur Lusotitan atalaiensis (Macronaria) and the evolutionary history of basal titanosauriforms". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 168 (1): 98–206. doi:10.1111/zoj.12029.
- ^ a b Victoria M. Arbour; Philip J. Currie (2013). "Euoplocephalus tutus and the Diversity of Ankylosaurid Dinosaurs in the Late Cretaceous of Alberta, Canada, and Montana, USA". PLOS ONE. 8 (5): e62421. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...862421A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062421. PMC 3648582. PMID 23690940.
- ^ David C. Evans; Derek W. Larson; Philip J. Currie (2013). "A new dromaeosaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) with Asian affinities from the latest Cretaceous of North America". Naturwissenschaften. 100 (11): 1041–1049. Bibcode:2013NW....100.1041E. doi:10.1007/s00114-013-1107-5. PMID 24248432. S2CID 14978813.
- ^ David C. Evans; Ryan K. Schott; Derek W. Larson; Caleb M. Brown; Michael J. Ryan (2013). "The oldest North American pachycephalosaurid and the hidden diversity of small-bodied ornithischian dinosaurs". Nature Communications. 4: Article number 1828. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.1828E. doi:10.1038/ncomms2749. PMID 23652016.
- ^ Jesse Easter (2013). "A new name for the oviraptorid dinosaur "Ingenia" yanshini (Barsbold, 1981; preoccupied by Gerlach, 1957)". Zootaxa. 3737 (2): 184–190. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3737.2.6. PMID 25112747. S2CID 36962160.
- ^ G.F. Funston; S.E. Mendonca; P.J. Currie; R. Barsbold (2018). "Oviraptorosaur anatomy, diversity and ecology in the Nemegt Basin". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 494: 101–120. Bibcode:2018PPP...494..101F. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.10.023.
- ^ Caleb Marshall Brown; David C. Evans; Michael J. Ryan; Anthony P. Russell (2013). "New data on the diversity and abundance of small-bodied ornithopods (Dinosauria, Ornithischia) from the Belly River Group (Campanian) of Alberta". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (3): 495–520. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.746229. S2CID 129160518.
- ^ Jonah N. Choiniere; James M. Clark; Catherine A. Forster; Mark A. Norell; David A. Eberth; Gregory M. Erickson; Hongjun Chu; Xing Xu (2014). "A juvenile specimen of a new coelurosaur (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Middle–Late Jurassic Shishugou Formation of Xinjiang, People's Republic of China". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 12 (2): 177–215. doi:10.1080/14772019.2013.781067. S2CID 53538348.
- ^ "Choiniere, Jonah N., James M. Clark, Hongjun Chu, Catherine A. Forster, Mark A. Norell, David A. Eberth, Gregory M. Erickson & Xing Xu. 2013. A juvenile specimen of a new coelurosaur (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Middle-Late Jurassic Shishugou Formation of Xinjiang, People's Republic of China". Archived from the original on 2020-05-07. Retrieved 2014-01-10.
- ^ a b Pascal Godefroit; Andrea Cau; Hu Dong-Yu; François Escuillié; Wu Wenhao; Gareth Dyke (2013). "A Jurassic avialan dinosaur from China resolves the early phylogenetic history of birds". Nature. 498 (7454): 359–362. Bibcode:2013Natur.498..359G. doi:10.1038/nature12168. PMID 23719374. S2CID 4364892.
- ^ Stephen L. Brusatte; Graeme T. Lloyd; Steve C. Wang; Mark A. Norell (2014). "Gradual assembly of avian body plan culminated in rapid rates of evolution across the dinosaur-bird transition". Current Biology. 24 (20): 2386–2392. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.08.034. PMID 25264248. S2CID 8879023.
- ^ Elaine B. Machado; Leonardo dos S. Avilla; William R. Nava; Diogenes de A. Campos; Alexander W. A. Kellner (2013). "A new titanosaur sauropod from the Late Cretaceous of Brazil". Zootaxa. 3701 (3): 301–321. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3701.3.1. PMID 26191585.
- ^ Steven L. Wick; Thomas M. Lehman (2013). "A new ceratopsian dinosaur from the Javelina Formation (Maastrichtian) of West Texas and implications for chasmosaurine phylogeny". Naturwissenschaften. 100 (7): 667–682. Bibcode:2013NW....100..667W. doi:10.1007/s00114-013-1063-0. PMID 23728202. S2CID 16048008.
- ^ Albert Prieto-Márquez; Fabio M. Dalla Vecchia; Rodrigo Gaete; Àngel Galobart (2013). "Diversity, Relationships, and Biogeography of the Lambeosaurine Dinosaurs from the European Archipelago, with Description of the New Aralosaurin Canardia garonnensis". PLOS ONE. 8 (7): e69835. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...869835P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069835. PMC 3724916. PMID 23922815.
- ^ Andrew A. Farke; Joseph J. W. Sertich (2013). "An Abelisauroid Theropod Dinosaur from the Turonian of Madagascar". PLOS ONE. 8 (4): e62047. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...862047F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062047. PMC 3630149. PMID 23637961.
- ^ Rongjun Chen; Wenjie Zheng; Yoichi Azuma; Masateru Shibata; Tianliang Lou; Qiang Jin; Xingsheng Jin (2013). "A New Nodosaurid Ankylosaur from the Chaochuan Formation of Dongyang, Zhejiang Province, China". Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition). 87 (3): 658–671. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12077. S2CID 128421549.
- ^ Pascal Godefroit; Helena Demuynck; Gareth Dyke; Dongyu Hu; François Escuillié; Philippe Claeys (2013). "Reduced plumage and flight ability of a new Jurassic paravian theropod from China". Nature Communications. 4: Article number 1394. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.1394G. doi:10.1038/ncomms2389. PMID 23340434.
- ^ James I. Kirkland; Luis Alcalá; Mark A. Loewen; Eduardo Espílez; Luis Mampel; Jelle P. Wiersma (2013). "The Basal Nodosaurid Ankylosaur Europelta carbonensis n. gen., n. sp. from the Lower Cretaceous (Lower Albian) Escucha Formation of Northeastern Spain". PLOS ONE. 8 (12): e80405. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...880405K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080405. PMC 3847141. PMID 24312471.
- ^ Junchang Lü; Laiping Yi; Hui Zhong; Xuefang Wei (2013). "A New Somphospondylan Sauropod (Dinosauria, Titanosauriformes) from the Late Cretaceous of Ganzhou, Jiangxi Province of Southern China". Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition). 87 (3): 678–685. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12079. S2CID 140623061.
- ^ Shuo Wang; Chengkai Sun; Corwin Sullivan; Xing Xu (2013). "A new oviraptorid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous of southern China". Zootaxa. 3640 (2): 242–257. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3640.2.7. PMID 26000415.
- ^ Hanyong Pu; Yoshitsugu Kobayashi; Junchang Lü; Li Xu; Yanhua Wu; Huali Chang; Jiming Zhang; Songhai Jia (2013). "An Unusual Basal Therizinosaur Dinosaur with an Ornithischian Dental Arrangement from Northeastern China". PLOS ONE. 8 (5): e63423. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...863423P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063423. PMC 3667168. PMID 23734177.
- ^ Xuefang Wei; Hanyong Pu; Li Xu; Di Liu; Junchang Lü (2013). "A New Oviraptorid Dinosaur (Theropoda: Oviraptorosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Jiangxi Province, Southern China". Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition). 87 (4): 899–904. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12098. S2CID 129797420.
- ^ Nicholas R. Longrich (2013). "Judiceratops tigris, a New Horned Dinosaur from the Middle Campanian Judith River Formation of Montana". Bulletin of the Peabody Museum of Natural History. 54 (1): 51–65. doi:10.3374/014.054.0103. S2CID 129801786.
- ^ Stephen L. Brusatte; Roger B.J. Benson (2013). "The systematics of Late Jurassic tyrannosauroids (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from Europe and North America". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 58 (1): 47–54. doi:10.4202/app.2011.0141. hdl:20.500.11820/31f38145-54e7-48f8-819a-262601e93f2b. S2CID 53973677.
- ^ Lucio M. Ibiricu; Gabriel A. Casal; Rubén D. Martínez; Matthew C. Lamanna; Marcelo Luna; Leonardo Salgado (2013). "Katepensaurus goicoecheai, gen. et sp. nov., a Late Cretaceous rebbachisaurid (Sauropoda, Diplodocoidea) from central Patagonia, Argentina". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (6): 1351–1366. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.776562. hdl:11336/5389. S2CID 130685837.
- ^ Phil R. Bell; Kirstin S. Brink (2013). "Kazaklambia convincens comb. nov., a primitive juvenile lambeosaurine from the Santonian of Kazakhstan". Cretaceous Research. 45: 265–274. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2013.05.003.
- ^ a b Nicholas R. Longrich; Ken Barnes; Scott Clark; Larry Millar (2013). "Caenagnathidae from the Upper Campanian Aguja Formation of West Texas, and a Revision of the Caenagnathinae". Bulletin of the Peabody Museum of Natural History. 54 (1): 23–49. doi:10.3374/014.054.0102. S2CID 128444961.
- ^ Nicholas R. Longrich; Ken Barnes; Scott Clark; Larry Millar (2013). "Correction to "Caenagnathidae from the Upper Campanian Aguja Formation of West Texas, and a Revision of the Caenagnathinae"". Bulletin of the Peabody Museum of Natural History. 54 (2): 263–264. doi:10.3374/014.054.0204. S2CID 128898931.
- ^ Gregory Funston (2020). "Caenagnathids of the Dinosaur Park Formation (Campanian) of Alberta, Canada: anatomy, osteohistology, taxonomy, and evolution". Vertebrate Anatomy Morphology Palaeontology. 8: 105–153. doi:10.18435/vamp29362. S2CID 221067979.
- ^ Mark A. Loewen; Randall B. Irmis; Joseph J. W. Sertich; Philip J. Currie; Scott D. Sampson (2013). "Tyrant Dinosaur Evolution Tracks the Rise and Fall of Late Cretaceous Oceans". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e79420. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...879420L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079420. PMC 3819173. PMID 24223179.
- ^ Junchang Lü; Laiping Yi; Hui Zhong; Xuefang Wei (2013). "A New Oviraptorosaur (Dinosauria: Oviraptorosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Southern China and Its Paleoecological Implications". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e80557. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...880557L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080557. PMC 3842309. PMID 24312233.
- ^ Scott D. Sampson; Eric K. Lund; Mark A. Loewen; Andrew A. Farke; Katherine E. Clayton (2013). "A remarkable short-snouted horned dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (late Campanian) of southern Laramidia". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 280 (1766): 20131186. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.1186. PMC 3730592. PMID 23864598.
- ^ Jean Le Loeuff; Suravech Suteethorn; Eric Buffetaut (2013). "A new sauropod dinosaur from the Albian of Le Havre (Normandy, France)". Oryctos. 10: 23–30. Archived from the original on 2013-10-13. Retrieved 2014-01-10.
- ^ Sterling J. Nesbitt; Paul M. Barrett; Sarah Werning; Christian A. Sidor; Alan J. Charig (2013). "The oldest dinosaur? A Middle Triassic dinosauriform from Tanzania". Biology Letters. 9 (1): 20120949. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2012.0949. PMC 3565515. PMID 23221875.
- ^ Paul Penkalski (2014). "A new ankylosaurid from the late Cretaceous Two Medicine Formation of Montana, USA". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 59 (3): 617–634. doi:10.4202/app.2012.0125. S2CID 55806847.
- ^ http://zoobank.org/References/518CF8C9-4900-426B-82B9-E2AE286046F4 [dead link]
- ^ Rodolfo A. Coria; Leonardo S. Filippi; Luis M. Chiappe; Rodolfo García; Andrea B. Arcucci (2013). "Overosaurus paradasorum gen. et sp. nov. , a new sauropod dinosaur (Titanosauria: Lithostrotia) from the Late Cretaceous of Neuquén, Patagonia, Argentina". Zootaxa. 3683 (4): 357–376. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3683.4.2. hdl:11336/21928. PMID 25250458.
- ^ Prieto-Márquez, A.; and Wagner, J.R. (2013). "Saurolophus morrisi, a new species of hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of the Pacific coast of North America". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 58 (2): 255–268. doi:10.4202/app.2011.0049. S2CID 55969908.
- ^ Albert Prieto-Márquez; Jonathan R. Wagner; Phil R. Bell; Luis M. Chiappe (2015). "The late-surviving 'duck-billed' dinosaur Augustynolophus from the upper Maastrichtian of western North America and crest evolution in Saurolophini". Geological Magazine. 152 (2): 225–241. Bibcode:2015GeoM..152..225P. doi:10.1017/S0016756814000284. S2CID 131049979.
- ^ Andrea Cau; Fabio M. Dalla Vecchia; Matteo Fabbri (2013). "A thick-skulled theropod (Dinosauria, Saurischia) from the Upper Cretaceous of Morocco with implications for carcharodontosaurid cranial evolution". Cretaceous Research. 40: 251–260. Bibcode:2013CrRes..40..251C. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2012.09.002.
- ^ Lindsay E. Zanno; Peter J. Makovicky (2013). "Neovenatorid theropods are apex predators in the Late Cretaceous of North America". Nature Communications. 4: Article number 2827. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.2827Z. doi:10.1038/ncomms3827. PMID 24264527.
- ^ Jing-Tao Yang; Hai-Lu You; Da-Qing Li; De-Lai Kong (2013). "First discovery of polacanthine ankylosaur dinosaur in Asia" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 51 (4): 265–277. doi:10.19615/j.cnki.1000-3118.2013.04.002.
- ^ Federico Fanti; Andrea Cau; Mohsen Hassine; Michela Contessi (2013). "A new sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Tunisia with extreme avian-like pneumatization". Nature Communications. 4: 2080. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.2080F. doi:10.1038/ncomms3080. PMID 23836048.
- ^ Rodolfo A. Coria; Juan J. Moly; Marcelo Reguero; Sergio Santillana; Sergio Marenssi (2013). "A new ornithopod (Dinosauria; Ornithischia) from Antarctica". Cretaceous Research. 41: 186–193. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2012.12.004. hdl:11336/76749.
- ^ Xing Xu; Qing-Wei Tan; Shuo Wang; Corwin Sullivan; David W. E. Hone; Feng-Lu Han; Qing-Yu Ma; Lin Tan; Dong Xiao (2013). "A new oviraptorid from the Upper Cretaceous of Nei Mongol, China, and its stratigraphic implications" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 51 (2): 85–101. doi:10.19615/j.cnki.1000-3118.2013.02.001.
- ^ Wen-hao Wu; Chang-fu Zhou; Oliver Wings; Toru Sekiya; Zhi-ming Dong (2013). "A new gigantic sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic of Shanshan, Xinjiang". Global Geology. 32 (3): 437–446. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.03.002.
- ^ Junchang Lü; Philip J. Currie; Li Xu; Xingliao Zhang; Hanyong Pu; Songhai Jia (2013). "Chicken-sized oviraptorid dinosaurs from central China and their ontogenetic implications". Naturwissenschaften. 100 (2): 165–175. Bibcode:2013NW....100..165L. doi:10.1007/s00114-012-1007-0. PMID 23314810. S2CID 206871470.
- ^ Run-Fu Wang; Hai-Lu You; Shi-Chao Xu; Suo-Zhu Wang; Jian Yi; Li-Juan Xie; Lei Jia; Ya-Xian Li (2013). "A New Hadrosauroid Dinosaur from the Early Late Cretaceous of Shanxi Province, China". PLOS ONE. 8 (10): e77058. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...877058W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077058. PMC 3800054. PMID 24204734.
- ^ Junchang Lü; Li Xu; Hanyong Pu; Xingliao Zhang; Yiyang Zhang; Songhai Jia; Huali Chang; Jiming Zhang; Xuefang Wei (2013). "A new sauropod dinosaur (Dinosauria, Sauropoda) from the late Early Cretaceous of the Ruyang Basin (central China)". Cretaceous Research. 44: 202–213. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2013.04.009.
- ^ Delphine Angst; Eric Buffetaut; Christophe Lécuyer; Romain Amiot (2013). ""Terror Birds" (Phorusrhacidae) from the Eocene of Europe Imply Trans-Tethys Dispersal". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e80357. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...880357A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080357. PMC 3842325. PMID 24312212.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv Eugen Kessler (2013). "Neogene songbirds (Aves, Passeriformes) from Hungary" (PDF). Hantkeniana. Contributions of the Department of Palaeontology. Eötvös University. 8: 37–149. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-01-09. Retrieved 2014-01-10.
- ^ a b N. Adam Smith (2014). "The fossil record and phylogeny of the auklets (Pan-Alcidae, Aethiini)" (PDF). Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 12 (2): 217–236. doi:10.1080/14772019.2012.742147. S2CID 73590587. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-08. Retrieved 2014-07-31.
- ^ a b http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:357ECC1A-DFE5-4C72-9BF2-260A547574C4 [dead link]
- ^ a b Albrecht Manegold (2013). "Two new parrot species (Psittaciformes) from the early Pliocene of Langebaanweg, South Africa, and their palaeoecological implications". Ibis. 155 (1): 127–139. doi:10.1111/ibi.12009.
- ^ a b c Eugen Kessler (2013). A Kárpát-medence madárvilágának őslénytani kézikönyve. Könyvmühely Kiadó Miskolc. pp. 1–458.
- ^ Nikita V. Zelenkov (2016). "Revision of Non-Passeriform Birds from Polgárdi (Hungary, Late Miocene): 1. Anseriformes". Paleontological Journal. 50 (5): 514–517. doi:10.1134/S0031030116050142. S2CID 88844648.
- ^ Z. N. Boev (2013). "Aquila kurochkini sp. n., a new Late Pliocene eagle (Aves, Accipitriformes) from Varshets (NW Bulgaria)". Paleontological Journal. 47 (11): 1344–1354. doi:10.1134/s003103011311004x. S2CID 140163441.
- ^ a b Kenneth E. Campbell, Jr.; Zbigniew M. Bocheński (2013). "Two new late Pleistocene miniature owls from Rancho La Brea, California" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 58 (4): 707–721. doi:10.4202/app.2011.0125. S2CID 129841219.
- ^ Richard D. Benson; Bruce R. Erickson (2013). "A new genus and species of booby (Sulidae: Aves) from the Pliocene of South Carolina, with a new corollary to the nature of sister taxa" (PDF). Science Museum of Minnesota Monograph (Paleontology). 7: 1–37.
- ^ Washington Jones; Andrés Rinderknecht; Rafael Migot; R. Ernesto Blanco (2013). "Body Mass Estimations and Paleobiological Inferences on a New Species of Large Caracara (Aves, Falconidae) from the Late Pleistocene of Uruguay". Journal of Paleontology. 87 (1): 151–158. doi:10.1666/12-026r.1. S2CID 83648963.
- ^ a b Cécile Mourer-Chauviré; Rodolphe Tabuce; El Mabrouk Essid; Laurent Marivaux; Hayet Khayati; Monique Vianey-Liaud; Mustapha Ben Haj Ali (2013). "A new taxon of stem group Galliformes and the earliest record for stem group Cuculidae from the Eocene of Djebel Chambi, Tunisia" (PDF). In Ursula B. Göhlich; Andreas Kroh (eds.). Paleornithological Research 2013. Proceedings of the 8th International Meeting of the Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution, Vienna, 2012. Naturhistorisches Museum Wien. pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-3-902421-82-1.
- ^ a b c Ya-Ming Wang; Jingmai K. O'Connor; Da-Qing Li; Hai-Lu You (2013). "Previously Unrecognized Ornithuromorph Bird Diversity in the Early Cretaceous Changma Basin, Gansu Province, Northwestern China". PLOS ONE. 8 (10): e77693. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...877693W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077693. PMC 3795672. PMID 24147058.
- ^ Trevor H. Worthy; Atholl Anderson; Christophe Sand (2013). "An extinct Austral snipe (Aves : Coenocorypha) from New Caledonia". Emu. 113 (4): 383–393. doi:10.1071/mu13019. S2CID 85169982.
- ^ Storrs L. Olson (2013). "Fossil woodpeckers from Bermuda with the description of a new species of Colaptes (Aves: Picidae)". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 126 (1): 17–24. doi:10.2988/0006-324X-126.1.17. S2CID 84248107.
- ^ N. Adam Smith (2013). "A New Species of Auk (Charadriiformes, Pan-Alcidae) from the Miocene of Mexico" (PDF). The Condor. 115 (1): 77–83. doi:10.1525/cond.2012.120066. S2CID 198154218. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-08. Retrieved 2014-07-31.
- ^ Daniel T. Ksepka; Julia A. Clarke; Sterling J. Nesbitt; Felicia B. Kulp; Lance Grande (2013). "Fossil evidence of wing shape in a stem relative of swifts and hummingbirds (Aves, Pan-Apodiformes)". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 280 (1761): 20130580. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.0580. PMC 3652446. PMID 23760643.
- ^ Vanesa L. De Pietri (2013). "Interrelationships of the Threskiornithidae and the phylogenetic position of the Miocene ibis 'Plegadis' paganus from the Saint-Gérand-le-Puy area in central France". Ibis. 155 (3): 544–560. doi:10.1111/ibi.12062.
- ^ E. N. Kurochkin; S. Chatterjee; K. E. Mikhailov (2013). "An embryonic enantiornithine bird and associated eggs from the Cretaceous of Mongolia". Paleontological Journal. 47 (11): 1252–1269. doi:10.1134/S0031030113110087. S2CID 86747842.
- ^ Jacqueline M. T. Nguyen; Trevor H. Worthy; Walter E. Boles; Suzanne J. Hand; Michael Archer (2013). "A new cracticid (Passeriformes : Cracticidae) from the Early Miocene of Australia". Emu. 113 (4): 374–382. doi:10.1071/mu13017. S2CID 85069421.
- ^ Cécile Mourer-Chauviré; Jean-Baptiste Peyrouse; Marguerite Hugueney (2013). "A new roller (Aves: Coraciiformes s. s.: Coraciidae) from the Early Miocene of the Saint-Gérand-le-Puy area, Allier, France" (PDF). In Ursula B. Göhlich; Andreas Kroh (eds.). Paleornithological Research 2013. Proceedings of the 8th International Meeting of the Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution, Vienna, 2012. Naturhistorisches Museum Wien. pp. 81–92. ISBN 978-3-902421-82-1.
- ^ Ursula B. Göhlich; Peter Ballmann (2013). "A new barn owl (Aves: Strigiformes: Tytonidae) from the Middle Miocene of the Nördlinger Ries (Germany) with remarks on the history of the owls" (PDF). In Ursula B. Göhlich; Andreas Kroh (eds.). Paleornithological Research 2013. Proceedings of the 8th International Meeting of the Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution, Vienna, 2012. Naturhistorisches Museum Wien. pp. 103–122. ISBN 978-3-902421-82-1.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (2013). "Late Oligocene mousebird converges on parrots in skull morphology". Ibis. 155 (2): 384–396. doi:10.1111/ibi.12034.
- ^ V. L. De Pietri; C. Mourer-Chauviré; U. Menkveld-Gfeller; C. A. Meyer; L. Costeur (2013). "An assessment of the Cenozoic avifauna of Switzerland, with a description of two fossil owls (Aves, Strigiformes)". Swiss Journal of Geosciences. 106 (2): 187–197. doi:10.1007/s00015-013-0127-7. S2CID 128688076.
- ^ a b Zlatozar Boev; Georgios Lazaridis; Evangelia Tsoukala (2013). "Otis hellenica sp. nov., a new Turolian bustard (Aves: Otididae) from Kryopigi (Chalkidiki, Greece)" (PDF). Geologica Balcanica. 42 (1–3): 59–65. doi:10.52321/GeolBalc.42.1-3.59. S2CID 246377339.
- ^ Nikita Zelenkov; Zlatozar Boev; Georgios Lazaridis (2016). "A large ergilornithine (Aves, Gruiformes) from the Late Miocene of the Balkan Peninsula". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 90 (1): 145–151. doi:10.1007/s12542-015-0279-z. S2CID 131264199.
- ^ Juan C. Rando; Josep A. Alcover; Storrs L. Olson; Harald Pieper (2013). "A new species of extinct scops owl (Aves: Strigiformes: Strigidae: Otus) from São Miguel Island (Azores Archipelago, North Atlantic Ocean)". Zootaxa. 3647 (2): 343–357. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3647.2.6. hdl:10261/85708. PMID 26295111.
- ^ Nikita V. Zelenkov (2013). "Cenozoic phoenicopteriform birds from central Asia" (PDF). Paleontological Journal. 47 (11): 1323–1330. doi:10.1134/S0031030113110178. S2CID 84607510.
- ^ Nikita V. Zelenkov (2013). "New finds and revised taxa of Early Pliocene birds from Western Mongolia" (PDF). In Ursula B. Göhlich; Andreas Kroh (eds.). Paleornithological Research 2013. Proceedings of the 8th International Meeting of the Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution, Vienna, 2012. Naturhistorisches Museum Wien. pp. 153–170. ISBN 978-3-902421-82-1.
- ^ Trevor H. Worthy; Jennifer P. Worthy; Alan J. D. Tennyson; R. Paul Scofield (2013). "A bittern (Aves: Ardeidae) from the early Miocene of New Zealand". Paleontological Journal. 47 (11): 1331–1343. doi:10.1134/s0031030113110154. hdl:2328/35957. S2CID 85257680.
- ^ Trevor H. Worthy; Jennifer P. Worthy; Alan J. D. Tennyson; Steven W. Salisbury; Suzanne J. Hand; R. Paul Scofield (2013). "Miocene fossils show that kiwi (Apteryx, Apterygidae) are probably not phyletic dwarves" (PDF). In Ursula B. Göhlich; Andreas Kroh (eds.). Paleornithological Research 2013. Proceedings of the 8th International Meeting of the Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution, Vienna, 2012. Naturhistorisches Museum Wien. pp. 63–80. ISBN 978-3-902421-82-1.
- ^ Gerald Mayr; Jian Yang; Eric De Bast; Cheng-Sen Li; Thierry Smith (2013). "A Strigogyps-like bird from the middle Paleocene of China with an unusual grasping foot". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (4): 895–901. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.748059. S2CID 86051919.
- ^ David W. Steadman; J. R. Morris; N. A. Wright (2013). "A new species of Late Pleistocene rail (Aves: Rallidae) from Abaco, the Bahamas" (PDF). Paleontological Journal. 47 (11): 1355–1364. doi:10.1134/s0031030113110130. S2CID 129917862. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-12-28. Retrieved 2017-06-28.
- ^ Zbigniew M. Bocheński; Teresa Tomek; Krzysztof Wertz; Ewa Świdnicka (2013). "The third nearly complete passerine bird from the early Oligocene of Europe". Journal of Ornithology. 154 (4): 923–931. doi:10.1007/s10336-013-0958-z. S2CID 15312012.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (2013). "Parvigruidae (Aves, core Gruiformes) from the early Oligocene of Belgium". Palaeobiodiversity and Palaeoenvironments. 93 (1): 77–89. doi:10.1007/s12549-012-0083-7. S2CID 129818639.
- ^ Gerald Mayr; Vanesa L. De Pietri (2013). "A goose-sized anseriform bird from the late Oligocene of France: the youngest record and largest species of Romainvilliinae". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 87 (3): 423–430. doi:10.1007/s12542-013-0165-5. S2CID 84593598.
- ^ Sara Bertelli; Bent E. K. Lindow; Gareth J. Dyke; Gerald Mayr (2013). "Another charadriiform-like bird from the lower Eocene of Denmark". Paleontological Journal. 47 (11): 1282–1301. doi:10.1134/S0031030113110026. hdl:11336/7192. S2CID 85141394.
- ^ Jingmai K. O’Connor; Yuguang Zhang; Luis M. Chiappe; Qingjin Meng; Li Quanguo; Liu Di (2013). "A new enantiornithine from the Yixian Formation with the first recognized avian enamel specialization". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.719176. S2CID 85261944.
- ^ Nathan D. Smith; Lance Grande; Julia A. Clarke (2013). "A new species of Threskiornithidae-like bird (Aves, Ciconiiformes) from the Green River Formation (Eocene) of Wyoming". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (2): 363–381. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.722898. S2CID 86753750.
- ^ Walter E. Boles; Melanie A. Finch; Rene H. Hofheins; Patricia Vickers-Rich; Mary Walters; Thomas H. Rich (2013). "A fossil stone-curlew (Aves: Burhinidae) from the Late Oligocene/Early Miocene of South Australia" (PDF). In Ursula B. Göhlich; Andreas Kroh (eds.). Paleornithological Research 2013. Proceedings of the 8th International Meeting of the Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution, Vienna, 2012. Naturhistorisches Museum Wien. pp. 43–61. ISBN 978-3-902421-82-1.
- ^ Vanesa L. De Pietri; R. Paul Scofield; Nikita Zelenkov; Walter E. Boles; Trevor H. Worthy (2016). "The unexpected survival of an ancient lineage of anseriform birds into the Neogene of Australia: the youngest record of Presbyornithidae". Royal Society Open Science. 3 (2): 150635. Bibcode:2016RSOS....350635D. doi:10.1098/rsos.150635. PMC 4785986. PMID 26998335.
- ^ Xuri Wang; Luis M. Chiappe; Fangfang Teng; Qiang Ji (2013). "Xinghaiornis lini (Aves: Ornithothoraces) from the Early Cretaceous of Liaoning: An Example of Evolutionary Mosaic in Early Birds". Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition). 87 (3): 686–689. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12080. S2CID 84484606.
- ^ Xu-ri Wang; Qiang Ji; Fang-fang Teng; Ke-mo Jin (2013). "A new species of Yanornis (Aves: Ornithurae) from the Lower Cretaceous strata of Yixian, Liaoning Province". Geological Bulletin of China. 32 (4): 601–606.
- ^ Zihui Zhang; Luis M. Chiappe; Gang Han; Anusuya Chinsamy (2013). "A large bird from the Early Cretaceous of China: new information on the skull of enantiornithines". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 33 (5): 1176–1189. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.762708. S2CID 84677039.
- ^ a b Brian Andres; Timothy S. Myers (2013). "Lone Star Pterosaurs". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 103 (3–4): 383–398. doi:10.1017/S1755691013000303. S2CID 84617119.
- ^ S. Christopher Bennett (2013). "New information on body size and cranial display structures of Pterodactylus antiquus, with a revision of the genus". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 87 (2): 269–289. doi:10.1007/s12542-012-0159-8. S2CID 83722829.
- ^ a b c d Taissa Rodrigues; Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner (2013). "Taxonomic review of the Ornithocheirus complex (Pterosauria) from the Cretaceous of England". ZooKeys (308): 1–112. doi:10.3897/zookeys.308.5559. PMC 3689139. PMID 23794925.
- ^ Borja Holgado; Rodrigo V. Pêgas (2020). "A taxonomic and phylogenetic review of the anhanguerid pterosaur group Coloborhynchinae and the new clade Tropeognathinae". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 65. doi:10.4202/app.00751.2020. S2CID 222075296.
- ^ Alexander W. A. Kellner (2013). "A new unusual tapejarid (Pterosauria, Pterodactyloidea) from the Early Cretaceous Romualdo Formation, Araripe Basin, Brazil". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 103 (3–4): 409–421. doi:10.1017/S1755691013000327. S2CID 131574480.
- ^ David M. Martill; Steve Etches (2013). "A new monofenestratan pterosaur from the Kimmeridge Clay Formation (Upper Jurassic, Kimmeridgian) of Dorset, England". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 58 (2): 285–294. doi:10.4202/app.2011.0071. S2CID 55336060.
- ^ Mátyás Vremir; Alexander W. A. Kellner; Darren Naish; Gareth J. Dyke (2013). "A New Azhdarchid Pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous of the Transylvanian Basin, Romania: Implications for Azhdarchid Diversity and Distribution". PLOS ONE. 8 (1): e54268. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...854268V. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054268. PMC 3559652. PMID 23382886.
- ^ Darren Naish; Martin Simpson; Gareth Dyke (2013). "A New Small-Bodied Azhdarchoid Pterosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of England and Its Implications for Pterosaur Anatomy, Diversity and Phylogeny". PLOS ONE. 8 (3): e58451. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...858451N. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058451. PMC 3601094. PMID 23526986.
- ^ Laura Codorniú; Zulma Gasparini (2013). "The Late Jurassic pterosaurs from northern Patagonia, Argentina". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 103 (3–4): 399–408. doi:10.1017/S1755691013000388. hdl:11336/1319. S2CID 130885184.











