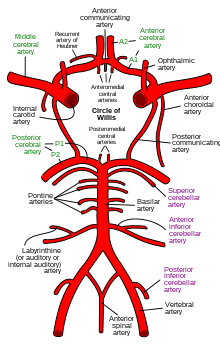
The cerebral arteries describe three main pairs of arteries and their branches, which perfuse the cerebrum of the brain. The three main arteries are the:
- Anterior cerebral artery (ACA), which supplies blood to the medial portion of the brain, including the superior parts of the frontal and anterior parietal lobes[1]
- Middle cerebral artery (MCA), which supplies blood to the majority of the lateral portion of the brain, including the temporal and lateral-parietal lobes.[2][3] It is the largest of the cerebral arteries and is often affected in strokes[4]
- Posterior cerebral artery (PCA), which supplies blood to the posterior portion of the brain, including the occipital lobe, thalamus, and midbrain[5]
Both the ACA and MCA originate from the cerebral portion of internal carotid artery, while PCA branches from the intersection of the posterior communicating artery and the anterior portion of the basilar artery. The three pairs of arteries are linked via the anterior communicating artery and the posterior communicating arteries. All three arteries send out arteries that perforate brain in the medial central portions prior to branching and bifurcating further.
The arteries are usually divided into different segments from 1–4 or 5 to denote how far the level of the branch with the lower numbers denoting vessels closer to the source artery. Even though the arteries branching off these vessels retain some aspect of constancy in terms of size and position, a great amount of variety in topography, position, source and prominence nevertheless exists.[6][7]
References
- ^ "Anterior Cerebral Artery". UMass Chan Medical School. 2015-07-21. Retrieved 2023-02-21.
- ^ "Middle Cerebral Artery". Physiopedia. Retrieved 2023-02-21.
- ^ "Middle Cerebral Artery: Cortical". UMass Chan Medical School. 2015-07-21. Retrieved 2023-02-21.
- ^ Nogles, Teryn E.; Galuska, Michael A. (2022), "Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 32310592, retrieved 2023-02-21
- ^ "Posterior cerebral artery". Kenhub. Retrieved 2023-02-21.
- ^ Krayenbühl, Hugo; Yaşargil, Mahmut Gazi; Huber, Peter; Bosse, George (1982), Cerebral Angiography, Thieme, pp. 79–91, ISBN 978-0-86577-067-6
- ^ Osborn, Anne G.; Jacobs, John M. (1999), Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, ISBN 978-0-397-58404-8








