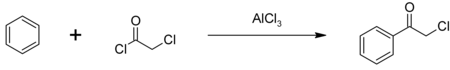
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
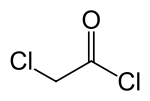
| Preferred IUPAC name
Chloroacetyl chloride | |
| Other names
2-Chloroacetyl chloride
Chloroacetic acid chloride Chloroacetic chloride Monochloroacetyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.065 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1752 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2Cl2O | |
| Molar mass | 112.94 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless to yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.42 g/mL |
| Melting point | −22 °C (−8 °F; 251 K) |
| Boiling point | 106 °C (223 °F; 379 K) |
| Reacts | |
| Vapor pressure | 19 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H311, H314, H331, H372, H400 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P311, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | noncombustible[1] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.05 ppm (0.2 mg/m3)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[1] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Oxford MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chloroacetyl chloride is a chlorinated acyl chloride. It is a bifunctional compound, making it a useful building block chemical.
Production
Industrially, it is produced by the carbonylation of methylene chloride, oxidation of vinylidene chloride, or the addition of chlorine to ketene.[3] It may be prepared from chloroacetic acid and thionyl chloride, phosphorus pentachloride, or phosgene.
Reactions
Chloroacetyl chloride is bifunctional—the acyl chloride easily forms esters[4] and amides, while the other end of the molecule is able to form other linkages, e.g. with amines. The use of chloroacetyl chloride in the synthesis of lidocaine is illustrative:[5]
Applications
The major use of chloroacetyl chloride is as an intermediate in the production of herbicides in the chloroacetanilide family including metolachlor, acetochlor, alachlor and butachlor; an estimated 100 million pounds are used annually. Some chloroacetyl chloride is also used to produce phenacyl chloride, another chemical intermediate, also used as a tear gas.[3] Phenacyl chloride is synthesized in a Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene, with an aluminium chloride catalyst:[6]
With anisole, it is used for the synthesis of venlafaxine.
Safety
Like other acyl chlorides, reaction with other protic compounds such as amines, alcohols, and water generates hydrochloric acid, making it a lachrymator.
There is no regulated permissible exposure limit set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. However, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health has set a recommended exposure limit at 0.05 ppm over an eight-hour work day.[7]
References
- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0120". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "OSHA Occupational Chemical Database". Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
- ^ a b Paul R. Worsham (1993). "15. Halogenated Derivatives" (Google Books excerpt). In Zoeller, Joseph R.; Agreda, V. H. (eds.). Acetic acid and its derivatives. New York: M. Dekker. pp. 288–298. ISBN 0-8247-8792-7.
- ^ Robert H. Baker and Frederick G. Bordwell (1955). "tert-Butyl acetate". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 3.
- ^ T. J. Reilly (1999). "The Preparation of Lidocaine". J. Chem. Educ. 76 (11): 1557. Bibcode:1999JChEd..76.1557R. doi:10.1021/ed076p1557.
- ^ Nathan Levin and Walter H. Hartung (1955). "ω-Chloroisonitrosoacetophenone". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 3, p. 191.
- ^ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2011.