| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
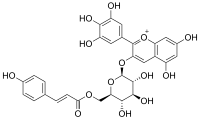
| IUPAC name
3′,4′,5,5′,7-Pentahydroxy-3-{6-O-[3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]-β-D-galactopyranosyloxy}flavylium
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(42S,43R,44S,45S,46R,8E)-13,14,15,25,27,43,44,45,104-Nonahydroxy-7-oxo-3,6-dioxa-21λ4-2(2,3)-[1]benzopyrana-4(2,6)-oxana-1,10(1)-dibenzenadecaphan-8-en-21-ylium | |
| Other names
Delphinidin-3-O-p-coumaroyl glucoside
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C 30H 27O+ 14 | |
| Molar mass | 611.52 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Delphinidin 3-O-(6-p-coumaroyl)glucoside is a p-coumaroylated anthocyanin. It can be found in some red Vitis vinifera grape cultivars (like Graciano[2]) and in red wine.[3]
It is formed by the enzyme anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6″-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase from delphinidin 3-O-glucoside and p-coumaroyl-CoA in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway.[4]
See also
References
- ^ "Showing Compound Delphinidin 3-(6-p-coumaroylglucoside) (FDB017204) - FooDB". foodb.ca.
- ^ Núñez, V.; Monagas, M.; Gomez Cordovés, M. C.; Bartolomé, B. (2004). "Vitis vinifera L. cv. Graciano grapes characterized by its anthocyanin profile". Postharvest Biology and Technology. 31: 69–79. doi:10.1016/S0925-5214(03)00140-6.
- ^ "Delphinidin 3-(6-p-coumaroyl)glucoside on www.phenol-explorer.eu". Archived from the original on 2011-12-30. Retrieved 2012-02-21.
- ^ Delphinidin 3-(6-p-coumaroyl)glucoside synthesis reaction on www.kegg.jp








