| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1′-(6,6′-Dihydroxy-5,5′-dimethoxy[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,3′-diyl)di(ethan-1-one) | |
| Other names
Diapocynin, 4′,4′′′-Dihydroxy-5′,5′′′-dimethoxy-3′,3′′′-biacetophenone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.233.239 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H18O6 | |
| Molar mass | 330.336 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | brown color |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H410 | |
| P273, P391, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
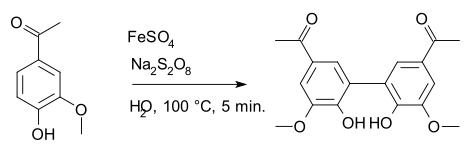
Diapocynin is a dimer of apocynin.
Synthesis
Diapocynin is synthesized by the activation of apocynin with ferrous sulfate and sodium persulfate.[1] Similar to apocynin, it is shown to have some beneficial effects against oxidative stress and reducing reactive oxygen species.[2][3]
References
- ^ Luchtefeld, Ron (2008). "Synthesis of diapocynin". Journal of Chemical Education. 85 (3): 411. Bibcode:2008JChEd..85..411L. doi:10.1021/ed085p411.
- ^ Dranka, B. P.; Gifford, A.; Ghosh, A.; Zielonka, J.; Joseph, J.; Kanthasamy, A. G.; Kalyanaraman, B. (2013). "Diapocynin prevents early Parkinson's disease symptoms in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2 R1441G) transgenic mouse". Neuroscience Letters. 549: 57–62. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2013.05.034. PMC 3729885. PMID 23721786.
- ^ Ismail, Hesham M.; Scapozza, Leonardo; Ruegg, Urs T.; Dorchies, Olivier M. (17 October 2014). "Diapocynin, a Dimer of the NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor Apocynin, Reduces ROS Production and Prevents Force Loss in Eccentrically Contracting Dystrophic Muscle". PLOS ONE. 9 (10): e110708. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9k0708I. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0110708. PMC 4201587. PMID 25329652.