Iroquois County | |
|---|---|
 | |
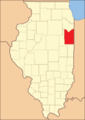
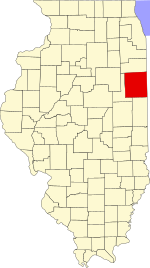 Location within the U.S. state of Illinois | |
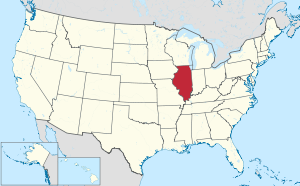 Illinois's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 40°44′N 87°49′W / 40.74°N 87.82°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1833 |
| Named for | Iroquois River |
| Seat | Watseka |
| Largest city | Watseka |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,119 sq mi (2,900 km2) |
| • Land | 1,117 sq mi (2,890 km2) |
| • Water | 1.6 sq mi (4 km2) 0.1% |
| Population (2020) | |
• Total | 27,077 |
• Estimate (2023) | 26,136
|
| • Density | 24/sq mi (9.3/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
| Website | www |
Iroquois County is a county located in the northeast part of the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2020 United States Census, it has a population of 27,077.[1] It is the only county in the United States named Iroquois.[2] The county seat is Watseka.[3] The county is located along the border with Indiana.
History
Iroquois County was created on February 26, 1833, out of a portion of Vermilion County. It was named for the Iroquois River, which was itself named for the Iroquois people.[4][5] The first county seat was established at the town of Iroquois in 1837, though no official buildings were constructed there and offices were rented. Several other sites for the county seat were examined, and in 1839 it was moved to Middleport; a court house and jail were built there. There was a long battle between Middleport and Watseka (also known as South Middleport) as to which should be the county seat; in 1865, it was finally moved to Watseka.[6] The town of Middleport no longer exists, but there is a township of that name. A courthouse was built in Watseka in 1866 at a cost of $28,000 and included a jail in the basement; this building was expanded in 1881, and a new jail was built in 1893 just east of the courthouse.[7]
-
Iroquois County from the time of its creation to 1836
-
Iroquois County between 1836 and 1853
-
Iroquois County in 1853, when the creation of Kankakee County reduced it to its current size.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,119 square miles (2,900 km2), of which 1,117 square miles (2,890 km2) is land and 1.6 square miles (4.1 km2) (0.1%) is water.[8] It is the third-largest county in Illinois by land area[2] and the fifth-largest by total area.
The northern border of the county is about 60 miles (97 km) south of the city of Chicago. The county is bordered on the east by the state of Indiana and its counties of Benton and Newton. To the north lies Kankakee County. Vermilion County, out of which Iroquois County was originally formed, lies to the south. To the west is Ford County.
The Iroquois River enters the county from Indiana and flows westward along the south side of the village of Iroquois, then along the north side of the city of Watseka, whereupon it veers to the north and joins the larger Kankakee River near the city of Kankakee in the county of the same name; the Kankakee River then flows into the Illinois River further to the northwest in Will County. Sugar Creek, further to the south, also flows from the east to the west, entering from Indiana east of Stockland; it passes through the south edge of Milford, is joined by Mud Creek coming up from the south, and winds to the north past the village of Woodland and meets the Iroquois River near Watseka.
The Iroquois County State Wildlife Area, a 2,400-acre (970 ha) state park, is located in the northeast corner of the county. There are also three nature preserves: Bonnie's Prairie,[9] Hooper Branch Savanna,[10] and Loda Cemetery Prairie.[11]
Climate and weather
| Watseka, Illinois | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In recent years, average temperatures in the county seat of Watseka have ranged from a low of 14 °F (−10 °C) in January to a high of 84 °F (29 °C) in July, although a record low of −28 °F (−33 °C) was recorded in January 1999 and a record high of 105 °F (41 °C) was recorded in August 1988. Average monthly precipitation ranged from 1.61 inches (41 mm) in January to 4.62 inches (117 mm) in June.[12]
Adjacent counties
- Kankakee County - north
- Newton County, Indiana - east
- Benton County, Indiana - east
- Vermilion County - south
- Ford County - west
Transportation
Transit service in the county is provided by SHOW Bus, which operates a local bus route within Watseka. Amtrak provides intercity passenger rail service on the Illini and Saluki at Gilman station.
Interstate 57 passes through the west part of the county on its route between Champaign and Chicago. From north to south, it passes through or near Chebanse, Clifton, Ashkum, Danforth, Gilman, Onarga, Buckley, and Loda.
The county is bisected by the east–west U.S. Route 24, which passes through Gilman, Crescent City, the county seat of Watseka, and Sheldon.
 Interstate 57
Interstate 57 U.S. Highway 45
U.S. Highway 45 U.S. Highway 52
U.S. Highway 52 Illinois Route 1
Illinois Route 1 Illinois Route 49
Illinois Route 49 Illinois Route 54
Illinois Route 54 Illinois Route 116
Illinois Route 116
Several railroad lines pass through the county. The Toledo, Peoria and Western Railway operates a line that begins in Peoria and runs from east to west through Iroquois County, passing through Gilman and Watseka and continuing into Indiana. A Canadian National Railway line runs nearly parallel with Interstate 57 on its way to Chicago. A CSX Transportation line passes from north to south through the eastern part of the county; a Union Pacific line joins it south of Woodland. Further east, the Kankakee, Beaverville and Southern Railroad operates a north–south line.[13]
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1840 | 1,695 | — | |
| 1850 | 4,149 | 144.8% | |
| 1860 | 12,325 | 197.1% | |
| 1870 | 25,782 | 109.2% | |
| 1880 | 35,451 | 37.5% | |
| 1890 | 35,167 | −0.8% | |
| 1900 | 38,014 | 8.1% | |
| 1910 | 35,543 | −6.5% | |
| 1920 | 34,841 | −2.0% | |
| 1930 | 32,913 | −5.5% | |
| 1940 | 32,496 | −1.3% | |
| 1950 | 32,348 | −0.5% | |
| 1960 | 33,562 | 3.8% | |
| 1970 | 33,532 | −0.1% | |
| 1980 | 32,976 | −1.7% | |
| 1990 | 30,787 | −6.6% | |
| 2000 | 31,334 | 1.8% | |
| 2010 | 29,718 | −5.2% | |
| 2020 | 27,077 | −8.9% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 26,136 | [14] | −3.5% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[15] 1790-1960[16] 1900-1990[17] 1990-2000[18] 2010-2013[19] | |||
As of the 2010 United States census, there were 29,718 people, 11,956 households, and 8,175 families residing in the county.[20] The population density was 26.6 inhabitants per square mile (10.3/km2). There were 13,452 housing units at an average density of 12.0 per square mile (4.6/km2).[8] The racial makeup of the county was 94.7% white, 0.8% black or African American, 0.3% Asian, 0.2% American Indian, 2.6% from other races, and 1.3% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 5.3% of the population.[20] In terms of ancestry, 36.5% were German, 14.1% were Irish, 12.2% were American, and 10.1% were English.[21]
Of the 11,956 households, 30.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.7% were married couples living together, 9.3% had a female householder with no husband present, 31.6% were non-families, and 27.2% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.45 and the average family size was 2.95. The median age was 43.4 years.[20]
The median income for a household in the county was $47,323 and the median income for a family was $56,541. Males had a median income of $43,416 versus $27,908 for females. The per capita income for the county was $23,400. About 8.2% of families and 10.0% of the population were below the poverty line, including 14.1% of those under age 18 and 7.8% of those age 65 or over.[22]
Communities
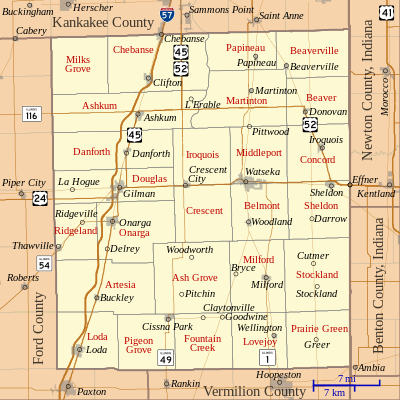
Cities
Villages
Townships
In 1855, a popular vote resulted in the adoption of township government, which was implemented in 1856. At that time, eleven townships were created;[23] they are listed below.
Over the next several decades, more townships were created from the existing ones, for a final total of twenty-six. The newer townships are listed below in order of creation.
- Martinton (1857)
- Iroquois (1858)
- Prairie Green (1858)
- Ashkum (1861)
- Douglas (1861)
- Artesia (1864)
- Fountain Creek (1868)
- Lovejoy (1868)
- Sheldon (1868)
- Milks Grove (1872)
- Pigeon Grove (1876)
- Crescent (1877)
- Danforth (1877)
- Ridgeland (1878)
- Beaverville (1916)
Unincorporated Communities
Notable people
- Fern Andra, movie actress and director from 1913 to 1930, born in Watseka in 1893
- John Moisant, pioneering aviator and aeronautical engineer, born in L'Erable in 1868
- John S. Darrough, recipient of the Medal of Honor, American Civil War, lived in the county from age 14.
- Henry Bacon, architect, born in Wateska in 1866
- Rex Everhart, Broadway actor who voiced the role of Maurice in the Disney Film "Beauty & The Beast," born in Watseka in 1920
- Scott Garrelts, Pitcher, San Francisco Giants, 1st round draft pick in 1979 amateur draft, grew up in Buckley, graduated from Buckley-Loda High School
- Ray A. Laird, president of Laredo Community College in Laredo, Texas, 1960 to 1974; born in Milford in 1907[24]
- Ole Rynning (1809–1838), Norwegian immigrant author
- Fred J. Schraeder (1923-2016), Illinois state representative and businessman, born in Clifton
Politics
Throughout the rest of its history, Iroquois County has been among the most solidly Republican counties in Illinois. Since 1940 only Lyndon Johnson in his 1964 landslide has garnered forty percent of the county's vote for the Democratic Party, and only Bill Clinton in 1996 has topped 35 percent since 1968.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party(ies) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2024 | 10,376 | 77.87% | 2,747 | 20.62% | 201 | 1.51% |
| 2020 | 10,877 | 77.45% | 2,908 | 20.71% | 258 | 1.84% |
| 2016 | 9,750 | 74.42% | 2,504 | 19.11% | 848 | 6.47% |
| 2012 | 9,120 | 71.19% | 3,413 | 26.64% | 278 | 2.17% |
| 2008 | 8,695 | 63.82% | 4,643 | 34.08% | 286 | 2.10% |
| 2004 | 9,914 | 71.66% | 3,832 | 27.70% | 89 | 0.64% |
| 2000 | 8,685 | 64.70% | 4,397 | 32.75% | 342 | 2.55% |
| 1996 | 6,564 | 51.53% | 4,559 | 35.79% | 1,614 | 12.67% |
| 1992 | 6,948 | 47.82% | 4,440 | 30.56% | 3,142 | 21.62% |
| 1988 | 9,596 | 69.11% | 4,221 | 30.40% | 69 | 0.50% |
| 1984 | 11,327 | 77.13% | 3,300 | 22.47% | 58 | 0.39% |
| 1980 | 11,247 | 73.38% | 3,362 | 21.94% | 718 | 4.68% |
| 1976 | 10,129 | 65.43% | 5,167 | 33.38% | 185 | 1.20% |
| 1972 | 11,995 | 75.99% | 3,723 | 23.59% | 66 | 0.42% |
| 1968 | 10,885 | 67.89% | 3,897 | 24.31% | 1,251 | 7.80% |
| 1964 | 9,423 | 57.28% | 7,029 | 42.72% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1960 | 11,376 | 66.09% | 5,821 | 33.82% | 16 | 0.09% |
| 1956 | 12,104 | 72.88% | 4,487 | 27.02% | 18 | 0.11% |
| 1952 | 12,456 | 72.81% | 4,634 | 27.09% | 17 | 0.10% |
| 1948 | 9,051 | 64.65% | 4,823 | 34.45% | 127 | 0.91% |
| 1944 | 10,389 | 66.39% | 5,168 | 33.03% | 91 | 0.58% |
| 1940 | 11,047 | 60.73% | 7,036 | 38.68% | 108 | 0.59% |
| 1936 | 7,908 | 46.05% | 8,654 | 50.39% | 611 | 3.56% |
| 1932 | 6,303 | 39.65% | 9,434 | 59.34% | 161 | 1.01% |
| 1928 | 8,453 | 60.71% | 5,421 | 38.94% | 49 | 0.35% |
| 1924 | 7,498 | 64.07% | 2,303 | 19.68% | 1,901 | 16.25% |
| 1920 | 9,186 | 77.79% | 2,429 | 20.57% | 194 | 1.64% |
| 1916 | 8,503 | 61.10% | 4,977 | 35.76% | 436 | 3.13% |
| 1912 | 1,866 | 24.83% | 2,474 | 32.92% | 3,176 | 42.26% |
| 1908 | 4,855 | 58.94% | 2,966 | 36.01% | 416 | 5.05% |
| 1904 | 5,067 | 62.44% | 2,376 | 29.28% | 672 | 8.28% |
| 1900 | 5,243 | 56.39% | 3,736 | 40.19% | 318 | 3.42% |
| 1896 | 5,325 | 58.01% | 3,658 | 39.85% | 196 | 2.14% |
| 1892 | 3,936 | 47.95% | 3,848 | 46.88% | 425 | 5.18% |
See also
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Iroquois County, Illinois
- Watseka Wonder, alleged spiritual possession of fourteen-year-old Lurancy Vennum in the late 19th century
References
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: Iroquois County, Illinois".
- ^ a b Dowling 1968, p. 9.
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ^ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. pp. 166.
- ^ Callary, Edward (2009). Place Names of Illinois. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. p. 173. ISBN 978-0-252-03356-8.
- ^ Kern 1907, p. 677.
- ^ Kern 1907, p. 678.
- ^ a b "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved July 11, 2015.
- ^ "Bonnie's Prairie". Illinois Department of Natural Resources. Archived from the original on March 4, 2012. Retrieved October 15, 2010.
- ^ "Hooper Branch Savanna". Illinois Department of Natural Resources. Archived from the original on March 4, 2012. Retrieved October 15, 2010.
- ^ "Loda Cemetery Prairie". Illinois Department of Natural Resources. Archived from the original on March 4, 2012. Retrieved October 15, 2010.
- ^ a b "Monthly Averages for Watseka, Illinois". The Weather Channel. Retrieved January 27, 2011.
- ^ "Illinois Railroad Map" (PDF). Illinois Department of Transportation. January 2006. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 3, 2006. Retrieved October 17, 2010.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Counties: April 1, 2020 to July 1, 2023". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 2, 2024.
- ^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 5, 2014.
- ^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved July 5, 2014.
- ^ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 5, 2014.
- ^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 27, 2010. Retrieved July 5, 2014.
- ^ "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved July 5, 2014.
- ^ a b c "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved July 11, 2015.
- ^ "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved July 11, 2015.
- ^ "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved July 11, 2015.
- ^ Dowling 1968, p. 21.
- ^ Ray A. Laird obituary, Kerrville Daily Times, Kerrville, Texas, October 7, 1986
- ^ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org.
Bibliography
- Dowling, John (1968). History of Iroquois County. Iroquois County Board of Supervisors. Retrieved October 15, 2010.
- Kern, J. W. (1907). Past and present of Iroquois County, Illinois. Chicago: The S. J. Clarke Publishing Company. Retrieved October 15, 2010.
- Beckwith, H. W. (1880). History of Iroquois County, Together with Historic Notes on the Northwest. Chicago: H. H. Hill and Company. Retrieved October 15, 2010.
External links
![]() Media related to Iroquois County, Illinois at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Iroquois County, Illinois at Wikimedia Commons