| Yuruá River | |
|---|---|
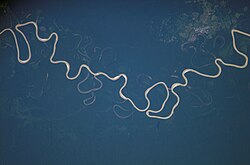 Yuruá River taken from the International Space Station | |
 Map of the Amazon Basin with the Juruá River highlighted | |
| Location | |
| Country | Brazil, Peru |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Ucayali Region, Peru |
| • coordinates | 10°5′36.4776″S 72°11′56.4576″W / 10.093466000°S 72.199016000°W |
| • elevation | 377 m (1,237 ft)[1] |
| Mouth | Amazon River |
• coordinates | 2°38′9″S 65°45′22″W / 2.63583°S 65.75611°W |
• elevation | 36 m (118 ft)[1] |
| Length | 2,682.29 km (1,666.70 mi)[1] 3,283 km (2,040 mi) |
| Basin size | 190,573 km2 (73,581 sq mi)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Confluence of Solimões, Amazonas State (near mouth) |
| • average | (Period: 1979–2015)6,004.1 m3/s (212,030 cu ft/s)[2]
(Period: 1973–1990)6,600 m3/s (230,000 cu ft/s)[3] (Period: 1971–2000)6,662.1 m3/s (235,270 cu ft/s)[4] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Gavião, Amazonas State (Basin size: 163,859 km2 (63,266 sq mi) |
| • average | (Period: 1979–2015)4,844 m3/s (171,100 cu ft/s)[2] (Period of data: 1970–1996)4,780 m3/s (169,000 cu ft/s)[5] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Cruzeiro do Sul, Acre State (Basin size: 38,537 km2 (14,879 sq mi) |
| • average | (Period of data: 1970–1996)913 m3/s (32,200 cu ft/s)[5] |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Amazon → Atlantic Ocean |
| River system | Solimões |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Môa, Ipixuna |
| • right | Gregório, Tarauaca, Xerua, Andirá |
The Juruá River (Portuguese: Rio Juruá [ʒuɾuˈa]; Spanish: Río Yuruá) is a southern affluent river of the Amazon River west of the Purus River, sharing with this the bottom of the immense inland Amazon depression, and having all the characteristics of the Purus as regards curvature, sluggishness and general features of the low, half-flooded forest country it traverses.
For most of its length, the river flows through the Purus várzea ecoregion.[6] This is surrounded by the Juruá-Purus moist forests ecoregion.[7] It rises among the Ucayali highlands, and is navigable and unobstructed for a distance of 1,133 km (704 mi) above its junction with the Amazon. It has a total length of approximately 3,283 km (2,040 mi), and is one of the longest tributaries of the Amazon.
The 251,577 hectares (621,660 acres) Médio Juruá Extractive Reserve, created in 1997, is on the left bank of the river as it meanders in a generally northeast direction through the municipality of Carauari.[8] The lower Juruá River forms the western boundary of the 187,982 hectares (464,510 acres) Baixo Juruá Extractive Reserve, created in 2001.[9] Since 2018, the lower portion of the river in Brazil has been designated a protected Ramsar site.[10]
References
- ^ a b c Perú: Anuario de Estadistícas Ambientales 2022 (PDF). 2022.
- ^ a b c "PLANO ESTADUAL DE RECURSOS HÍDRICOS DO AMAZONAS, (PERH/AM) - RT 03 - DIAGNÓSTICO, PROGNÓSTICO E CENÁRIOS FUTUROS DO RECURSOS HÍDRICOS DO ESTADO - TOMO III" (PDF). Jan 2019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-05-06. Retrieved 2021-10-03.
- ^ Théry, Hervé; Maurence, Pascale (1997). HYDROLOGIE DU BASSIN AMAZONIEN (PDF). ISBN 2-7011-1532-9.
- ^ "Amazon".
- ^ a b Michael, T. Coe; Marcos, Heil Costa; Aurélie, Botta; Charon, Birkett (23 Aug 2002). "Long-term simulations of discharge and floods in the Amazon Basin". CiteSeerX 10.1.1.549.3854.
- ^ "Purus varzea", Global Species, Myers Enterprises II, archived from the original on 2019-04-22, retrieved 2017-03-15
- ^ Sears, Robin, South America: Amazon Basin, northwestern Brazil (NT0133), WWF: World Wildlife Fund, retrieved 2017-03-28
- ^ RESEX do Médio Juruá (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-06-16
- ^ RESEX do Baixo Juruá (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-10-22
- ^ "Rio Juruá". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 11 January 2019.








