| Motorways of Pakistan | |
|---|---|
 Pakistan motorway sign | |
 | |
| System information | |
| Maintained by National Highway Authority | |
| Length | 2,567 km (1,595 mi) |
| Formed | 1997 |
| Highway names | |
| System links | |
Motorways of Pakistan (Urdu: پاکستان کے موٹروے) are a network of multiple-lane, high-speed, controlled-access highways in Pakistan which are owned, maintained, and operated federally by Pakistan's National Highway Authority. At present, 2567 km of motorways are operational, while an additional 1191 km are under construction. Motorways are a part of Pakistan's “National Trade Corridor Project” and “China-Pakistan Belt Road Initiative,” from Khunjerab Pass near the Chinese border to Gwadar in Balochistan. There are a total of 16 motorways, 11 of which are operational, while some are under construction and others are planned.
All motorways in Pakistan are prefixed with the letter 'M' (for "Motorway") followed by the unique numerical designation of the specific highway (with a hyphen in the middle), e.g. "M-1".[1]
History


Pakistan's motorways are an important part of Pakistan's "National Trade Corridor Project", which aims to link Pakistan's three Arabian Sea ports (Karachi Port, Port Bin Qasim and Gwadar Port) to the rest of the country through its national highways and motorways network and further north with Afghanistan, Central Asia and China.[2] The project was planned in 1990. The China Pakistan Economic Corridor project aims to link Gwadar Port and Kashgar (China) using Pakistani motorways, national highways, and expressways.
List of motorways
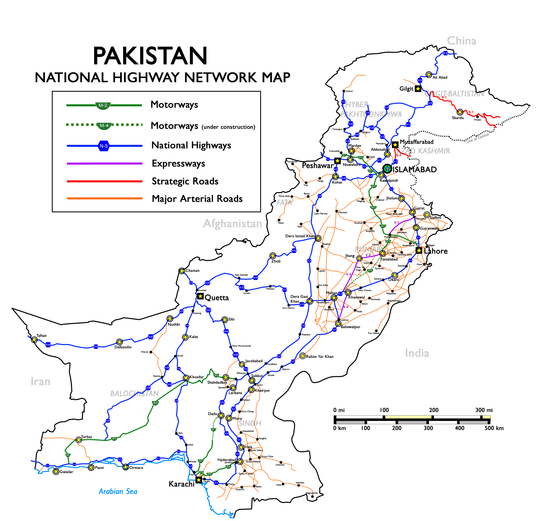
| Name | Route | Length (km) | Lanes | Completion Year | Status | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-1 Motorway | Peshawar–Islamabad | 155 | 6 | 2007 | Operational | ||
| M-2 Motorway | Islamabad–Lahore | 375 | 6 | 1997 | Operational | Repaved in 2016 | |
| M-3 Motorway | Lahore–Abdul Hakeem | 230 | 6 | 2019 |
Operational |
Construction began in December 2015. | |
| M-4 Motorway | Pindi Bhattian–Multan | 309 | 4-6 | 2019 |
Operational |
Construction began in 2009. | |
| M-5 Motorway | Multan–Sukkur | 392 | 6 | 2019 | Operational | Construction began in May 2016. | |
| M-6 Motorway | Sukkur-Hyderabad | 306 | 6 | 2024 | Under Construction | Ground breaking done on 13 December 2022 | |
| M-7 Motorway | Dadu–Hub | 270 | N/A | N/A | Planned | ||
| M-8 Motorway | Ratodero–Gwadar | 892 | 2 | 2022 | Partially Operational Under Construction |
||
| M-9 Motorway | Hyderabad–Karachi | 136 | 6 | 2018 | Operational | Upgradation planned into 8 lanes. | |
| M-10 Motorway | Karachi Northern Bypass | 57 | 2 | 2007 | Operational | Proposed for expansion into 4 lane. | |
| M-11 Motorway | Lahore–Sialkot | 103 | 4 | 2020 | Operational | Construction started in 2018 | |
| M-12 Motorway | Sialkot – Kharian | 69 | 6 | 2025 | Under Construction | Construction started in September 2021 | |
| M-13 Motorway | Kharian - Rawalpindi | 117 | 6 | 2026 | Under Construction | ||
| M-14 Motorway | Islamabad–D.I Khan | 285 | 4 | 2022 | Operational | Construction began in May 2016. | |
| M-15 Motorway | Hasan Abdal–Thakot | 180 | 6-4-2 | 2020 | Operational | Also called Hazara Motorway. Construction began in 2016 | |
| M-16 Motorway | Swabi – Chakdara | 160 | 4 | 2020 | Operational | Also called Swat Motorway. Phase 1 operational in October 2020.Phase 2 construction started in May 2022 & will be completed in 2025. | |
| Total Length | |||||||
Other proposed motorways
| Name | Route | Length (km) | Lanes | Completion Year | Status | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peshawar - D.I. Khan Motorway | Peshawar – D.I. Khan | 360 | 6 | 2026 | Approved by ECNEC on 10 Sep 2021[3][4] | |
| Dir–Swat motorway | Dir – Swat | 4 | -- | |||
| Mansehra–Muzaffarabad–Mirpur–Mangla Motorway (MMMM) | Mansehra–Muzaffarabad–Mirpur–Mangla | 174 | 4 | Planned[5] | ||
| Peshawar–Kabul–Dushanbe motorway | Peshawar–Kabul–Dushanbe | 6 | Planned | Under Feasibility | ||
| Shorkot–Layyah Motorway | Shorkot – Layyah | 119 | -- | Connection with two CPEC routes[6] | ||
| Lahore–Kartarpur Motorway | Lahore – Kartarpur | Connection to Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur[7] |
Patrolling and enforcement

Pakistan's Motorways are patrolled by Pakistan's National Highways & Motorway Police (NH&MP), which is responsible for enforcement of traffic and safety laws, security and recovery on the Pakistan Motorway network. The NH&MP use SUVs, cars and heavy motorbikes for patrolling purposes and use speed cameras for enforcing speed limits. The nationwide contact number from both mobiles and landlines is 130, and is available 24 hours a day.
M-TAG

In 2016, NHA implemented electronic toll collection on M2 motorway in partnership with One Network that uses a RFID-based tag called the "M-TAG".[8] The tag is attached to the windscreen of vehicles and is automatically scanned at toll plazas on entry and exit, meanwhile debiting the calculated toll tax from a prepaid M-TAG account.[9][10] The service has since been expanded to all motorways, except M-14 and M-8, and is also used on Lahore Ring Road.[11][12]
Emergency runways
The M-1 motorway (Peshawar-Islamabad) and the M-2 motorway (Islamabad-Lahore) each include two emergency runway sections of 9,000 feet (2,700 m) length. The four emergency runway sections become operational by removing removable concrete medians using forklifts. The Pakistan Air Force (PAF) has used the M-2 motorway as a runway on two occasions: the first time in 2000 when it landed an F-7P fighter, a Super Mushak trainer and a C-130 and, again, in 2010. On the last occasion, the PAF used a runway section on the M-2 motorway on 2 April 2010 to land, refuel and take-off two jet fighters, a Mirage III and an F-7P, during its Highmark 2010 exercise.[13]
See also
- National Highways of Pakistan
- Expressways of Pakistan
- Transport in Pakistan
- Speed limits in Pakistan
- Belt and Road Initiative
- National Highway Authority
References
- ^ "National Highways Authority – Committed to Excellence". Retrieved 2020-10-24.
- ^ "Pakistan's smart motorways strength for regional connectivity". Global Village Space. 2021-10-12. Retrieved 2022-02-28.
- ^ "KP CM congratulates people on approval of Peshawar-D.I Khan, Dir Motorway". dunyanews.tv. Retrieved 2021-09-12.
- ^ "Peshawar-DI Khan Motorway PC-1 approved". www.thenews.com.pk. Retrieved 2021-09-12.
- ^ "AJK terms MMMM Expressway project of exceptional significance". www.nation.com.pk. Archived from the original on 2018-12-30.
- ^ "Roznama Dunya Multan EDITION 11 December 2020 NEWS DETAIL | ID 5433077_36024805 |Daily Dunya ePaper|Roznama Dunya". e.dunya.com.pk. Retrieved 2021-01-06.
- ^ Bureau, Sikh24 Asia (17 December 2020). "New motorway approved to halve down the distance between Lahore and Kartarpur | Sikh24.com". Retrieved 2021-01-09.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Peshawar-Islamabad Motorway: Motorists demand restoration of e-tag system". The Express Tribune. 2016-09-10. Retrieved 2022-12-09.
- ^ "Vehicles without M-Tag banned on M2". The Express Tribune. 2021-12-06. Retrieved 2022-12-09.
- ^ "SERVICES". One Network. Retrieved 2022-12-09.
- ^ Gulrez, Ali (2022-12-03). "M-TAG Now Operational on Multan-Sukkur Motorway M-5". INCPak. Retrieved 2022-12-09.
- ^ Gulrez, Ali (2021-12-15). "MTag Registration Centers in Lahore". INCPak. Retrieved 2022-12-09.
- ^ PAF Conducts Fighter Operations from Motorway Pakistan Air Force, Government of Pakistan website, Published 2 April 2010, Retrieved 2 March 2022








