| Annular eclipse | |
 Partial from Minneapolis, Minnesota | |
| Gamma | 0.4089 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 0.9681 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 233 s (3 min 53 s) |
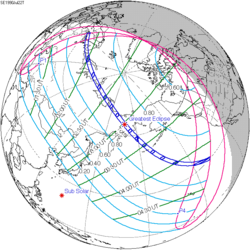
| Coordinates | 0°36′N 130°42′W / 0.6°N 130.7°W |
| Max. width of band | 126 km (78 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 20:53:01 |
| References | |
| Saros | 132 (45 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9512 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Friday, December 14, 2001,[1][2][3][4] with a magnitude of 0.9681. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because it occurred 7.9 days after perigee (on December 6, 2001, at 22:40 UTC) and 6.7 days before apogee (on December 21, 2001, at 13:00 UTC).[5]
Annularity was visible across the Pacific Ocean, southern Costa Rica, northern Nicaragua and San Andrés Island, Colombia. The central shadow passed just south of Hawaii in early morning and ended over Central America near sunset. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of North America, Central America, northwestern South America, and Hawaii.
Observation
[edit]
The path of annularity was mostly on the sea, so observers were concentrated in Central America, the only land covered by the path, especially in Costa Rica with the largest area covered by the path and highest solar zenith angle. However, it was cloudy or rainy in many parts of the country during the eclipse, and only a few observers saw the annular eclipse.[6] The International Occultation Timing Association made up of scientists from different countries planned to measure the diameter of the Sun with Baily's beads that appeared at the moment of the second and third contacts in Santa Rosa National Park on the northern edge of the path of annularity, but failed.[7] A team of professors from the University of Costa Rica and abroad traveled to Ostional Mixed Wildlife Refuge, kilometres north of Nosara. The Sun could be seen through the clouds after the eclipse started, but it was completely clouded out when 80% was blocked by the Moon. All the stages after that, including the annularity, could not be seen.[8]
Coincidentally, the 2001 Geminids peaked in the early morning of December 14 local time, less than 24 hours before the annular solar eclipse.[7]
Eclipse timing
[edit]Places experiencing annular eclipse
[edit]| Country or territory | City or place | Start of partial eclipse | Start of annular eclipse | Maximum eclipse | End of annular eclipse | End of partial eclipse | Duration of annularity (min:s) | Duration of eclipse (hr:min) | Maximum coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liberia | 15:11:39 | 16:30:42 | 16:32:02 | 16:33:22 | 17:21:53 (sunset) | 2:40 | 2:10 | 91.50% | |
| Alajuela | 15:13:44 | 16:31:57 | 16:32:55 | 16:33:53 | 17:18:05 (sunset) | 1:56 | 2:04 | 91.44% | |
| San José | 15:13:58 | 16:32:39 | 16:33:00 | 16:33:23 | 17:17:42 (sunset) | 0:44 | 2:04 | 91.44% | |
| San Andrés | 16:16:17 | 17:32:45 | 17:33:13 | 17:33:41 | 18:03:25 (sunset) | 0:56 | 1:47 | 91.27% | |
| References: [1] | |||||||||
Places experiencing partial eclipse
[edit]| Country or territory | City or place | Start of partial eclipse | Maximum eclipse | End of partial eclipse | Duration of eclipse (hr:min) | Maximum coverage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midway Atoll | 07:33:23 (sunrise) | 08:11:10 | 09:27:12 | 1:54 | 90.45% | ||||
| Honolulu | 08:08:06 | 09:26:54 | 11:00:47 | 2:53 | 78.80% | ||||
| Kiritimati[a] | 08:20:34 | 09:39:13 | 11:13:21 | 2:53 | 54.61% | ||||
| Taioha'e | 09:26:14 | 11:03:25 | 12:49:54 | 3:24 | 53.50% | ||||
| Washington, D.C. | 16:12:58 | 16:43:36 | 16:46:51 (sunset) | 0:34 | 15.76% | ||||
| Clipperton Island | 12:11:08 | 13:58:29 | 15:26:12 | 3:15 | 65.93% | ||||
| Santo Domingo | 17:24:17 | 18:03:00 | 18:05:31 (sunset) | 0:41 | 42.30% | ||||
| Cockburn Harbour | 16:21:47 | 17:03:27 | 17:06:02 (sunset) | 0:44 | 44.50% | ||||
| Caracas | 17:31:16 | 18:05:29 | 18:07:55 (sunset) | 0:37 | 35.06% | ||||
| Providenciales | 16:21:13 | 17:05:45 | 17:08:21 (sunset) | 0:47 | 47.94% | ||||
| Willemstad | 17:28:47 | 18:10:42 | 18:13:14 (sunset) | 0:44 | 46.96% | ||||
| Port-au-Prince | 16:22:43 | 17:12:27 | 17:14:59 (sunset) | 0:52 | 58.20% | ||||
| Mexico City | 14:44:53 | 16:12:54 | 17:26:20 | 2:41 | 48.92% | ||||
| Oranjestad | 17:27:45 | 18:14:25 | 18:16:52 (sunset) | 0:49 | 54.34% | ||||
| Nassau | 16:16:31 | 17:19:16 | 17:21:57 (sunset) | 1:05 | 56.96% | ||||
| Maracaibo | 17:27:45 | 18:23:55 | 18:26:33 (sunset) | 0:59 | 66.41% | ||||
| Havana | 16:12:34 | 17:26:24 | 17:46:04 (sunset) | 1:34 | 58.39% | ||||
| Belmopan | 15:04:59 | 16:26:31 | 17:23:11 (sunset) | 2:18 | 67.79% | ||||
| Guatemala City | 15:02:11 | 16:26:32 | 17:35:07 (sunset) | 2:33 | 73.73% | ||||
| San Salvador | 15:04:41 | 16:28:09 | 17:31:25 (sunset) | 2:27 | 78.45% | ||||
| Tegucigalpa | 15:07:57 | 16:29:28 | 17:22:44 (sunset) | 2:15 | 79.89% | ||||
| George Town | 16:14:30 | 17:29:47 | 17:49:42 (sunset) | 1:35 | 71.35% | ||||
| Galápagos Islands | 15:09:16 | 16:30:22 | 17:38:37 | 2:29 | 64.34% | ||||
| Managua | 15:09:54 | 16:30:58 | 17:22:28 (sunset) | 2:13 | 87.39% | ||||
| Kingston | 16:19:29 | 17:31:18 | 17:33:50 (sunset) | 1:14 | 81.60% | ||||
| Limón | 15:15:29 | 16:33:31 | 17:13:23 (sunset) | 1:58 | 90.68% | ||||
| Panama City | 16:20:39 | 17:35:09 | 18:01:06 (sunset) | 1:40 | 82.71% | ||||
| Barranquilla | 16:24:45 | 17:35:38 | 17:38:42 (sunset) | 1:14 | 82.33% | ||||
| Quito | 16:28:04 | 17:36:07 | 18:12:59 (sunset) | 1:45 | 50.82% | ||||
| Bogotá | 16:29:41 | 17:36:56 | 17:46:57 (sunset) | 1:17 | 60.14% | ||||
| References: [1] | |||||||||
Gallery
[edit]-
Partial from Siesta Key, Florida at sunset
Eclipse season
[edit]This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
| December 14 Descending node (new moon) |
December 30 Ascending node (full moon) |
|---|---|
 |

|
| Annular solar eclipse Solar Saros 132 |
Penumbral lunar eclipse Lunar Saros 144 |
Related eclipses
[edit]Eclipses in 2001
[edit]- A total lunar eclipse on January 9.
- A total solar eclipse on June 21.
- A partial lunar eclipse on July 5.
- An annular solar eclipse on December 14.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on December 30.
Metonic
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of February 26, 1998
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of October 3, 2005
Tzolkinex
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of November 3, 1994
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of January 26, 2009
Half-Saros
[edit]- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of December 9, 1992
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of December 21, 2010
Tritos
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of January 15, 1991
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of November 13, 2012
Solar Saros 132
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of December 4, 1983
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of December 26, 2019
Inex
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of January 4, 1973
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of November 25, 2030
Triad
[edit]- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of February 14, 1915
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of October 14, 2088
Solar eclipses of 2000–2003
[edit]This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[9]
The partial solar eclipses on February 5, 2000 and July 31, 2000 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2000 to 2003 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 117 | July 1, 2000 Partial |
−1.28214 | 122 Partial projection in Minneapolis, MN, USA |
December 25, 2000 Partial |
1.13669 | |
127 Totality in Lusaka, Zambia |
June 21, 2001 Total |
−0.57013 | 132 Partial in Minneapolis, MN, USA |
December 14, 2001 Annular |
0.40885 | |
137 Partial in Los Angeles, CA, USA |
June 10, 2002 Annular |
0.19933 | 142 Totality in Woomera, South Australia |
December 4, 2002 Total |
−0.30204 | |
147 Annularity in Culloden, Scotland |
May 31, 2003 Annular |
0.99598 | 152
|
November 23, 2003 Total |
−0.96381 | |
Saros 132
[edit]This eclipse is a part of Saros series 132, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 71 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on August 13, 1208. It contains annular eclipses from March 17, 1569 through March 12, 2146; hybrid eclipses on March 23, 2164 and April 3, 2182; and total eclipses from April 14, 2200 through June 19, 2308. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on September 25, 2470. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 25 at 6 minutes, 56 seconds on May 9, 1641, and the longest duration of totality will be produced by member 61 at 2 minutes, 14 seconds on June 8, 2290. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[10]
| Series members 34–56 occur between 1801 and 2200: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 34 | 35 | 36 | |
 August 17, 1803 |
 August 27, 1821 |
 September 7, 1839 | |
| 37 | 38 | 39 | |
 September 18, 1857 |
 September 29, 1875 |
 October 9, 1893 | |
| 40 | 41 | 42 | |
 October 22, 1911 |
 November 1, 1929 |
 November 12, 1947 | |
| 43 | 44 | 45 | |
 November 23, 1965 |
 December 4, 1983 |
 December 14, 2001 | |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | |
 December 26, 2019 |
 January 5, 2038 |
 January 16, 2056 | |
| 49 | 50 | 51 | |
 January 27, 2074 |
 February 7, 2092 |
 February 18, 2110 | |
| 52 | 53 | 54 | |
 March 1, 2128 |
 March 12, 2146 |
 March 23, 2164 | |
| 55 | 56 | ||
 April 3, 2182 |
 April 14, 2200 | ||
Metonic series
[edit]The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 eclipse events between July 22, 1971 and July 22, 2047 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 22 | May 9–11 | February 26–27 | December 14–15 | October 2–3 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 22, 1971 |
 May 11, 1975 |
 February 26, 1979 |
 December 15, 1982 |
 October 3, 1986 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
 July 22, 1990 |
 May 10, 1994 |
 February 26, 1998 |
 December 14, 2001 |
 October 3, 2005 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 22, 2009 |
 May 10, 2013 |
 February 26, 2017 |
 December 14, 2020 |
 October 2, 2024 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 22, 2028 |
 May 9, 2032 |
 February 27, 2036 |
 December 15, 2039 |
 October 3, 2043 |
| 156 | ||||
 July 22, 2047 | ||||
Tritos series
[edit]This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 June 26, 1805 (Saros 114) |
 May 27, 1816 (Saros 115) |
 April 26, 1827 (Saros 116) |
 March 25, 1838 (Saros 117) |
 February 23, 1849 (Saros 118) |
 January 23, 1860 (Saros 119) |
 December 22, 1870 (Saros 120) |
 November 21, 1881 (Saros 121) |
 October 20, 1892 (Saros 122) |
 September 21, 1903 (Saros 123) |
 August 21, 1914 (Saros 124) |
 July 20, 1925 (Saros 125) |
 June 19, 1936 (Saros 126) |
 May 20, 1947 (Saros 127) |
 April 19, 1958 (Saros 128) |
 March 18, 1969 (Saros 129) |
 February 16, 1980 (Saros 130) |
 January 15, 1991 (Saros 131) |
 December 14, 2001 (Saros 132) |
 November 13, 2012 (Saros 133) |
 October 14, 2023 (Saros 134) |
 September 12, 2034 (Saros 135) |
 August 12, 2045 (Saros 136) |
 July 12, 2056 (Saros 137) |
 June 11, 2067 (Saros 138) |
 May 11, 2078 (Saros 139) |
 April 10, 2089 (Saros 140) |
 March 10, 2100 (Saros 141) |
 February 8, 2111 (Saros 142) |
 January 8, 2122 (Saros 143) |
 December 7, 2132 (Saros 144) |
 November 7, 2143 (Saros 145) |
 October 7, 2154 (Saros 146) |
 September 5, 2165 (Saros 147) |
 August 4, 2176 (Saros 148) |
 July 6, 2187 (Saros 149) |
 June 4, 2198 (Saros 150) | |||
Inex series
[edit]This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||
|---|---|---|
 April 14, 1828 (Saros 126) |
 March 25, 1857 (Saros 127) |
 March 5, 1886 (Saros 128) |
 February 14, 1915 (Saros 129) |
 January 25, 1944 (Saros 130) |
 January 4, 1973 (Saros 131) |
 December 14, 2001 (Saros 132) |
 November 25, 2030 (Saros 133) |
 November 5, 2059 (Saros 134) |
 October 14, 2088 (Saros 135) |
 September 26, 2117 (Saros 136) |
 September 6, 2146 (Saros 137) |
 August 16, 2175 (Saros 138) |
||
Notes
[edit]- ^ The times listed for this location occur on December 15, 2001, local time.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c "December 14, 2001 Annular Solar Eclipse". timeanddate. Retrieved 11 August 2024.
- ^ "Eclipse anular". La Prensa. 2001-12-09. p. 71. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Moon shadow". South Florida Sun Sentinel. 2001-12-15. p. 15. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Hawaii, Costa Rica had best views". The Orlando Sentinel. 2001-12-15. p. 35. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 11 August 2024.
- ^ Paul Maley. "2001 Annular Solar Eclipse in Costa Rica". Eclipse Tours. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015.
- ^ a b "Eclipse Expedition to Costa Rica 2001". Argelander-Instituts für Astronomie. Archived from the original on 28 June 2013.
- ^ Jay M. Pasachoff. "Costa Rica Annular Eclipse Trip". ICSTARS Astronomy. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 132". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
- NASA Press release: Annular Solar Eclipse of 2001 December 14
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
Photos:
- Photos of solar eclipse around the world
- NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day: Partial Eclipse, Cloudy Day, near Des Moines, Iowa (21 December 2001)
- Partial Solar Eclipse from the USA
- SpaceWeather.com Dec 14, 2001, Solar Eclipse Gallery and [1]





