| Clitoris | |
|---|---|
 Human clitoris. Pubic hair has been deliberately removed to show anatomical detail. Location of (1) clitoral hood and (2) clitoral glans (the clitoral body is beneath the hood). | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Genital tubercle |
| Part of | Vulva |
| Artery | Dorsal artery of clitoris, deep artery of clitoris, artery of bulb, internal pudendal artery |
| Vein | Superficial dorsal veins of clitoris, deep dorsal vein of clitoris, vein of bulb, internal pudendal veins |
| Nerve | Dorsal nerve of clitoris, pudendal nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | clitoris |
| Greek | κλειτορίς |
| MeSH | D002987 |
| TA98 | A09.2.02.001 |
| TA2 | 3565 |
| FMA | 9909 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In amniotes, the clitoris (/ˈklɪtərɪs/ ⓘ KLIT-ər-iss or /klɪˈtɔːrɪs/ ⓘ klih-TOR-iss; pl.: clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ.[1] In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female sexual pleasure.[2] The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 nerve endings.[3][4]
Sexological, medical, and psychological debate has focused on the clitoris,[5] and it has been subject to social constructionist analyses and studies.[6] Such discussions range from anatomical accuracy, gender inequality, female genital mutilation, and orgasmic factors and their physiological explanation for the G-spot.[7] The only known purpose of the human clitoris is to provide sexual pleasure.[8]
Knowledge of the clitoris is significantly affected by its cultural perceptions. Studies suggest that knowledge of its existence and anatomy is scant in comparison with that of other sexual organs (especially male sex organs)[9] and that more education about it could help alleviate stigmas, such as the idea that the clitoris and vulva in general are visually unappealing or that female masturbation is taboo and disgraceful.[10][11][12]
The clitoris is homologous to the penis in males.[13]
Etymology and terminology
The Oxford English Dictionary states that the Neo-Latin word clītoris likely has its origin in the Ancient Greek κλειτορίς (kleitorís), which means "little hill", and perhaps derived from the verb κλείειν (kleíein), meaning "to shut" or "to sheathe".[14][15] Clitoris is also related to the Greek word κλείς (kleís), "key", "indicating that the ancient anatomists considered it the key" to female sexuality.[16][17] In addition, the Online Etymology Dictionary suggests other Greek candidates for this word's etymology include a noun meaning "latch" or "hook" or a verb meaning "to touch or titillate lasciviously", "to tickle".[15] The Oxford English Dictionary also states that the colloquially shortened form clit, the first occurrence of which was noted in the United States, has been used in print since 1958: until then, the common abbreviation was clitty.[14] Other slang terms for clitoris are bean, nub, and love button.[18][19][20] The term clitoris is commonly used to refer to the glans alone.[21] In recent anatomical works, the clitoris has also been referred to as the bulbo-clitoral organ.[22]
Structure

Most of the clitoris is composed of internal parts. Regarding humans, it consists of the glans, the body (which is composed of two erectile structures known as the corpora cavernosa), the prepuce, and the root. The frenulum is beneath the glans.[23]
Research indicates that clitoral tissue extends into the vaginal anterior wall.[24] Şenaylı et al. said that the histological evaluation of the clitoris, "especially of the corpora cavernosa, is incomplete because for many years the clitoris was considered a rudimentary and nonfunctional organ". They added that Baskin and colleagues examined the clitoris' masculinization after dissection and using imaging software after Masson's trichrome staining, put the serial dissected specimens together; this revealed that nerves surround the whole clitoral body.[25]
The clitoris, its bulbs, labia minora, and urethra involve two histologically distinct types of vascular tissue (tissue related to blood vessels), the first of which is trabeculated, erectile tissue innervated by the cavernous nerves. The trabeculated tissue has a spongy appearance; along with blood, it fills the large, dilated vascular spaces of the clitoris and the bulbs. Beneath the epithelium of the vascular areas is smooth muscle.[26] As indicated by Yang et al.'s research, it may also be that the urethral lumen (the inner open space or cavity of the urethra), which is surrounded by a spongy tissue, has tissue that "is grossly distinct from the vascular tissue of the clitoris and bulbs, and on macroscopic observation, is paler than the dark tissue" of the clitoris and bulbs.[27] The second type of vascular tissue is non-erectile, which may consist of blood vessels that are dispersed within a fibrous matrix and have only a minimal amount of smooth muscle.[26]
Glans
| Clitoral glans | |
|---|---|
 A fully exposed human clitoral glans, shown below the hood | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Genital tubercle |
| Artery | Dorsal arteries of clitoris |
| Vein | Dorsal veins of clitoris |
| Nerve | Dorsal nerve of clitoris |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | glans clitoridis |
| MeSH | D002987 |
| TA98 | A09.2.02.001 |
| TA2 | 3565 |
| FMA | 9909 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Highly innervated, the clitoral glans (glans means "acorn" in Latin),[28] also known as the "head" or "tip",[29][30] exists at the top of the clitoral body as a fibro-vascular cap[26] and is usually the size and shape of a pea, although it is sometimes much larger or smaller. The glans is separated from the clitoral body by a ridge of tissue called the corona.[31][32] The clitoral glans is estimated to have 8,000 and possibly 10,000 or more sensory nerve endings, making it the most sensitive erogenous zone.[3][4] The glans also has numerous genital corpuscles.[33] Research conflicts on whether the glans is composed of erectile or non-erectile tissue. Some sources describe the clitoral glans and labia minora as composed of non-erectile tissue; this is especially the case for the glans.[21][26] They state that the clitoral glans and labia minora have blood vessels that are dispersed within a fibrous matrix and have only a minimal amount of smooth muscle,[26] or that the clitoral glans is "a midline, densely neural, non-erectile structure".[21] The clitoral glans is homologous to the male penile glans.[34]
Other descriptions of the glans assert that it is composed of erectile tissue and that erectile tissue is present within the labia minora.[35] The glans may be noted as having glandular vascular spaces that are not as prominent as those in the clitoral body, with the spaces being separated more by smooth muscle than in the body and crura.[27] Adipose tissue is absent in the labia minora, but the organ may be described as being made up of dense connective tissue, erectile tissue and elastic fibers.[35]
Frenulum
| Clitoral frenulum | |
|---|---|
 Frenulum of the clitoris located at 3 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | frenulum clitoridis |
| MeSH | D002987 |
| TA98 | A09.2.02.001 |
| TA2 | 3565 |
| FMA | 9909 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The clitoral frenulum or frenum (frenulum clitoridis and crus glandis clitoridis in Latin; the former meaning "little bridle")[36] is a medial band of tissue formed between the undersurface of the glans and the top ends of the labia minora.[36][37] It is homologous to the penile frenulum in males.[36] The frenulum's main function is to maintain the clitoris in its innate position.[36]
Body
| Body of the clitoris | |
|---|---|
 Diagram of clitoris. Body (labeled as "shaft") at the top. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Genital tubercle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | corpus clitoridis |
| MeSH | D002987 |
| TA98 | A09.2.02.001 |
| TA2 | 3565 |
| FMA | 9909 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The clitoral body (also known as the shaft of the clitoris)[38][39][40] is a portion behind the glans that contains the union of the corpora cavernosa, a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue that hold most of the blood in the clitoris during erection. It is homologous to the penile shaft in the male.[39][41] The two corpora forming the clitoral body are surrounded by thick fibro-elastic tunica albuginea, a sheath of connective tissue. These corpora are separated incompletely from each other in the midline by a fibrous pectiniform septum – a comblike band of connective tissue extending between the corpora cavernosa.[25][26] The clitoral body is also connected to the pubic symphysis by the suspensory ligament.
The body of the clitoris is a bent shape, which makes the clitoral angle or elbow.[42][43] The angle divides the body into the ascending part (internal) near the pubic symphysis and the descending part (external), which can be seen and felt through the clitoral hood.[44][45][23]
Root

Lying in the perineum (space between the vulva and anus) and within the superficial perineal pouch is the root of the clitoris, which consists of the posterior ends of the clitoris, the crura and the bulbs of vestibule.[46]
The crura ("legs") are the parts of the corpora cavernosa extending from the clitoral body and form an upside-down "V" shape. Each crus (singular form of crura) is attached to the corresponding ischial ramus – extensions of the corpora beneath the descending pubic rami.[25][26] Concealed behind the labia minora, the crura end with attachment at or just below the middle of the pubic arch.[N 1][48] Associated are the urethral sponge, perineal sponge, a network of nerves and blood vessels, the suspensory ligament of the clitoris, muscles and the pelvic floor.[26][49]
The vestibular bulbs are more closely related to the clitoris than the vestibule because of the similarity of the trabecular and erectile tissue within the clitoris and its bulbs, and the absence of trabecular tissue in other parts of the vulva, with the erectile tissue's trabecular nature allowing engorgement and expansion during sexual arousal.[26][50] The vestibular bulbs are typically described as lying close to the crura on either side of the vaginal opening; internally, they are beneath the labia majora. The anterior sections of the bulbs unite to create the bulbar commissure, which forms a long strip of erectile tissue dubbed the infra-corporeal residual spongy part (RSP)[51][52] that expands from the ventral shaft and terminates as the glans. The RSP is also connected to the shaft via the pars intermedia (venous plexus of Kobelt).[53][54] When engorged with blood, the bulbs cuff the vaginal opening and cause the vulva to expand outward.[26] Although several texts state that they surround the vaginal opening, Ginger et al. state that this does not appear to be the case and tunica albuginea does not envelop the erectile tissue of the bulbs.[26] In Yang et al.'s assessment of the bulbs' anatomy, they conclude that the bulbs "arch over the distal urethra, outlining what might be appropriately called the 'bulbar urethra' in women".[27]
Hood

The clitoral hood or prepuce projects at the front of the labia commissure, where the edges of the labia majora meet at the base of the pubic mound. It is partially formed by fusion of the upper labia minora. The hood's function is to cover and protect the glans and external shaft.[55] There is considerable variation in how much of the glans protrudes from the hood and how much is covered by it, ranging from completely covered to fully exposed,[56] and tissue of the labia minora also encircles the base of the glans.[50]
Size and length
There is no identified correlation between the size of the glans or clitoris as a whole, and a woman's age, height, weight, use of hormonal contraception, or being postmenopausal, although women who have given birth may have significantly larger clitoral measurements.[57] Centimetre and millimetre measurements of the clitoris show variations in size. The clitoral glans has been cited as typically varying from 2 mm to 1 cm (less than an inch) and usually being estimated at 4 to 5 mm in both the transverse and longitudinal planes.[58]
A 1992 study concluded that the total clitoral length, including glans and body, is 16.0 ± 4.3 mm (0.63 ± 0.17 in), where 16 mm (0.63 in) is the mean and 4.3 mm (0.17 in) is the standard deviation.[56] Concerning other studies, researchers from the Elizabeth Garrett Anderson and Obstetric Hospital in London measured the labia and other genital structures of 50 women from the age of 18 to 50, with a mean age of 35.6., from 2003 to 2004, and the results given for the clitoral glans were 3–10 mm for the range and 5.5 [1.7] mm for the mean.[59] Other research indicates that the clitoral body can measure 5–7 centimetres (2.0–2.8 in) in length, while the clitoral body and crura together can be 10 centimetres (3.9 in) or more in length.[26]
Development

The clitoris develops from a phallic outgrowth in the embryo called the genital tubercle. In the absence of testosterone, the genital tubercle allows for the formation of the clitoris; the initially rapid growth of the phallus gradually slows and the body and glans of the clitoris are formed along with its other structures.[60]
Function
Sexual stimulation and arousal
The clitoris has an abundance of nerve endings, and is the human female's most erogenous part of the body.[2] When sexually stimulated, it may incite sexual arousal, which may result from mental stimulation (sexual fantasy), activity with a sexual partner, or masturbation, and can lead to orgasm.[61] The most effective sexual stimulation of this organ is usually manually or orally, which is often referred to as direct clitoral stimulation; in cases involving sexual penetration, these activities may also be referred to as additional or assisted clitoral stimulation.[62]
Direct stimulation involves physical stimulation to the external anatomy of the clitoris – glans, hood, and shaft.[63] Stimulation of the labia minora, due to it being connected with the glans and hood, may have the same effect as direct clitoral stimulation.[64] Though these areas may also receive indirect physical stimulation during sexual activity, such as when in friction with the labia majora,[65] indirect clitoral stimulation is more commonly attributed to penile-vaginal penetration.[66][67] Penile-anal penetration may also indirectly stimulate the clitoris by the shared sensory nerves (especially the pudendal nerve, which gives off the inferior anal nerves and divides into two terminal branches: the perineal nerve and the dorsal nerve of the clitoris).[68]
Due to the glans' high sensitivity, direct stimulation to it is not always pleasurable; instead, direct stimulation to the hood or near the glans is often more pleasurable, with the majority of women preferring to use the hood to stimulate the glans, or to have the glans rolled between the labia, for indirect touch.[69] It is also common for women to enjoy the shaft being softly caressed in concert with the occasional circling of the glans. This might be with or without digital penetration of the vagina, while other women enjoy having the entire vulva caressed.[70] As opposed to the use of dry fingers, stimulation from well-lubricated fingers, either by vaginal lubrication or a personal lubricant, is usually more pleasurable for the external clitoris.[71][72]
As the clitoris' external location does not allow for direct stimulation by penetration, any external clitoral stimulation while in the missionary position usually results from the pubic bone area. As such, some couples may engage in the woman-on-top position or the coital alignment technique, a sex position combining the "riding high" variation of the missionary position with pressure-counterpressure movements performed by each partner in rhythm with sexual penetration, to maximize clitoral stimulation.[73][74] Same-sex female couples may engage in tribadism (vulva-to-vulva or vulva-to-body rubbing) for ample or mutual clitoral stimulation during whole-body contact.[N 2][76][77] Pressing the penis in a gliding or circular motion against the clitoris or stimulating it by the movement against another body part may also be practiced.[78][79] A vibrator (such as a clitoral vibrator), dildo or other sex toy may be used.[78][80] Other women stimulate the clitoris by use of a pillow or other inanimate object, by a jet of water from the faucet of a bathtub or shower, or by closing their legs and rocking.[81][82][83]
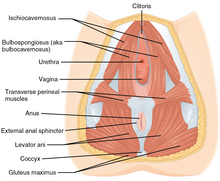

During sexual arousal, the clitoris and the rest of the vulva engorge and change color as the erectile tissues fill with blood (vasocongestion), and the individual experiences vaginal contractions.[84] The ischiocavernosus and bulbocavernosus muscles, which insert into the corpora cavernosa, contract and compress the dorsal vein of the clitoris (the only vein that drains the blood from the spaces in the corpora cavernosa), and the arterial blood continues a steady flow and having no way to drain out, fills the venous spaces until they become turgid and engorged with blood. This is what leads to clitoral erection.[16][85]
The prepuce has retracted and the glans becomes more visible. The glans doubles in diameter upon arousal and further stimulation becomes less visible as it is covered by the swelling of the clitoral hood.[84][86] The swelling protects the glans from direct contact, as direct contact at this stage can be more irritating than pleasurable.[86][87] Vasocongestion eventually triggers a muscular reflex, which expels the blood that was trapped in surrounding tissues, and leads to an orgasm.[88] A short time after stimulation has stopped, especially if orgasm has been achieved, the glans becomes visible again and returns to its normal state,[89] with a few seconds (usually 5–10) to return to its normal position and 5–10 minutes to return to its original size.[N 3][86][91] If orgasm is not achieved, the clitoris may remain engorged for a few hours, which women often find uncomfortable.[73] Additionally, the clitoris is very sensitive after orgasm, making further stimulation initially painful for some women.[92]
Clitoral and vaginal orgasmic factors
General statistics indicate that 70–80 percent of women require direct clitoral stimulation (consistent manual, oral, or other concentrated friction against the external parts of the clitoris) to reach orgasm.[N 4][N 5][N 6][96] Indirect clitoral stimulation (for example, by means of vaginal penetration) may also be sufficient for female orgasm.[N 7][21][98] The area near the entrance of the vagina (the lower third) contains nearly 90 percent of the vaginal nerve endings, and there are areas in the anterior vaginal wall and between the top junction of the labia minora and the urinary meatus that are especially sensitive, but intense sexual pleasure, including orgasm, solely from vaginal stimulation is occasional or otherwise absent because the vagina has significantly fewer nerve endings than the clitoris.[99]
The prominent debate over the quantity of vaginal nerve endings began with Alfred Kinsey. Although Sigmund Freud's theory that clitoral orgasms are a prepubertal or adolescent phenomenon and that vaginal (or G-spot) orgasms are something that only physically mature females experience had been criticized before, Kinsey was the first researcher to harshly criticize the theory.[100][101] Through his observations of female masturbation and interviews with thousands of women,[102] Kinsey found that most of the women he observed and surveyed could not have vaginal orgasms,[103] a finding that was also supported by his knowledge of sex organ anatomy.[104] Scholar Janice M. Irvine stated that he "criticized Freud and other theorists for projecting male constructs of sexuality onto women" and "viewed the clitoris as the main center of sexual response". He considered the vagina to be "relatively unimportant" for sexual satisfaction, relaying that "few women inserted fingers or objects into their vaginas when they masturbated". Believing that vaginal orgasms are "a physiological impossibility" because the vagina has insufficient nerve endings for sexual pleasure or climax, he "concluded that satisfaction from penile penetration [is] mainly psychological or perhaps the result of referred sensation".[105]
Masters and Johnson's research, as well as Shere Hite's, generally supported Kinsey's findings about the female orgasm.[106] Masters and Johnson were the first researchers to determine that the clitoral structures surround and extend along and within the labia. They observed that both clitoral and vaginal orgasms have the same stages of physical response, and found that the majority of their subjects could only achieve clitoral orgasms, while a minority achieved vaginal orgasms. On that basis, they argued that clitoral stimulation is the source of both kinds of orgasms,[107] reasoning that the clitoris is stimulated during penetration by friction against its hood.[108] The research came at the time of the second-wave feminist movement, which inspired feminists to reject the distinction made between clitoral and vaginal orgasms.[100][109] Feminist Anne Koedt argued that because men "have orgasms essentially by friction with the vagina" and not the clitoral area, this is why women's biology had not been properly analyzed. "Today, with extensive knowledge of anatomy, with [C. Lombard Kelly], Kinsey, and Masters and Johnson, to mention just a few sources, there is no ignorance on the subject [of the female orgasm]", she stated in her 1970 article The Myth of the Vaginal Orgasm. She added, "There are, however, social reasons why this knowledge has not been popularized. We are living in a male society which has not sought change in women's role".[100]
Supporting an anatomical relationship between the clitoris and vagina is a study published in 2005, which investigated the size of the clitoris; Australian urologist Helen O'Connell, described as having initiated discourse among mainstream medical professionals to refocus on and redefine the clitoris, noted a direct relationship between the legs or roots of the clitoris and the erectile tissue of the bulbs and corpora, and the distal urethra and vagina while using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology.[110][111] While some studies, using ultrasound, have found physiological evidence of the G-spot in women who report having orgasms during vaginal intercourse,[98] O'Connell argues that this interconnected relationship is the physiological explanation for the conjectured G-spot and experience of vaginal orgasms, taking into account the stimulation of the internal parts of the clitoris during vaginal penetration. "The vaginal wall is, in fact, the clitoris", she said. "If you lift the skin off the vagina on the side walls, you get the bulbs of the clitoris – triangular, crescental masses of erectile tissue".[21] O'Connell et al., having performed dissections on the vulvas of cadavers and used photography to map the structure of nerves in the clitoris, made the assertion in 1998 that there is more erectile tissue associated with the clitoris than is generally described in anatomical textbooks and were thus already aware that the clitoris is more than just its glans.[112] They concluded that some females have more extensive clitoral tissues and nerves than others, especially having observed this in young cadavers compared to elderly ones,[112] and therefore whereas the majority of females can only achieve orgasm by direct stimulation of the external parts of the clitoris, the stimulation of the more generalized tissues of the clitoris via vaginal intercourse may be sufficient for others.[21]
French researchers Odile Buisson (fr) and Pierre Foldès reported similar findings to that of O'Connell's. In 2008, they published the first complete 3D sonography of the stimulated clitoris and republished it in 2009 with new research, demonstrating how erectile tissue of the clitoris engorges and surrounds the vagina. Based on their findings, they argued that women may be able to achieve vaginal orgasm through stimulation of the G-spot because the clitoris is pulled closely to the anterior wall of the vagina when the woman is sexually aroused and during vaginal penetration. They assert that since the front wall of the vagina is inextricably linked with the internal parts of the clitoris, stimulating the vagina without activating the clitoris may be next to impossible. In their 2009 published study, it states the "coronal planes during perineal contraction and finger penetration demonstrated a close relationship between the root of the clitoris and the anterior vaginal wall". Buisson and Foldès suggested "that the special sensitivity of the lower anterior vaginal wall could be explained by pressure and movement of clitoris' root during a vaginal penetration and subsequent perineal contraction".[113][114]
Researcher Vincenzo Puppo, who, while agreeing that the clitoris is the center of female sexual pleasure and believing that there is no anatomical evidence of the vaginal orgasm, disagrees with O'Connell and other researchers' terminological and anatomical descriptions of the clitoris (such as referring to the vestibular bulbs as the "clitoral bulbs") and states that "the inner clitoris" does not exist because the penis cannot come in contact with the congregation of multiple nerves/veins situated until the angle of the clitoris, detailed by Georg Ludwig Kobelt, or with the root of the clitoris, which does not have sensory receptors or erogenous sensitivity, during vaginal intercourse.[115] Puppo's belief contrasts the general belief among researchers that vaginal orgasms are the result of clitoral stimulation; they reaffirm that clitoral tissue extends, or is at least stimulated by its bulbs, even in the area most commonly reported to be the G-spot.[116]
The G-spot is analogous to the base of the penis and has additionally been theorized, with the sentiment from researcher Amichai Kilchevsky that because female fetal development is the "default" state in the absence of substantial exposure to male hormones and therefore the penis is essentially a clitoris enlarged by such hormones, there is no evolutionary reason why females would have an entity in addition to the clitoris that can produce orgasms.[117] The general difficulty of achieving orgasms vaginally, which is a predicament that is likely due to nature easing the process of childbearing by drastically reducing the number of vaginal nerve endings,[118] challenge arguments that vaginal orgasms help encourage sexual intercourse to facilitate reproduction.[119][120] Supporting a distinct G-spot, however, is a study by Rutgers University, published in 2011, which was the first to map the female genitals onto the sensory portion of the brain; the scans indicated that the brain registered distinct feelings between stimulating the clitoris, the cervix and the vaginal wall – where the G-spot is reported to be – when several women stimulated themselves in a functional magnetic resonance machine.[114][121] Barry Komisaruk, head of the research findings, stated that he feels that "the bulk of the evidence shows that the G-spot is not a particular thing" and that it is "a region, it's a convergence of many different structures".[119]
Vestigiality, adaptionist and reproductive views
Whether the clitoris is vestigial, an adaptation, or serves a reproductive function has been debated.[122][123] Geoffrey Miller stated that Helen Fisher, Meredith Small and Sarah Blaffer Hrdy "have viewed the clitoral orgasm as a legitimate adaptation in its own right, with major implications for female sexual behavior and sexual evolution".[124] Like Lynn Margulis and Natalie Angier, Miller believes, "The human clitoris shows no apparent signs of having evolved directly through male mate choice. It is not especially large, brightly colored, specifically shaped or selectively displayed during courtship". He contrasts this with other female species that have clitorises as long as their male counterparts. He said the human clitoris "could have evolved to be much more conspicuous if males had preferred sexual partners with larger brighter clitorises" and that "its inconspicuous design combined with its exquisite sensitivity suggests that the clitoris is important not as an object of male mate choice, but as a mechanism of female choice".[124]
While Miller stated that male scientists such as Stephen Jay Gould and Donald Symons "have viewed the female clitoral orgasm as an evolutionary side-effect of the male capacity for penile orgasm" and that they "suggested that clitoral orgasm cannot be an adaptation because it is too hard to achieve",[124] Gould acknowledged that "most female orgasms emanate from a clitoral, rather than vaginal (or some other), site" and that his nonadaptive belief "has been widely misunderstood as a denial of either the adaptive value of female orgasm in general or even as a claim that female orgasms lack significance in some broader sense". He said that although he accepts that "clitoral orgasm plays a pleasurable and central role in female sexuality and its joys", "[a]ll these favorable attributes, however, emerge just as clearly and just as easily, whether the clitoral site of orgasm arose as a spandrel or an adaptation". He added that the "male biologists who fretted over [the adaptionist questions] simply assumed that a deeply vaginal site, nearer the region of fertilization, would offer greater selective benefit" due to their Darwinian, summum bonum beliefs about enhanced reproductive success.[125]
Similar to Gould's beliefs about adaptionist views and that "females grow nipples as adaptations for suckling, and males grow smaller unused nipples as a spandrel based upon the value of single development channels",[125] American philosopher Elisabeth Lloyd suggested that there is little evidence to support an adaptionist account of female orgasm.[120][123] Canadian sexologist Meredith L. Chivers stated that "Lloyd views female orgasm as an ontogenetic leftover; women have orgasms because the urogenital neurophysiology for orgasm is so strongly selected for in males that this developmental blueprint gets expressed in females without affecting fitness" and this is similar to "males hav[ing] nipples that serve no fitness-related function".[123]
At the 2002 conference for Canadian Society of Women in Philosophy, Nancy Tuana argued that the clitoris is unnecessary in reproduction; she stated that it has been ignored because of "a fear of pleasure. It is pleasure separated from reproduction. That's the fear". She reasoned that this fear causes ignorance, which veils female sexuality.[126] O'Connell stated, "It boils down to rivalry between the sexes: the idea that one sex is sexual and the other reproductive. The truth is that both are sexual and both are reproductive". She reiterated that the vestibular bulbs appear to be part of the clitoris and that the distal urethra and vagina are intimately related structures, although they are not erectile in character, forming a tissue cluster with the clitoris that appears to be the location of female sexual function and orgasm.[21][27]
Clinical significance
Modification
Genital modification may be for aesthetic, medical or cultural reasons.[127] This includes female genital mutilation (FGM), sex reassignment surgery (for trans men as part of transitioning), intersex surgery, and genital piercings.[25][128][129] Use of anabolic steroids by bodybuilders and other athletes can result in significant enlargement of the clitoris along with other masculinizing effects on their bodies.[130][131] Abnormal enlargement of the clitoris may be referred to as clitoromegaly or macroclitoris, but clitoromegaly is more commonly seen as a congenital anomaly of the genitalia.[132]
Clitoroplasty, a sex reassignment surgery for trans women, involves the construction of a clitoris from penile tissue.[133]
People taking hormones or other medications as part of a gender transition usually experience dramatic clitoral growth; individual desires and the difficulties of phalloplasty (construction of a penis) often result in the retention of the original genitalia with the enlarged clitoris as a penis analog (metoidioplasty).[25][129] However, the clitoris cannot reach the size of the penis through hormones.[129] A surgery to add function to the clitoris, such as metoidioplasty, is an alternative to phalloplasty that permits the retention of sexual sensation in the clitoris.[129]
In clitoridectomy, the clitoris may be removed as part of a radical vulvectomy to treat cancer such as vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia; however, modern treatments favor more conservative approaches, as invasive surgery can have psychosexual consequences.[134] Clitoridectomy more often involves parts of the clitoris being partially or completely removed during FGM, which may be additionally known as female circumcision or female genital cutting (FGC).[135][136] Removing the glans does not mean that the whole structure is lost, since the clitoris reaches deep into the genitals.[21]
In reduction clitoroplasty, a common intersex surgery, the glans is preserved and parts of the erectile bodies are excised.[25] Problems with this technique include loss of sensation, loss of sexual function, and sloughing of the glans.[25] One way to preserve the clitoris with its innervations and function is to imbricate and bury the glans; however, Şenaylı et al. state that "pain during stimulus because of trapped tissue under the scarring is nearly routine. In another method, 50 percent of the ventral clitoris is removed through the level base of the clitoral shaft, and it is reported that good sensation and clitoral function are observed in follow-up"; additionally, it has "been reported that the complications are from the same as those in the older procedures for this method".[25]
Concerning females who have the condition congenital adrenal hyperplasia, the largest group requiring surgical genital correction, researcher Atilla Şenaylı stated, "The main expectations for the operations are to create a normal female anatomy, with minimal complications and improvement of life quality". Şenaylı added that "[c]osmesis, structural integrity, the coital capacity of the vagina, and absence of pain during sexual activity are the parameters to be judged by the surgeon". (Cosmesis usually refers to the surgical correction of a disfiguring defect.) He stated that although "expectations can be standardized within these few parameters, operative techniques have not yet become homogeneous. Investigators have preferred different operations for different ages of patients".[25]
Gender assessment and surgical treatment are the two main steps in intersex operations. "The first treatments for clitoromegaly were simply resection of the clitoris. Later, it was understood that the clitoris glans and sensory input are important to facilitate orgasm", stated Atilla. The clitoral glans' epithelium "has high cutaneous sensitivity, which is important in sexual responses", and it is because of this that "recession clitoroplasty was later devised as an alternative, but reduction clitoroplasty is the method currently performed".[25]

What is often referred to as a "clitoris piercing" is the more common (and significantly less complicated) clitoral hood piercing. Since piercing the clitoris is difficult and very painful, piercing the clitoral hood is more common than piercing the clitoral shaft or glans, owing to the small percentage of people who are anatomically suited for it.[128] Clitoral hood piercings are usually channeled in the form of vertical piercings, and, to a lesser extent, horizontal piercings. The triangle piercing is a very deep horizontal hood piercing and is done behind the clitoris as opposed to in front of it. For styles such as the Isabella piercing, which passes through the clitoral shaft but is placed deep at the base, they provide unique stimulation and still require the proper genital build. The Isabella starts between the clitoral glans and the urethra, exiting at the top of the clitoral hood; this piercing is highly risky concerning the damage that may occur because of intersecting nerves.[128] (See Clitoral index.)
Sexual disorders
Persistent genital arousal disorder (PGAD) results in spontaneous, persistent, and uncontrollable genital arousal in women, unrelated to any feelings of sexual desire.[137] Clitoral priapism is a rare, potentially painful medical condition and is sometimes described as an aspect of PGAD.[137] With PGAD, arousal lasts for an unusually extended period (ranging from hours to days);[138] it can also be associated with morphometric and vascular modifications of the clitoris.[139]
Drugs may cause or affect clitoral priapism. The drug trazodone is known to cause male priapism as a side effect, but there is only one documented report that it may have caused clitoral priapism, in which case discontinuing the medication may be a remedy.[140] Additionally, nefazodone is documented to have caused clitoral engorgement, as distinct from clitoral priapism, in one case,[140] and clitoral priapism can sometimes start as a result of, or only after, the discontinuation of antipsychotics or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).[141]
Because PGAD is relatively rare and, as its concept apart from clitoral priapism, has only been researched since 2001, there is little research into what may cure or remedy the disorder.[137] In some recorded cases, PGAD was caused by or caused, a pelvic arterial-venous malformation with arterial branches to the clitoris; surgical treatment was effective in these cases.[142]
In 2022, an article in The New York Times reported several instances of women experiencing reduced clitoral sensitivity or inability to orgasm following various surgical procedures, including biopsies of the vulva, pelvic mesh surgeries (sling surgeries), and labiaplasties. The Times quoted several researchers who suggest that surgeons' lack of training in clitoral anatomy and nerve distribution may have been a factor.[143]
As it is part of the vulva, the clitoris is susceptible to pain (clitorodynia) from various conditions such as sexually transmitted infections and pudendal nerve entrapment.[144] The clitoris may also be affected by vulvar cancer, although at a much lower rate.[145]
Clitoral phimosis (or clitoral adhesions) is when the prepuce cannot be retracted, limiting exposure of the glans.[146]
Smegma
The secretion of smegma (smegma clitoridis) comes from the apocrine glands of the clitoris (sweat), the sebaceous glands of the clitoris (sebum) and desquamating epithelial cells.[147]
Society and culture
Ancient Greek–16th century knowledge and vernacular
Concerning historical and modern perceptions of the clitoris, the clitoris and the penis were considered equivalent by some scholars for more than 2,500 years in all respects except their arrangement.[148] Due to it being frequently omitted from, or misrepresented in, historical and contemporary anatomical texts, it was also subject to a continual cycle of male scholars claiming to have discovered it.[149] The ancient Greeks, ancient Romans, and Greek and Roman generations up to and throughout the Renaissance, were aware that male and female sex organs are anatomically similar,[150][151] but prominent anatomists such as Galen and Vesalius regarded the vagina as the structural equivalent of the penis, except for being inverted; Vesalius argued against the existence of the clitoris in normal women, and his anatomical model described how the penis corresponds with the vagina, without a role for the clitoris.[152]
Ancient Greek and Roman sexuality additionally designated penetration as "male-defined" sexuality. The term tribas, or tribade, was used to refer to a woman or intersex individual who actively penetrated another person (male or female) through the use of the clitoris or a dildo. As any sexual act was believed to require that one of the partners be "phallic" and that therefore sexual activity between women was impossible without this feature, mythology popularly associated lesbians with either having enlarged clitorises or as incapable of enjoying sexual activity without the substitution of a phallus.[153][154]
In 1545, Charles Estienne was the first writer to identify the clitoris in a work based on dissection, but he concluded that it had a urinary function.[21] Following this study, Realdo Colombo (also known as Renaldus Columbus), a lecturer in surgery at the University of Padua, Italy, published a book called De re anatomica in 1559, in which he describes the "seat of woman's delight".[155] In his role as researcher, Colombo concluded, "Since no one has discerned these projections and their workings, if it is permissible to give names to things discovered by me, it should be called the love or sweetness of Venus.", about the mythological Venus, goddess of erotic love.[156][157] Colombo's claim was disputed by his successor at Padua, Gabriele Falloppio (discoverer of the fallopian tube), who claimed that he was the first to discover the clitoris. In 1561, Falloppio stated, "Modern anatomists have entirely neglected it ... and do not say a word about it ... and if others have spoken of it, know that they have taken it from me or my students". This caused an upset in the European medical community, and, having read Colombo's and Falloppio's detailed descriptions of the clitoris, Vesalius stated, "It is unreasonable to blame others for incompetence on the basis of some sport of nature you have observed in some women and you can hardly ascribe this new and useless part, as if it were an organ, to healthy women". He concluded, "I think that such a structure appears in hermaphrodites who otherwise have well-formed genitals, as Paul of Aegina describes, but I have never once seen in any woman a penis (which Avicenna called albaratha and the Greeks called an enlarged nympha and classed as an illness) or even the rudiments of a tiny phallus".[158]
The average anatomist had difficulty challenging Galen's or Vesalius' research; Galen was the most famous physician of the Greek era and his works were considered the standard of medical understanding up to and throughout the Renaissance (i.e. for almost two thousand years),[151][152] and various terms being used to describe the clitoris seemed to have further confused the issue of its structure. In addition to Avicenna's naming it the albaratha or virga ("rod") and Colombo's calling it the sweetness of Venus, Hippocrates used the term columella ("little pillar"), and Albucasis, an Arabic medical authority, named it tentigo ("tension"). The names indicated that each description of the structures was about the body and glans of the clitoris but usually the glans.[21] It was additionally known to the Romans, who named it (vulgar slang) landica.[159] However, Albertus Magnus, one of the most prolific writers of the Middle Ages, felt that it was important to highlight "homologies between male and female structures and function" by adding "a psychology of sexual arousal" that Aristotle had not used to detail the clitoris. While in Constantine's treatise Liber de Coitu, the clitoris is referred to a few times, Magnus gave an equal amount of attention to male and female organs.[21]
Like Avicenna, Magnus also used the word virga for the clitoris, but employed it for the male and female genitals; despite his efforts to give equal ground to the clitoris, the cycle of suppression and rediscovery of the organ continued, and a 16th-century justification for clitoridectomy appears to have been confused with intersex conditions and the imprecision created by the word nymphae substituted for the word clitoris. Nymphotomy was a medical operation to excise an unusually large clitoris, but what was considered "unusually large" was often a matter of perception.[21] The procedure was routinely performed on Egyptian women,[160][161] due to physicians such as Jacques Daléchamps who believed that this version of the clitoris was "an unusual feature that occurred in almost all Egyptian women [and] some of ours, so that when they find themselves in the company of other women, or their clothes rub them while they walk or their husbands wish to approach them, it erects like a male penis and indeed they use it to play with other women, as their husbands would do ... Thus the parts are cut".[21]
17th century–present day knowledge and vernacular

Caspar Bartholin (whom Bartholin's glands are named after), a 17th-century Danish anatomist, dismissed Colombo's and Falloppio's claims that they discovered the clitoris, arguing that the clitoris had been widely known to medical science since the second century.[162] Although 17th-century midwives recommended to men and women that women should aspire to achieve orgasms to help them get pregnant for general health and well-being and to keep their relationships healthy,[151] debate about the importance of the clitoris persisted, notably in the work of Regnier de Graaf in the 17th century[50][163] and Georg Ludwig Kobelt in the 19th.[21]
Like Falloppio and Bartholin, de Graaf criticized Colombo's claim of having discovered the clitoris; his work appears to have provided the first comprehensive account of clitoral anatomy.[164] "We are extremely surprised that some anatomists make no more mention of this part than if it did not exist at all in the universe of nature", he stated. "In every cadaver, we have so far dissected we have found it quite perceptible to sight and touch". De Graaf stressed the need to distinguish nympha from clitoris, choosing to "always give [the clitoris] the name clitoris" to avoid confusion; this resulted in the frequent use of the correct name for the organ among anatomists, but considering that nympha was also varied in its use and eventually became the term specific to the labia minora, more confusion ensued.[21] Debate about whether orgasm was even necessary for women began in the Victorian era, and Freud's 1905 theory about the immaturity of clitoral orgasms (see above) negatively affected women's sexuality throughout most of the 20th century.[151][165]
Toward the end of World War I, a maverick British MP named Noel Pemberton Billing published an article entitled "The Cult of the Clitoris", furthering his conspiracy theories and attacking the actress Maud Allan and Margot Asquith, wife of the prime minister. The accusations led to a sensational libel trial, which Billing eventually won; Philip Hoare reports that Billing argued that "as a medical term, 'clitoris' would only be known to the 'initiated', and was incapable of corrupting moral minds".[166] Jodie Medd argues regarding "The Cult of the Clitoris" that "the female non-reproductive but desiring body [...] simultaneously demands and refuses interpretative attention, inciting scandal through its very resistance to representation".[167]
From the 18th to the 20th century, especially during the 20th, details of the clitoris from various genital diagrams presented in earlier centuries were omitted from later texts.[151][168] The full extent of the clitoris was alluded to by Masters and Johnson in 1966, but in such a muddled fashion that the significance of their description became obscured; in 1981, the Federation of Feminist Women's Health Clinics (FFWHC) continued this process with anatomically precise illustrations identifying 18 structures of the clitoris.[70][151] Despite the FFWHC's illustrations, Josephine Lowndes Sevely, in 1987, described the vagina as more of the counterpart of the penis.[169]
Concerning other beliefs about the clitoris, Hite (1976 and 1981) found that, during sexual intimacy with a partner, clitoral stimulation was more often described by women as foreplay than as a primary method of sexual activity, including orgasm.[170] Further, although the FFWHC's work significantly propelled feminist reformation of anatomical texts, it did not have a general impact.[111][171] Helen O'Connell's late 1990s research motivated the medical community to start changing the way the clitoris is anatomically defined.[111] O'Connell describes typical textbook descriptions of the clitoris as lacking detail and including inaccuracies, such as older and modern anatomical descriptions of the female human urethral and genital anatomy having been based on dissections performed on elderly cadavers whose erectile (clitoral) tissue had shrunk.[112] She instead credits the work of Georg Ludwig Kobelt as the most comprehensive and accurate description of clitoral anatomy.[21] MRI measurements, which provide a live and multi-planar method of examination, now complement the FFWHC's, as well as O'Connell's, research efforts concerning the clitoris, showing that the volume of clitoral erectile tissue is ten times that which is shown in doctors' offices and anatomy textbooks.[50][111]
In Bruce Bagemihl's survey of The Zoological Record (1978–1997) – which contains over a million documents from over 6,000 scientific journals – 539 articles focusing on the penis were found, while seven were found focusing on the clitoris.[9] In 2000, researchers Shirley Ogletree and Harvey Ginsberg concluded that there is a general neglect of the word clitoris in the common vernacular. They looked at the terms used to describe genitalia in the PsycINFO database from 1887 to 2000 and found that penis was used in 1,482 sources, vagina in 409, while clitoris was only mentioned in 83. They additionally analyzed 57 books listed in a computer database for sex instruction. In the majority of the books, penis was the most commonly discussed body part – mentioned more than clitoris, vagina, and uterus put together. They last investigated terminology used by college students, ranging from Euro-American (76%/76%), Hispanic (18%/14%), and African American (4%/7%), regarding the students' beliefs about sexuality and knowledge on the subject. The students were overwhelmingly educated to believe that the vagina is the female counterpart of the penis. The authors found that the student's belief that the inner portion of the vagina is the most sexually sensitive part of the female body correlated with negative attitudes toward masturbation and strong support for sexual myths.[172][173]

A study in 2005 reported that, among a sample of undergraduate students, the most frequently cited sources for knowledge about the clitoris were school and friends, and that this was associated with the least tested knowledge. Knowledge of the clitoris by self-exploration was the least cited, but "respondents correctly answered, on average, three of the five clitoral knowledge measures". The authors stated that "[k]nowledge correlated significantly with the frequency of women's orgasm in masturbation but not partnered sex" and that their "results are discussed in light of gender inequality and a social construction of sexuality, endorsed by both men and women, that privileges men's sexual pleasure over women's, such that orgasm for women is pleasing but ultimately incidental". They concluded that part of the solution to remedying "this problem" requires that males and females are taught more about the clitoris than is currently practiced.[174]
The humanitarian group Clitoraid launched the first annual International Clitoris Awareness Week, from 6 to 12 May in 2015. Clitoraid spokesperson Nadine Gary stated that the group's mission is to raise public awareness about the clitoris because it has "been ignored, vilified, made taboo, and considered sinful and shameful for centuries".[11][12] (See also Vulva activism)
Odile Fillod created a 3D printable, open source, full-size model of the clitoris, for use in a set of anti-sexist videos she had been commissioned to produce. Fillod was interviewed by Stephanie Theobald, whose article in The Guardian stated that the 3D model would be used for sex education in French schools, from primary to secondary level, from September 2016 onwards;[175] this was not the case, but the story went viral across the world.[176]
A questionnaire in a 2019 study was administered to a sample of educational sciences postgraduate students to trace the level of their knowledge concerning the organs of the female and male reproductive system. The authors reported that about two-thirds of the students failed to name parts of the vulva, such as the clitoris and labia, even after detailed pictures were provided to them.[177] An analysis in 2022 reported that the clitoris is mentioned in only one out of 113 Greek secondary education textbooks used in biology classes from the 1870s to present.[178]
Contemporary art
New York artist Sophia Wallace started work in 2012 on a multimedia project to challenge misconceptions about the clitoris. Based on O'Connell's 1998 research, Wallace's work emphasizes the sheer scope and size of the human clitoris. She says that ignorance of this still seems to be pervasive in modern society. "It is a curious dilemma to observe the paradox that on the one hand, the female body is the primary metaphor for sexuality, its use saturates advertising, art, and the mainstream erotic imaginary", she said. "Yet, the clitoris, the true female sexual organ, is virtually invisible". The project is called Cliteracy and it includes a "clit rodeo", which is interactive, climb-on model of a giant golden clitoris, including its inner parts, produced with the help of sculptor Kenneth Thomas. "It's been a showstopper wherever it's been shown. People are hungry to be able to talk about this", Wallace said. "I love seeing men standing up for the clit [...] Cliteracy is about not having one's body controlled or legislated [...] Not having access to the pleasure that is your birthright is a deeply political act".[179]
Another project started in New York, in 2016, street art that has since spread to almost 100 cities: Clitorosity, a "community-driven effort to celebrate the full structure of the clitoris", combining chalk drawings and words to spark interaction and conversation with passers-by, which the team documents on social media.[180][181] In 2016, Lori-Malépart Traversy made an animated documentary about the unrecognized anatomy of the clitoris.[182]
Alli Sebastian Wolf created a golden 100∶1 scale model of the clitoris in 2017, called the Glitoris and said, she hopes knowledge of the clitoris will soon become so uncontroversial that making art about them would be as irrelevant as making art about penises.[183]
Other projects listed by the BBC include Clito Clito, body-positive jewellery made in Berlin; Clitorissima, a documentary intended to normalize mother-daughter conversations about the clitoris; and a ClitArt festival in London, encompassing spoken word performances as well as visual art.[181] French art collective Les Infemmes (a blend word of "infamous" and "women") published a fanzine whose title can be translated as "The Clit Cheatsheet".[184]
Influence on female genital mutilation
Significant controversy surrounds female genital mutilation (FGM),[135][136] with the World Health Organization (WHO) being one of many health organizations that have campaigned against the procedures on behalf of human rights, stating that "FGM has no health benefits" and that it is "a violation of the human rights of girls and women" which "reflects deep-rooted inequality between the sexes".[136] The practice has existed at one point or another in almost all human civilizations,[160] most commonly to exert control over the sexual behavior, including masturbation, of girls and women, but also to change the clitoris' appearance.[136][161][185] Custom and tradition are the most frequently cited reasons for FGM, with some cultures believing that not performing it has the possibility of disrupting the cohesiveness of their social and political systems, such as FGM also being a part of a girl's initiation into adulthood. Often, a girl is not considered an adult in an FGM-practicing society unless she has undergone FGM,[136][161] and the "removal of the clitoris and labia – viewed by some as the male parts of a woman's body – is thought to enhance the girl's femininity, often synonymous with docility and obedience".[161]
Female genital mutilation is carried out in several societies, especially in Africa, with 85 percent of genital mutilations performed in Africa consisting of clitoridectomy or excision,[161][186] and to a lesser extent in other parts of the Middle East and Southeast Asia, on girls from a few days old to mid-adolescent, often to reduce the sexual desire to preserve vaginal virginity.[136][161][185] The practice of FGM has spread globally, as immigrants from Asia, Africa, and the Middle East bring the custom with them.[187] In the United States, it is sometimes practiced on girls born with a clitoris that is larger than usual.[135] Comfort Momoh, who specializes in the topic of FGM, states that FGM might have been "practiced in ancient Egypt as a sign of distinction among the aristocracy"; there are reports that traces of infibulation are on Egyptian mummies.[160] FGM is still routinely practiced in Egypt.[161][188] Greenberg et al. report that "one study found that 97 percent of married women in Egypt had had some form of genital mutilation performed".[188] Amnesty International estimated in 1997 that more than two million FGM procedures are performed every year.[161]
Other animals

Although the clitoris (and clitoral prepuce/sheath)[189][190] exists in all mammal species,[9] there are few detailed studies of the anatomy of the clitoris in non-humans.[191] Studies have been done on the clitoris of cats, sheep and mice.[192][193][191] Some mammals have clitoral glands. The clitoris is especially developed in fossas,[194] non-human apes, lemurs, moles,[195] and often contains a small bone known as the os clitoridis.[196] Many species of talpid moles exhibit peniform clitorises that are tunneled by the urethra and are found to have erectile tissue.[197] The clitoris is contained in fossa, which is a small pouch of tissue in horses and dogs.[198][199] The clitoris is found in other amniotic creatures[200] including reptiles such as turtles and crocodilians,[201] and birds such as ratites (e.g., cassowaries, ostriches)[202][203] and anatids (e.g., swans, ducks).[204] The hemiclitoris is one-half of a paired structure in squamates (lizards and snakes). Some intersex female bears mate and give birth through the tip of the clitoris; these species are grizzly bears, brown bears, American black bears and polar bears. Although the bears have been described as having "a birth canal that runs through the clitoris rather than forming a separate vagina" (a feature that is estimated to make up 10 to 20 percent of the bears' population),[205] scientists state that female spotted hyenas are the only non-intersex female mammals devoid of an external vaginal opening, and whose sexual anatomy is distinct from usual intersex cases.[206]

Non-human primates
In spider monkeys, the clitoris is especially developed and has an interior passage, or urethra, that makes it almost identical to the penis, and it retains and distributes urine droplets as the female spider monkey moves around. Scholar Alan F. Dixson stated that this urine "is voided at the bases of the clitoris, flows down the shallow groove on its perineal surface, and is held by the skin folds on each side of the groove".[207] Because spider monkeys of South America have pendulous and erectile clitorises long enough to be mistaken for a penis, researchers and observers of the species look for a scrotum to determine the animal's sex; a similar approach is to identify scent-marking glands that may also be present on the clitoris.[208]
The clitoris erects in squirrel monkeys during dominance displays, which indirectly influences the squirrel monkeys' reproductive success.[209]
The clitoris of bonobos is larger and more externalized than in most mammals;[210] Natalie Angier said that a young adolescent "female bonobo is maybe half the weight of a human teenager, but her clitoris is three times bigger than the human equivalent, and visible enough to waggle unmistakably as she walks".[211] Female bonobos often engage in the practice of genital-genital (GG) rubbing. Ethologist Jonathan Balcombe stated that female bonobos rub their clitorises together rapidly for ten to twenty seconds, and this behavior, "which may be repeated in rapid succession, is usually accompanied by grinding, shrieking, and clitoral engorgement"; he added that, on average, they engage in this practice "about once every two hours", and as bonobos sometimes mate face-to-face, "evolutionary biologist Marlene Zuk has suggested that the position of the clitoris in bonobos and some other primates has evolved to maximize stimulation during sexual intercourse".[210]
Many strepsirrhine species exhibit elongated clitorises that are either fully or partially tunneled by the urethra, including mouse lemurs, dwarf lemurs, all Eulemur species, lorises and galagos.[212][213][214] Some of these species also exhibit a membrane seal across the vagina that closes the vaginal opening during the non-mating seasons, most notably mouse and dwarf lemurs.[212] The clitoral morphology of the ring-tailed lemur is the most well-studied. They are described as having "elongated, pendulous clitorises that are [fully] tunneled by a urethra". The urethra is surrounded by erectile tissue, which allows for significant swelling during breeding seasons, but this erectile tissue differs from the typical male corpus spongiosum.[215] Non-pregnant adult ring-tailed females do not show higher testosterone levels than males, but they do exhibit higher A4 and estrogen levels during seasonal aggression. During pregnancy, estrogen, A4, and testosterone levels are raised, but female fetuses are still "protected" from excess testosterone.[216] These "masculinized" genitalia are often found alongside other traits, such as female-dominated social groups, reduced sexual dimorphism that makes females the same size as males, and even ratios of sexes in adult populations.[216][217] This phenomenon that has been dubbed the "lemur syndrome".[218] A 2014 study of Eulemur masculinization proposed that behavioral and morphological masculinization in female Lemuriformes is an ancestral trait that likely emerged after their split from Lorisiformes.[217]
Spotted hyenas

While female spotted hyenas were sometimes referred to as pseudohermaphrodites[208] and scientists of ancient and later historical times believed that they were hermaphrodites,[208][206][219] modern scientists do not refer to them as such.[206][220] That designation is typically reserved for those who simultaneously exhibit features of both sexes;[220] the genetic makeup of female spotted hyenas "are clearly distinct" from male spotted hyenas.[206][220]
Female spotted hyenas have a clitoris 90 percent as long and the same diameter as a male penis (171 millimetres long and 22 millimetres in diameter),[208] and this pseudo-penis' formation seems largely androgen-independent because it appears in the female fetus before differentiation of the fetal ovary and adrenal gland.[206] The spotted hyenas have a highly erectile clitoris, complete with a false scrotum; author John C. Wingfield stated that "the resemblance to male genitalia is so close that sex can be determined with confidence only by palpation of the scrotum".[209] The pseudo-penis can also be distinguished from the males' genitalia by its greater thickness and more rounded glans.[206] The female possesses no external vagina, as the labia are fused to form a pseudo-scrotum. In the females, this scrotum consists of soft adipose tissue.[209][206][221] Like male spotted hyenas with regard to their penises, the female spotted hyenas have small spines on the head of their clitorises, which scholar Catherine Blackledge said makes "the clitoris tip feel like soft sandpaper". She added that the clitoris "extends away from the body in a sleek and slender arc, measuring, on average, over 17 cm from root to tip. Just like a penis, [it] is fully erectile, raising its head in hyena greeting ceremonies, social displays, games of rough and tumble or when sniffing out peers".[222]

Due to their higher levels of androgen exposure during fetal development, the female hyenas are significantly more muscular and aggressive than their male counterparts; social-wise, they are of higher rank than the males, being dominant or dominant and alpha, and the females who have been exposed to higher levels of androgen than average become higher-ranking than their female peers. Subordinate females lick the clitorises of higher-ranked females as a sign of submission and obedience, but females also lick each other's clitorises as a greeting or to strengthen social bonds; in contrast, while all males lick the clitorises of dominant females, the females will not lick the penises of males because males are considered to be of lowest rank.[221][224]
The female spotted hyenas urinate, copulate and give birth through the clitoris since the urethra and vagina exit through the clitoral glans.[209][206][222][225] This trait makes mating more laborious for the male than in other mammals, and also makes attempts to sexually coerce (physically force sexual activity on) females futile.[221] Joan Roughgarden, an ecologist and evolutionary biologist, said that because the hyena's clitoris is higher on the belly than the vagina in most mammals, the male hyena "must slide his rear under the female when mating so that his penis lines up with [her clitoris]". In an action similar to pushing up a shirtsleeve, the "female retracts the [pseudo-penis] on itself, and creates an opening into which the male inserts his own penis".[208] The male must practice this act, which can take a couple of months to successfully perform.[224] Female spotted hyenas exposed to larger doses of androgen have significantly damaged ovaries, making it difficult to conceive.[224] After giving birth, the pseudo-penis is stretched and loses much of its original aspects; it becomes a slack-walled and reduced prepuce with an enlarged orifice with split lips.[226] Approximately 15% of the females die during their first time giving birth, and over 60% of their species' firstborn young die.[208]
A 2006 Baskin et al. study concluded, "The basic anatomical structures of the corporeal bodies in both sexes of humans and spotted hyenas were similar. As in humans, the dorsal nerve distribution was unique in being devoid of nerves at the 12 o'clock position in the penis and clitoris of the spotted hyena" and that "[d]orsal nerves of the penis/clitoris in humans and male spotted hyenas tracked along both sides of the corporeal body to the corpus spongiosum at the 5 and 7 o'clock positions. The dorsal nerves penetrated the corporeal body and distally the glans in the hyena", and in female hyenas, "the dorsal nerves fanned out laterally on the clitoral body. Glans morphology was different in appearance in both sexes, being wide and blunt in the female and tapered in the male".[225]
See also
- Clitoral enlargement
- Clitoral pump
- Clitoria, a type of tropical plant
- The Evolution of Human Sexuality
- Nocturnal clitoral tumescence
Notes
- ^ "The long, narrow crura arise from the inferior surface of the ischiopubic rami and fuse just below the middle of the pubic arch."[47]
- ^ "A common variation is 'tribadism,' where two women lie face to face, one on top of the other. The genitals are pressed tightly together while the partners move in a grinding motion. Some rub their clitoris against their partner's pubic bone."[75]
- ^ "Within a few seconds the clitoris returns to its normal position, and after 5–10 minutes shrinks to its normal size."[90]
- ^ "Most women report the inability to achieve orgasm with vaginal intercourse and require direct clitoral stimulation ... About 20% have coital climaxes ..."[93]
- ^ "Women rated clitoral stimulation as at least somewhat more important than vaginal stimulation in achieving orgasm; only about 20% indicated that they did not require additional clitoral stimulation during intercourse."[94]
- ^ "a. The amount of time of sexual arousal needed to reach orgasm is variable – and usually much longer – in women than in men; thus, only 20–30% of women attain a coital climax. b. Many women (70–80%) require manual clitoral stimulation ..."[95]
- ^ "In sum, it seems that approximately 25% of women always have orgasm with intercourse, while a narrow majority of women have orgasm with intercourse more than half the time ... According to the general statistics, cited in Chapter 2, [women who can consistently and easily have orgasms during unassisted intercourse] represent perhaps 20% of the adult female population, and thus cannot be considered representative."[97]
References
- ^ Goodman 2009; Roughgarden 2004, pp. 37–40; Wingfield 2006, p. 2023
- ^ a b Rodgers 2003, pp. 92–93; O'Connell, Sanjeevan & Hutson 2005, pp. 1189–1195; Greenberg, Bruess & Conklin 2010, p. 95; Weiten, Dunn & Hammer 2011, p. 386; Carroll 2012, pp. 110–111, 252
- ^ a b Carroll 2012, pp. 110–111, 252; Di Marino 2014, p. 81
- ^ a b
- White, Franny (27 October 2022). "Pleasure-producing human clitoris has more than 10,000 nerve fibers". News. Oregon Health & Science University. Archived from the original on 1 November 2022. Retrieved 2 November 2022.
Blair Peters, M.D., an assistant professor of surgery in the OHSU School of Medicine and a plastic surgeon who specializes in gender-affirming care as part of the OHSU Transgender Health Program, led the research and presented the findings. Peters obtained clitoral nerve tissue from seven adult transmasculine volunteers who underwent gender-affirming genital surgery. Tissues were dyed and magnified 1,000 times under a microscope so individual nerve fibers could be counted with the help of image analysis software.
- Peters, B; Uloko, M; Isabey, P; How many Nerve Fibers Innervate the Human Clitoris? A Histomorphometric Evaluation of the Dorsal Nerve of the Clitoris Archived 2 November 2022 at the Wayback Machine 2 p.m. ET 27 October 2022, 23rd annual joint scientific meeting of Sexual Medicine Society of North America and International Society for Sexual Medicine
- White, Franny (27 October 2022). "Pleasure-producing human clitoris has more than 10,000 nerve fibers". News. Oregon Health & Science University. Archived from the original on 1 November 2022. Retrieved 2 November 2022.
- ^ Moore & Clarke 1995; Shrage & Stewart 2015, pp. 225–229; Blechner 2017
- ^ Moore & Clarke 1995; Wade, Kremer & Brown 2005, pp. 117–138; Labuski 2015, p. 19
- ^ Shrage & Stewart 2015, pp. 225–229; Schwartz & Kempner 2015, p. 24; Wood 2017, pp. 68–69; Blechner 2017
- ^ Rodgers 2003, pp. 92–93; O'Connell, Sanjeevan & Hutson 2005, pp. 1189–1195; Kilchevsky et al. 2012, pp. 719–726
- ^ a b c Balcombe 2007, p. 111
- ^ Ogletree & Ginsburg 2000, pp. 917–926; Wade, Kremer & Brown 2005, pp. 117–138; Waskul, Vannini & Wiesen 2007, pp. 151–174
- ^ a b "Clitoraid launches 'International Clitoris Awareness Week'". Clitoraid. 3 May 2013. Archived from the original on 28 January 2018. Retrieved 8 May 2013.
- ^ a b Moye, David (2 May 2013). "'International Clitoris Awareness Week' Takes Place May 6–12 (NSFW)". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 6 May 2013. Retrieved 19 June 2013.
- ^ Tortora, Gerard J; Anagnostakos, Nicholas P (1987). Principles of anatomy and physiology (5th ed.). New York: Harper & Row. pp. 727–728. ISBN 978-0060466695.
- ^ a b "clitoris". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ a b Harper, Douglas. "clitoris". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ^ a b Sloane 2002, pp. 32–33
- ^ Basavanthappa 2006, p. 24
- ^ Green, Jonathon (2005). Cassell's Dictionary of Slang. Weidenfeld & Nicolson. p. 82. ISBN 978-0-30436-636-1.
- ^ Victor, Terry; Dalzell, Tom (2015). The New Partridge Dictionary of Slang and Unconventional English. Taylor & Francis. p. 1601. ISBN 978-1-31737-252-3.
- ^ Victor, Terry; Dalzell (2014). The Concise New Partridge Dictionary of Slang and Unconventional English. Taylor & Francis. p. 491. ISBN 978-1-31762-512-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p O'Connell, Sanjeevan & Hutson 2005, pp. 1189–1195
- ^ Stecco, Carla; Driscoll, Mark; Huijing, Peter; Schleip, Robert (2021). Fascia: The Tensional Network of the Human Body - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 129. ISBN 978-0-70208-413-3.
- ^ a b Sloane 2002, p. 32; Crooks & Baur 2010, pp. 54–56; Angier 1999, pp. 64–65; Jones & Lopez 2013, p. 352
- ^ O'Connell & Sanjeevan 2006, pp. 105–112; Kilchevsky et al. 2012, pp. 719–726; Di Marino 2014, p. 81
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Şenaylı & Ankara 2011, pp. 273–277
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Ginger & Yang 2011, pp. 13–22
- ^ a b c d Yang et al. 2006, pp. 766–772
- ^ Hodgson, Charles (2015). Carnal Knowledge: A Navel Gazer's Dictionary of Anatomy, Etymology, and Trivia. St. Martin's Publishing Group. p. 179. ISBN 978-1-46689-043-5.
- ^ Kinsey, Alfred C. (1998). Sexual Behavior in the Human Female. Indiana University Press. p. 574. ISBN 978-0-25333-411-4.
- ^ Waters, Sophie (2007). Seeing the Gynecologist. Rosen Publishing Group. p. 17. ISBN 978-1-40421-948-9.
- ^ Iglesia, Cheryl B. (2016). Medical and Advanced Surgical Management of Pelvic Floor Disorders, An Issue of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Elselvier Health Sciences. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-32341-656-6.
- ^ Quicke, Donald Lambert Jesse (2023). Female Arousal and Orgasm: Anatomy, Physiology, Behaviour and Evolution. Bentham Science Publishers. p. 65. ISBN 978-9-81512-464-4.
- ^ Olausson, Håkan; Wessberg, Johan; Morrison, India; McGlone, Francis (14 October 2016). Affective Touch and the Neurophysiology of CT Afferents. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4939-6418-5.
- ^ Chapple, Christopher R.; Steers, William D. (2011). Practical Urology: Essential Principles and Practice. Springer London. p. 67. ISBN 978-1-84882-034-0. Retrieved 29 September 2023.
- ^ a b Yang et al. 2006, pp. 766–772; Wilkinson 2012, p. 5; Farage & Maibach 2013, p. 4
- ^ a b c d Baky Fahmy, Mohamed (2020). Normal and Abnormal Prepuce. Springer International Publishing. pp. 269–283. ISBN 978-3-03037-621-5. Retrieved 29 October 2023.
- ^ Sloane 2002, pp. 32–33; O'Connell & Sanjeevan 2006, pp. 105–112; Crooks & Baur 2010, pp. 54–56; Ginger & Yang 2011, pp. 13–22
- ^ Gormley-Fleming, Elizabeth; Peate, Ian (2021). Fundamentals of Children and Young People's Anatomy and Physiology: A Textbook for Nursing and Healthcare Students. Wiley. p. 307. ISBN 978-1-11961-924-6. Retrieved 29 September 2023.
- ^ a b Rodgers 2003, p. 92
- ^ Buy, Jean; Ghossain, Michel (2013). Gynecological Imaging: A Reference Guide to Diagnosis. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 31. ISBN 978-3-64231-012-6. Retrieved 11 October 2023.
- ^ Greenberg, Jerrold S.; Bruess, Clint E.; Oswalt, Sara B. (2014). Exploring the Dimensions of Human Sexuality. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 259. ISBN 978-1-44964-851-0. Retrieved 29 September 2023.
- ^ Nagy, D. (2013). Radiological anatomy. Elsevier Science. p. 345. ISBN 978-1-48328-076-9.
- ^ Di Marino 2014, p. 46.
- ^ Quicke, Donald Lambert Jesse (2023). Female Arousal and Orgasm: Anatomy, Physiology, Behaviour and Evolution. Bentham Science Publishers. pp. 56–57. ISBN 978-9-81512-464-4.
- ^ Reiffenstuhl, Günther; Platzer, Werner; Platzer, Warner; Knapstein, Paul Georg; Imig, John R. (1996). Vaginal Operations: Surgical Anatomy and Technique. Williams & Wilkins. p. 4. ISBN 978-9-81512-464-4.
- ^ Singh, Vishram (2023). Textbook of Anatomy- Abdomen and Lower Limb, Volume 2- E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-3-66243-680-6.
- ^ Cunningham 2005, p. 17
- ^ Farage & Maibach 2013, p. 4
- ^ Francoeur 2000, p. 180
- ^ a b c d O'Connell & Sanjeevan 2006, pp. 105–112
- ^ Goldstein, Irwin; Meston, Cindy M.; Davis, Susan; Traish, Abdulmaged (2006). Women's Sexual Function and Dysfunction: Study, Diagnosis and Treatment. Taylor & Francis. p. 675. ISBN 978-1-84214-263-9.
- ^ Di Marino 2014, pp. 51–52.
- ^ Clemente, Carmine D. (2010). Clemente's Anatomy Dissector: Guides to Individual Dissections in Human Anatomy with Brief Relevant Clinical Notes (applicable for Most Curricula). Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health. p. 205. ISBN 978-1-60831-384-6. Retrieved 29 September 2023.
- ^ FIPAT Federative International Programme (2013). Terminologia Embryologica: International Embryological Terminology. Thieme. p. 78. ISBN 978-3-13170-151-0.
- ^ Sloane 2002, p. 31; Kahn & Fawcett 2008, p. 105; Crooks & Baur 2010, p. 54
- ^ a b Verkauf, Von Thron & O'Brien 1992, pp. 41–44
- ^ Verkauf, Von Thron & O'Brien 1992, pp. 41–44; Farage & Maibach 2013, p. 4
- ^ Alexander 2017, p. 117
- ^ Lloyd et al. 2005, pp. 643–646
- ^ Sloane 2002, p. 148; Merz & Bahlmann 2004, p. 129; Schünke et al. 2006, p. 192
- ^ Francoeur 2000, p. 180; Carroll 2012, pp. 110–111, 252; Rosenthal 2012, p. 134
- ^ Rosenthal 2012, p. 134; Weiten, Dunn & Hammer 2011, p. 386; Greenberg, Bruess & Conklin 2010, p. 96; Lloyd 2005, pp. 21–53; Flaherty, Davis & Janicak 1993, p. 217; Kaplan 1983, pp. 204, 209–210
- ^ Boston Women's Health 1976, p. 45; O'Connell & Sanjeevan 2006, pp. 105–112; Krychman 2009, p. 194; Greenberg, Bruess & Conklin 2010, p. 96; Carroll 2012, pp. 110–111, 252
- ^ Kahn & Fawcett 2008, p. 105
- ^ Casper 2008, p. 39; Crooks & Baur 2010, p. 54 Carroll 2012, pp. 110–111, 252
- ^ "I Want a Better Orgasm!". WebMD. Archived from the original on 13 January 2009. Retrieved 18 August 2011.
- ^ Kaplan 1983, pp. 204, 209–210; Lloyd 2005, pp. 21–53.
- ^ Komisaruk et al. 2009, pp. 108–109
- ^ Carroll 2012, pp. 110–111, 252; Crooks & Baur 2010, p. 54; Hooper 2001, pp. 48–50; Reinisch & Beasley 1991, pp. 28–29; Roberts 2006, p. 42
- ^ a b Carroll 2012, pp. 110–111, 252
- ^ Carroll 2009, p. 264
- ^ Rosenthal 2012, p. 271
- ^ a b Roberts 2006, p. 145
- ^ Greenberg, Bruess & Conklin 2010, p. 96
- ^ Westheimer 2000, p. 166
- ^ Carroll 2009, p. 272
- ^ Crooks & Baur 2010, p. 239
- ^ a b Hite 2003, pp. 277–284
- ^ Halberstam 1998, p. 61; Greenberg, Bruess & Conklin 2010, p. 96
- ^ Taormino 2009, p. 52
- ^ Hooper 2001, p. 68
- ^ Hite 2003, p. 99
- ^ Hyde 2006, p. 231
- ^ a b Sloane 2002, pp. 32–33; Archer & Lloyd 2002, pp. 85–88; Porst & Buvat 2008, pp. 296–297
- ^ Porst & Buvat 2008, pp. 296–297
- ^ a b c Roberts 2006, p. 42
- ^ Reinisch & Beasley 1991, pp. 28–29; McAnulty & Burnette 2003, pp. 68, 118
- ^ Rosenthal 2012, p. 133
- ^ Reinisch & Beasley 1991, pp. 28–29
- ^ Dennerstein, Dennerstein & Burrows 1983, p. 108
- ^ Fogel & Woods 2008, p. 92
- ^ Carroll 2012, p. 244; Rosenthal 2012, p. 134; Archer & Lloyd 2002, pp. 85–88; Dennerstein, Dennerstein & Burrows 1983, p. 108
- ^ Kammerer-Doak & Rogers 2008, pp. 169–183
- ^ Mah & Binik 2001, pp. 823–856
- ^ Flaherty, Davis & Janicak 1993, p. 217
- ^ Lloyd 2005, pp. 21–53; Rosenthal 2012, pp. 134–135
- ^ Lloyd 2005, pp. 21–53
- ^ a b Acton 2012, p. 145
- ^ Weiten, Dunn & Hammer 2011, p. 386; Cavendish 2010, p. 590; Archer & Lloyd 2002, pp. 85–88; Lief 1994, pp. 65–66
- ^ a b c Koedt, Anne (1970). "The Myth of the Vaginal Orgasm". The CWLU Herstory Website Archive. Chicago Women's Liberation Union. Archived from the original on 6 January 2013. Retrieved 12 December 2011.
- ^ Tavris, Wade & Offir 1984, p. 95; Williams 2008, p. 162; Irvine 2005, pp. 37–38
- ^ Archer & Lloyd 2002, pp. 85–88; Andersen & Taylor 2007, p. 338; Williams 2008, p. 162
- ^ Pomeroy 1982, p. 8; Irvine 2005, pp. 37–38; Williams 2008, p. 162
- ^ Pomeroy 1982, p. 8
- ^ Irvine 2005, pp. 37–38
- ^ Pomeroy 1982, p. 8; Archer & Lloyd 2002, pp. 85–92; Hite 2003; Irvine 2005, pp. 37–38; Williams 2008, p. 162
- ^ Archer & Lloyd 2002, pp. 85–88; Williams 2008, p. 162; Rosenthal 2012, p. 134
- ^ Lloyd 2005, p. 53
- ^ Fahs 2011, pp. 38–45
- ^ O'Connell, Sanjeevan & Hutson 2005, pp. 1189–1195; Archer & Lloyd 2002, pp. 85–92
- ^ a b c d Graves, Jen (27 March 2012). "In Her Pants". The Stranger. Seattle. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ^ a b c Sloane 2002, pp. 32–33; Archer & Lloyd 2002, pp. 85–88
- ^ Foldès & Buisson 2009, pp. 1223–1231; Acton 2012, p. 145; Carroll 2013, p. 103
- ^ a b Pappas, Stephanie (9 April 2012). "Does the Vaginal Orgasm Exist? Experts Debate". LiveScience. Archived from the original on 11 October 2016. Retrieved 28 November 2012.
- ^ Puppo 2011, p. 5
- ^ Cavendish 2010, p. 590; Kilchevsky et al. 2012, pp. 719–726; Carroll 2013, p. 103
- ^ Alexander, Brian (18 January 2012). "Does the G-spot really exist? Scientist can't find it". MSNBC. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 2 March 2012.
- ^ Balon & Segraves 2009, p. 58; Weiten, Dunn & Hammer 2011, p. 386; Rosenthal 2012, p. 271
- ^ a b Kilchevsky et al. 2012, pp. 719–726
- ^ a b Lloyd 2005
- ^ Komisaruk et al. 2011, p. 2822; Lehmiller 2013, p. 120
- ^ Angier 1999, pp. 71–76; Gould 2002, pp. 1262–1263; Lloyd 2005; Miller 2011, pp. 238–239
- ^ a b c Chivers 2007, pp. 104–105
- ^ a b c Miller 2011, pp. 238–239
- ^ a b Gould 2002, pp. 1262–1263
- ^ Cairney, Richard (21 October 2002). "Exploring female sexuality". ExpressNews. University of Alberta. Archived from the original on 21 December 2011. Retrieved 21 December 2011.
- ^ Ogletree & Ginsburg 2000, pp. 917–926; Chalker 2002, p. 60; Momoh 2005, pp. 5–11
- ^ a b c Morris 2007, p. 218; Pitts-Taylor 2008, pp. 233–234
- ^ a b c d Brandes & Morey 2013, pp. 493–504; Lehmiller 2013, p. 134
- ^ Freberg 2009, p. 300
- ^ "A Dangerous and Illegal Way to Seek Athletic Dominance and Better Appearance. A Guide for Understanding the Dangers of Anabolic Steroids". Drug Enforcement Administration. March 2004. Archived from the original on 9 April 2004. Retrieved 7 November 2012.
- ^ Copcu et al. 2004, p. 4; Kaufman, Faro & Brown 2005, p. 22
- ^ Koch, Anne L. (2019). It Never Goes Away: Gender Transition at a Mature Age. Rutgers University Press. p. 89. ISBN 978-0-81359-839-0.
- ^ Ghaem-Maghami & Souter 2014, p. 440
- ^ a b c Crooks & Baur 2010, pp. 54–56
- ^ a b c d e f "Female genital mutilation". World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 2 July 2011. Retrieved 22 August 2012.
- ^ a b c Porst & Buvat 2008, pp. 293–297; Lehmiller 2013, p. 319; Andriole 2013, pp. 160–161
- ^ Gordon & Katlic 2017, p. 259
- ^ Battaglia & Venturoli 2009, pp. 2896–2900
- ^ a b Schatzberg, Cole & DeBattista 2010, p. 90
- ^ Goldmeier & Leiblum 2006, pp. 2896–2900; Collins, Drake & Deacon 2013, p. 147
- ^ Goldstein, Irwin (1 March 2004). "Persistent Sexual Arousal Syndrome". Boston University Medical Campus Institute for Sexual Medicine. Archived from the original on 8 October 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2013.
- ^ Gross, Rachel E. (17 October 2022). "Half the World Has a Clitoris. Why Don't Doctors Study It?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 October 2022. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- ^ "What is Vulvodynia?". The National Vulvodynia Association. Retrieved 29 January 2019.
- ^ "Vulvar Cancer Treatment". National Cancer Institute. 9 April 2019. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ^ Munarriz R, Talakoub L, Kuohung W, Gioia M, Hoag L, Flaherty E, Min K, Choi S, Goldstein I (2002). "The prevalence of phimosis of the clitoris in women presenting to the sexual dysfunction clinic: lack of correlation to disorders of desire, arousal and orgasm". Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy. 28 (Suppl 1): 181–5. doi:10.1080/00926230252851302. PMID 11898701. S2CID 45521652.
- ^ "Medical Dictionary". Medilexicon.
- ^ "The Clitoral Truth: The Secret World at Your Fingertips". Federation of Feminist Women's Health Clinics (FFWHC). Archived from the original on 13 November 2012. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
- ^ Harvey 2002; O'Connell, Sanjeevan & Hutson 2005, pp. 1189–1195; Ginger & Yang 2011, pp. 13–22
- ^ Chalker 2002, p. 77
- ^ a b c d e f Raab, Barbara (5 March 2001). "The clit conspiracy". Salon. Archived from the original on 8 January 2014. Retrieved 28 June 2012.
- ^ a b Angier 1999, p. 92; O'Connell, Sanjeevan & Hutson 2005, pp. 1189–1195
- ^ Swancutt 2007, pp. 11–21; Halberstam 1998, pp. 61–62
- ^ Norton, Rictor (12 July 2002). "A Critique of Social Constructionism and Postmodern Queer Theory, The 'Sodomite' and the 'Lesbian'". Archived from the original on 15 February 2008. Retrieved 30 July 2011.
- ^ Pitts-Taylor 2008, p. 80; Di Marino 2014, p. 7
- ^ Harvey 2002
- ^ Neil, Sigal & Chuchiak, IV 2007, p. 167
- ^ O'Connell, Sanjeevan & Hutson 2005, pp. 1189–1195; Di Marino 2014, p. 8
- ^ Adams 1982, pp. 97–98
- ^ a b c Momoh 2005, pp. 5–11
- ^ a b c d e f g h Koroma, Hannah (30 September 1997). "What is Female Genital Mutilation?" (PDF). Amnesty International. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 May 2016. Retrieved 25 April 2010.
- ^ Chalker 2002, pp. 78–79
- ^ Jocelyn & Setchell 1972
- ^ O'Connell, Sanjeevan & Hutson 2005, pp. 1189–1195; O'Connell & Sanjeevan 2006, pp. 105–112; Di Marino 2014, p. 9
- ^ Chalker 2002, p. 83
- ^ Philip Hoare, 1998. Oscar Wilde's Last Stand: Decadence, Conspiracy, and the Most Outrageous Trial of the Century
- ^ Lesbian Scandal and the Culture of Modernism by Jodie Medd. 2012, Cambridge University Press ISBN 978-1-107-02163-1
- ^ Chalker 2002, p. 85; O'Connell & Sanjeevan 2006, pp. 105–112; Ginger & Yang 2011, pp. 13–22
- ^ Frayser & Whitby 1995, pp. 198–199
- ^ Hite 2003, pp. 261–264
- ^ Seidman, Fischer & Meeks 2006, pp. 112–113
- ^ Ogletree & Ginsburg 2000, pp. 917–926
- ^ Waskul, Vannini & Wiesen 2007, pp. 151–174
- ^ Wade, Kremer & Brown 2005, pp. 117–138
- ^ Theobald, Stephanie (15 August 2016). "How a 3D clitoris will help teach French schoolchildren about sex". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- ^ Fillod, Odile (30 August 2016). "3D clitoris: the researcher Odile Fillod reviews the summer buzz". Makery. Archived from the original on 28 January 2020. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- ^ Ampatzidis, Georgios; Georgakopoulou, Despoina; Kapsi, Georgia (15 October 2019). "Clitoris, the unknown: what do postgraduate students of educational sciences know about reproductive physiology and anatomy?". Journal of Biological Education. 55 (3): 254–263. doi:10.1080/00219266.2019.1679658. ISSN 0021-9266. S2CID 208590370.
- ^ Ampatzidis, Georgios; Armeni, Anastasia (2022), Korfiatis, Konstantinos; Grace, Marcus (eds.), "Human Reproduction in Greek Secondary Education Textbooks (1870s to Present)", Current Research in Biology Education, Contributions from Biology Education Research, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 257–268, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-89480-1_20, ISBN 978-3030894795, archived from the original on 26 February 2023, retrieved 28 March 2022
- ^ Mosbergen, Dominique (29 August 2013). "Cliteracy 101: Artist Sophia Wallace Wants You To Know The Truth About The Clitoris". Women. The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 16 March 2015. Retrieved 2 September 2013.
- ^ "About". Clitorosity. Archived from the original on 21 December 2019. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- ^ a b Frymorgen, Tomasz (12 December 2017). "This woman is creating clitoris street art to get people talking about female pleasure". BBC Three. Archived from the original on 12 March 2018. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- ^ Malépart-Traversy, Lori (2016). "Le clitoris – Animated Documentary (2016)". www.youtube.com. Archived from the original on 3 November 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- ^ Wahlquist, Calla (31 October 2020). "The sole function of the clitoris is female orgasm. Is that why it's ignored by medical science?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 10 February 2021. Retrieved 10 January 2021.
- ^ Douard, Paul (18 August 2016). "We Spoke to the Woman Who Designed a 3D-Printed Clitoris". Vice. Archived from the original on 15 January 2020. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- ^ a b Momoh 2005, pp. 5–11; Greenberg, Bruess & Conklin 2010, p. 95
- ^ Fuller 2008, p. 45
- ^ Crawford & Unger 2004
- ^ a b Greenberg, Bruess & Conklin 2010, p. 95
- ^ Kitalyi, A.; Owen, E.; Jayasuria, N.; Smith, T. (2020). Livestock and Wealth Creation: Improving the Husbandry of Animals Kept By Resource-Poor People in Developing Countries. 5m publishing. p. 337. ISBN 978-1-91045-577-7.
- ^ Hodges, Frederick Mansfield; Denniston, George C.; Milos, Marilyn Fayre (2007). Male and Female Circumcision: Medical, Legal, and Ethical Considerations in Pediatric Practice. Springer US. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-58539-937-9.
- ^ a b Martin-Alguacil et al. 2008, pp. 1407–1413
- ^ Kawatani, Tanowitza & de Groata 1994, pp. 26–36
- ^ Smith et al. 2000, pp. 574–578
- ^ Hawkins et al. 2002
- ^ Sinclair et al. 2016
- ^ Angier 1999, pp. 68–69; Hall 2005, p. 344; Goodman 2009.
- ^ Jiménez, R.; Barrionuevo, F.J.; Burgos, M. (2013). "Natural Exceptions to Normal Gonad Development in Mammals". Sexual Development. 7 (1–3): 147–162. doi:10.1159/000338768. ISSN 1661-5433. PMID 22626995. S2CID 8721211.
- ^ Kustritz, Margaret V. Root (2006). The Dog Breeder's Guide to Successful Breeding and Health Management. Saunders Elsevier. p. 116. ISBN 978-1-41603-139-0.
- ^ Budras, Klaus-Dieter; Sack, W. O.; Rock, Sabine; Wünsche, Anita; Henschel, Ekkehard (2003). Anatomy of the Horse: An Illustrated Text. Wiley. p. 76. ISBN 978-3-89993-003-0.
- ^ Prum, Richard O. (2023). Performance All the Way Down: Genes, Development, and Sexual Difference. University of Chicago Press. p. 219. ISBN 978-0-22682-978-4.
- ^ Fishbeck & Sebastiani 2015, p. 64
- ^ Kotpal 2010, p. 394
- ^ McAloose, Denise; St. Leger, Judy; Terio, Karen A. (2018). Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals. Elsevier Science. p. 633. ISBN 978-0-12809-219-4.
- ^ Maxwell, Kenneth E. (2013). The Sex Imperative: An Evolutionary Tale of Sexual Survival. Springer US. p. 99. ISBN 978-1-48995-988-1.
- ^ Girshick & Green 2009, p. 24; Roughgarden 2004, pp. 37–40
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Glickman et al. 2006, pp. 349–356
- ^ Dixson 2012, p. 364
- ^ a b c d e f Roughgarden 2004, pp. 37–40
- ^ a b c d Wingfield 2006, p. 2023
- ^ a b Balcombe 2011, p. 88
- ^ Angier 1999, p. 68
- ^ a b Petter-Rousseaux, A. (1964). "Reproductive Physiology and Behavior of the Lemuroidea". Evolutionary and Genetic Biology of Primates. Elsevier. pp. 91–132. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-395562-3.50009-6. ISBN 978-0-12-395562-3.
- ^ Hill, W. C. Osman (William Charles Osman) (1957). Primates : comparative anatomy and taxonomy. Edinburgh U.P. OCLC 504203609.
- ^ Petty, Joseph M. A.; Drea, Christine M. (7 May 2015). "Female rule in lemurs is ancestral and hormonally mediated". Scientific Reports. 5 (1): 9631. Bibcode:2015NatSR...5E9631P. doi:10.1038/srep09631. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 4423346. PMID 25950904.
- ^ Drea, Christine M.; Weil, Anne (30 October 2007). "External genital morphology of the ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta): Females are naturally "masculinized"". Journal of Morphology. 269 (4): 451–463. doi:10.1002/jmor.10594. ISSN 0362-2525. PMID 17972270. S2CID 29073999.
- ^ a b Drea, Christine M. (August 2009). "Endocrine Mediators of Masculinization in Female Mammals". Current Directions in Psychological Science. 18 (4): 221–226. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8721.2009.01640.x. ISSN 0963-7214. S2CID 145424854.
- ^ a b Kappeler, Peter M; Fichtel, Claudia (2015). "Eco-evo-devo of the lemur syndrome: did adaptive behavioral plasticity get canalized in a large primate radiation?". Frontiers in Zoology. 12 (Suppl 1): S15. doi:10.1186/1742-9994-12-s1-s15. ISSN 1742-9994. PMC 4722368. PMID 26816515.
- ^ Kappeler, Peter M.; Schäffler, Livia (18 December 2007). "The lemur syndrome unresolved: extreme male reproductive skew in sifakas (Propithecus verreauxi), a sexually monomorphic primate with female dominance". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 62 (6): 1007–1015. doi:10.1007/s00265-007-0528-6. ISSN 0340-5443.
- ^ Rosenzweig, Leiman & Breedlove 1996, p. 438
- ^ a b c Blumberg 2009, pp. 232–236
- ^ a b c Szykman et al. 2007, pp. 815–846
- ^ a b Blackledge 2003, p. 90
- ^ Schmotzer & Zimmerman 1922, p. 260
- ^ a b c Carey, Bjorn (26 April 2006). "The Painful Realities of Hyena Sex". LiveScience. Archived from the original on 19 November 2012. Retrieved 7 November 2012.
- ^ a b Baskin et al. 2006, pp. 276–283
- ^ Rosevear 1974, pp. 357–358
Journals
- Baskin, Laurence S.; Yucel, Selcuk; Cunha, Gerald R.; Glickman, Stephen E.; Place, Ned J. (January 2006). "A Neuroanatomical Comparison of Humans and Spotted Hyena, a Natural Animal Model for Common Urogenital Sinus: Clinical Reflections on Feminizing Genitoplasty". Journal of Urology. 175 (1): 276–283. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)00014-5. PMID 16406926.
- Battaglia, Cesare; Venturoli, Stefano (August 2009). "Persistent Genital Arousal Disorder and Trazodone. Morphometric and Vascular Modifications of the Clitoris. A Case Report". The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 6 (10): 2896–2900. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01418.x. PMID 19674253.
- Foldès, Pierre; Buisson, Odile (2009). "The clitoral complex: a dynamic sonographic study". The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 6 (5): 1223–1231. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01231.x. PMID 19453931. S2CID 5096396.
- Blechner, Mark J. (2017). "The Clitoris: Anatomical and Psychological Issues". Studies in Gender and Sexuality. 18 (3): 190–200. doi:10.1080/15240657.2017.1349509. S2CID 148717326.
- Chivers, Meredith L. (2007). Wiederman, Michael W (ed.). "A Narrow (But Thorough) Examination of the Evolutionary Significance of Female Orgasm". Journal of Sex Research. 44 (1): 104–105. doi:10.1080/00224490709336797.
- Copcu, Eray; Aktas, Alper; Sivrioglu, Nazan; Copcu, Ozgen; Oztan, Yucel (2004). "Idiopathic isolated clitoromegaly: A report of two cases". Reprod Health. 1 (1): 4. doi:10.1186/1742-4755-1-4. PMC 523860. PMID 15461813.
- Glickman, Stephen E.; Cunha, Gerald R.; Drea, Christine M.; Conley, Alan J.; Place, Ned J. (2006). "Mammalian sexual differentiation: lessons from the spotted hyena". Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism. 17 (9): 349–356. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2006.09.005. PMID 17010637. S2CID 18227659.
- Goldmeier, D; Leiblum, SR (2006). "Persistent genital arousal in women – a new syndrome entity". International Journal of STD & AIDS. 17 (4): 215–216. doi:10.1258/095646206776253480. PMID 16595040. S2CID 38012437.
- Harvey, Elizabeth D. (Winter 2002). "Anatomies of Rapture: Clitoral Politics/Medical Blazons". Signs. 27 (2): 315–346. doi:10.1086/495689. JSTOR 3175784. S2CID 144437433.
- Hawkins, C. E.; Dallas, J. F.; Fowler, P. A.; Woodroffe, R.; Racey, P. A. (1 March 2002). "Transient Masculinization in the Fossa, Cryptoprocta ferox (Carnivora, Viverridae)". Biology of Reproduction. 66 (3): 610–615. doi:10.1095/biolreprod66.3.610. PMID 11870065.
- Jocelyn, Henry David; Setchell, Brian Peter (1972). "Regnier de Graaf on the human reproductive organs. An annotated translation of 'Tractatus de Virorum Organis Generationi Inservientibus' (1668) and 'De Mulierub Organis Generationi Inservientibus Tractatus Novus' (1672)". Journal of Reproduction and Fertility. Supplement. 17: 1–222. OCLC 468341279. PMID 4567037.
- Kammerer-Doak, Dorothy; Rogers, Rebecca G. (June 2008). "Female Sexual Function and Dysfunction". Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America. 35 (2): vii, 169–183. doi:10.1016/j.ogc.2008.03.006. PMID 18486835.
- Kawatani, Masahito; Tanowitza, Michael; et al. (February 1994). "Morphological and electrophysiological analysis of the peripheral and central afferent pathways from the clitoris of the cat". Brain Research. 646 (1): 26–36. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(94)90054-X. PMID 7519963. S2CID 20616698.
- Kilchevsky, Amichai; Vardi, Yoram; Lowenstein, Lior; Gruenwald, Ilan (January 2012). "Is the Female G-Spot Truly a Distinct Anatomic Entity?". The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 9 (3): 719–726. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02623.x. PMID 22240236.
- Cox, Lauren (19 January 2012). "G-Spot Does Not Exist, 'Without A Doubt,' Say Researchers". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 10 March 2019. Retrieved 2 March 2012.
- Komisaruk, Barry R.; Wise, Nan; Frangos, Eleni; Liu, Wen-Ching; Allen, Kachina; Brody, Stuart (October 2011). "Women's Clitoris, Vagina, and Cervix Mapped on the Sensory Cortex: fMRI Evidence". The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 8 (10): 2822–2830. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02388.x. PMC 3186818. PMID 21797981.
- "Surprise finding in response to nipple stimulation". CBS News. 5 August 2011. Archived from the original on 9 November 2013. Retrieved 2 March 2012.
- Lloyd, Jillian; Crouch, Naomi S.; Minto, Catherine L.; Liao, Lih-Mei; Creighton, Sarah M (May 2005). "Female genital appearance: 'normality' unfolds" (PDF). British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 112 (6): 643–646. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.585.1427. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00517.x. PMID 15842291. S2CID 17818072. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 October 2011. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
- Mah, Kenneth; Binik, Yitzchak M (August 2001). "The nature of human orgasm: a critical review of major trends". Clinical Psychology Review. 21 (6): 823–856. doi:10.1016/S0272-7358(00)00069-6. PMID 11497209.
- Martin-Alguacil, Nieves; Pfaff, Donald W.; Shelley, Deborah N.; Schober, Justine M. (June 2008). "Clitoral sexual arousal: an immunocytochemical and innervation study of the clitoris". BJUI. 101 (11): 1407–1413. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.07625.x. PMID 18454796. S2CID 31132967.
- O'Connell, Helen E.; Sanjeevan, Kalavampara V.; Hutson, John M. (October 2005). "Anatomy of the clitoris". The Journal of Urology. 174 (4): 1189–1195. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000173639.38898.cd. PMID 16145367. S2CID 26109805.
- Mascall, Sharon (11 June 2006). "Time for rethink on the clitoris". BBC News. Archived from the original on 9 September 2019. Retrieved 22 April 2010.
- Ogletree, Shirley Matile; Ginsburg, Harvey J. (2000). "Kept Under the Hood: Neglect of the Clitoris in Common Vernacular". Sex Roles. 43 (11–12): 917–926. doi:10.1023/A:1011093123517. S2CID 140325571.
- Moore, Lisa Jean; Clarke, Adele E. (April 1995). "Clitoral Conventions and Transgressions: Graphic Representations in Anatomy Texts, c1900-1991". Feminist Studies. 21 (2): 255–301. doi:10.2307/3178262. hdl:2027/spo.0499697.0021.204. JSTOR 3178262.
- Puppo, Vincenzo (September 2011). "Anatomy of the Clitoris: Revision and Clarifications about the Anatomical Terms for the Clitoris Proposed (without Scientific Bases) by Helen O'Connell, Emmanuele Jannini, and Odile Buisson". ISRN Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2011 (ID 261464): 261464. doi:10.5402/2011/261464. PMC 3175415. PMID 21941661.
- Rubenstein, N. M.; Cunha, G. R.; Wang, Y. Z.; Campbell, K. L.; Conley, A. J.; Catania, K. C.; Glickman, S. E.; Place, N. J. (December 2003). "Variation in ovarian morphology in four species of New World moles with a peniform clitoris". Reproduction. 126 (6): 713–719. doi:10.1530/rep.0.1260713. PMID 14748690.
- Schmotzer, B.; Zimmerman, A. (15 April 1922). von Eggeling, H. (ed.). "Über die weiblichen Begattungsorgane der gefleckten Hyäne" [About the female sexual organs of the spotted hyena]. Anatomischer Anzeiger (in German). 55 (12/13): 257–264.
- Şenaylı, Atilla; Ankara, Etlik (December 2011). "Controversies on clitoroplasty". Therapeutic Advances in Urology. 3 (6): 273–277. doi:10.1177/1756287211428165. PMC 3229251. PMID 22164197.
- Sinclair, Adriane Watkins; Glickman, Stephen E.; Baskin, Laurence; Cunha, Gerald R. (March 2016). "Anatomy of mole external genitalia: setting the record straight". The Anatomical Record. 299 (3): 385–399. doi:10.1002/ar.23309. PMC 4752857. PMID 26694958.
- Smith, K. C.; Parkinson, T. J.; Long, S. E.; Barr, F. J. (2000). "Anatomical, cytogenetic and behavioural studies of freemartin ewes". Veterinary Record. 146 (20): 574–578. doi:10.1136/vr.146.20.574. PMID 10839234. S2CID 35207213.
- Szykman, Micaela; Engh, Anne; Van Horn, Russell; Holekamp, Kay; Boydston, Erin (2007). "Courtship and mating in free-living spotted hyenas" (PDF). Behaviour. 144 (7): 815–846. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.630.5755. doi:10.1163/156853907781476418. JSTOR 4536481. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 November 2012. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- Verkauf, BS; Von Thron, J; O'Brien, WF (1992). "Clitoral size in normal women". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 80 (1): 41–44. PMID 1603495.
- Wade, Lisa D.; Kremer, Emily C.; Brown, Jessica (2005). "The Incidental Orgasm: The Presence of Clitoral Knowledge and the Absence of Orgasm for Women". Women & Health. 42 (1): 117–138. doi:10.1300/J013v42n01_07. PMID 16418125. S2CID 39966093. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 22 December 2020.
- Waskul, Dennis D.; Vannini, Phillip; Wiesen, Desiree (2007). "Women and Their Clitoris: Personal Discovery, Signification, and Use". Symbolic Interaction. 30 (2): 151–174. doi:10.1525/si.2007.30.2.151. hdl:10170/157.
- Yang, Claire C.; Cold, Christopher J.; Yilmaz, Ugur; Maravilla, Kenneth R. (April 2006). "Sexually responsive vascular tissue of the vulva". BJUI. 97 (4): 766–772. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05961.x. PMID 16536770.
Bibliography
- Acton, Ashton (2012). Issues in Sexuality and Sexual Behavior Research: 2011 Edition. ScholarlyEditions. ISBN 978-1-4649-6686-6. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Adams, J. N. (1982). The Latin Sexual Vocabulary. Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Andersen, Margaret L.; Taylor, Howard Francis (2007). Sociology: Understanding a Diverse Society. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0-495-00742-5. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Andriole, Gerald L. Jr. (2013). Year Book of Urology 2013. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-1-4557-7316-9. Archived from the original on 18 December 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Angier, Natalie (1999). Woman: An Intimate Geography. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 978-0-395-69130-4.
- Alexander, Ivy M (2017). Women's Health Care in Advanced Practice Nursing, Second Edition. Springer Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-8261-9004-8. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- Archer, John; Lloyd, Barbara (2002). Sex and Gender. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-63533-2.
- Bagemihl, Bruce (2000). Biological Exuberance: Animal Homosexuality and Natural Diversity. Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4668-0927-7. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Balcombe, Jonathan (2007). Pleasurable Kingdom: Animals and the Nature of Feeling Good. Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-8602-3. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Balcombe, Jonathan Peter (2011). The Exultant Ark: A Pictorial Tour of Animal Pleasure. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-26024-5. Archived from the original on 27 May 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Balon, Richard; Segraves, Robert Taylor (2009). Clinical Manual of Sexual Disorders. American Psychiatric Pub. ISBN 978-1-58562-905-3. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Basavanthappa, BT (2006). Textbook of Midwifery and Reproductive Health Nursing. Jaypee Brothers Publishers. ISBN 978-81-8061-799-7. Archived from the original on 17 June 2016. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Blackledge, Catherine (2003). The Story of V: A Natural History of Female Sexuality. Rutgers University Press. ISBN 978-0-8135-3455-8.
- Boston Women's Health Book Collective (1976). Our bodies, Ourselves: A Book by and for Women. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-22145-4.
- Blumberg, Mark S. (2009). Freaks of Nature: And what they tell us about evolution and development. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-988994-5. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Brandes, Steven B.; Morey, Allen F. (2013). Advanced Male Urethral and Genital Reconstructive Surgery. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4614-7708-2. Archived from the original on 24 December 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Carroll, Janell L. (2009). Sexuality Now: Embracing Diversity. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0-495-60274-3. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Carroll, Janell L. (2012). Sexuality Now: Embracing Diversity. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1-111-83581-1. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Carroll, Janell L. (2013). Discovery Series: Human Sexuality (1st ed.). Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1-111-84189-8. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Casper, Regina C. (2008). Women's Health: Hormones, Emotions and Behavior. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-06020-2. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Cavendish, Marshall (2010). Sex and Society. Vol. 2. Marshall Cavendish Corporation. ISBN 978-0-7614-7907-9. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Chalker, Rebecca (2002) [2000]. The Clitoral Truth. Seven Seas Press. ISBN 978-1-58322-473-1. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- Chapple, C. R.; Steers, William D. (2010). Practical Urology: Essential Principles and Practice. Springer. ISBN 978-1-84882-033-3. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Collins, Eve; Drake, Mandy; Deacon, Maureen (2013). The Physical Care of People with Mental Health Problems: A Guide For Best Practice. SAGE. ISBN 978-1-4462-7468-2. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- Crawford, Mary; Unger, Rhoda (2004). Women and Gender: A Feminist Psychology (4th ed.). Boston: McGraw Hill.
- Crooks, Robert; Baur, Karla (2010). Our Sexuality. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0-495-81294-4. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Cunningham, F Gary (2005). Williams Obstetrics: 22nd Edition. McGraw Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-150125-5. Archived from the original on 21 December 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Dennerstein, Dorraine; Dennerstein, Lorraine; Burrows, Graham D (1983). Handbook of psychosomatic obstetrics and gynaecology. Elsevier Biomedical Press. ISBN 978-0-444-80444-0.
- Di Marino, Vincent (2014). Anatomic Study of the Clitoris and the Bulbo-Clitoral Organ. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-04894-9. Archived from the original on 6 September 2014. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- Dixson, Alan F. (2012). Primate Sexuality: Comparative Studies of the Prosimians, Monkeys, Apes, and Humans. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-954464-6. Archived from the original on 11 May 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Drenth, Jelto (2005). The Origin of the World: Science and Fiction of the Vagina. Reaktion Books. ISBN 978-1-86189-210-2. Archived from the original on 21 December 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Fahs, Breanne (2011). Performing Sex: The Making and Unmaking of Women's Erotic Lives. SUNY Press. ISBN 978-1-4384-3781-1. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Farage, Miranda A.; Maibach, Howard I. (2013). The Vulva: Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-0531-8. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- Fishbeck, Dale W.; Sebastiani, Aurora (2015). Comparative Anatomy: Manual of Vertebrate Dissection. Morton Publishing Company. ISBN 978-1-61731-439-1.
- Flaherty, Joseph A.; Davis, John Marcell; Janicak, Philip G. (1993). Psychiatry: Diagnosis & therapy. A Lange clinical manual. Appleton & Lange. ISBN 978-0-8385-1267-8.
- Fogel, Ingram; Woods, Fugate (2008). Women's Health Care in Advanced Practice Nursing. Springer Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-8261-0235-5. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Francoeur, Robert T. (2000). The Complete Dictionary of Sexology. The Continuum Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-8264-0672-9.
- Frayser, Suzanne G.; Whitby, Thomas J (1995). Studies in Human Sexuality: A Selected Guide. Libraries Unlimited. ISBN 978-1-56308-131-6. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Freberg, Laura A. (2009). Discovering Biological Psychology. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0-547-17779-3. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Fuller, Linda K (2008). African Women's Unique Vulnerabilities to HIV/AIDS: Communication Perspectives and Promises. Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-8405-0. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Ghaem-Maghami, Sadaf; Souter, William Patrick (2014). "Carcinoma of the vagina and vulva". In Price, Pat; Sikora, Karol (eds.). Treatment of Cancer. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4822-1494-9.
- Ginger, V A T; Yang, C C (2011). "Chapter 2: Functional Anatomy of the Female Sex Organs". In Mulhall, John P.; Incrocci, Luca; Goldstein, Irwin; Rosen, Ray (eds.). Cancer and Sexual Health. Springer Publishing. ISBN 978-1-60761-915-4. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- Girshick, Lori B.; Green, Jamison (2009). Transgender Voices: Beyond Women and Men. University Press of New England. ISBN 978-1-58465-683-8. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Goodman, S. (2009). "Family Eupleridae (Madagascar Carnivores)". In Wilson, D; Mittermeier, R (eds.). Handbook of the Mammals of the World. Vol. 1: Carnivores. Lynx Edicions. ISBN 978-84-96553-49-1. Archived from the original on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- Gordon, David A.; Katlic, Mark R (2017). Pelvic Floor Dysfunction and Pelvic Surgery in the Elderly: An Integrated Approach. Springer. p. 259. ISBN 978-1-4939-6554-0.
- Gould, Stephen Jay (2002). The Structure of Evolutionary Theory. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-00613-3. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Greenberg, Jerrold S.; Bruess, Clint E.; Conklin, Sarah C (2010). Exploring the Dimensions of Human Sexuality. Jones & Bartlett Learning. ISBN 978-0-7637-7660-2. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Halberstam, Judith (1998). Female Masculinity. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-2243-6.
- Hall, Brian Keith (2005). Bones and Cartilage: Developmental and Evolutionary Skeletal Biology. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-12-319060-4. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Heffner, Linda (2001). Human Reproduction at a Glance. Blackwell Sciences. ISBN 978-0-632-05461-9.
- Hite, Shere (2003). The Hite Report: A Nationwide Study of Female Sexuality. New York: Seven Stories Press. ISBN 978-1-58322-569-1. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Hooper, Anne (2001). Sex Q & A. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-7566-6347-6. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Hyde, Janet Shibley (2006). Understanding Human Sexuality. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-298636-5.
- Jones, Richard E.; Lopez, Kristin H. (2013). Human Reproductive Biology. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-382185-0. Archived from the original on 9 August 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Irvine, Janice M. (2005). Disorders of desire: sexuality and gender in modern American sexology. Temple University Press. ISBN 978-1-59213-151-8. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Kahn, Ada P.; Fawcett, Jan (2008). The Encyclopedia of Mental Health. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8160-6454-0. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Kaplan, Helen Singer (1983). The Evaluation of Sexual Disorders: Psychological and Medical Aspects. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-87630-329-0. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Kaufman, Raymond H; Faro, Sebastian; Brown, Dale (2005). Benign Diseases of the Vulva And Vagina. Elsevier Mosby. ISBN 978-0-323-01474-8. Archived from the original on 23 December 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
The external genitalia of a female fetus may become masculinized if exposed to excess androgens in utero. ... Besides enlargement, congenital abnormalities of the clitoris may also include agenesis or hypoplasia. ... After the 13th to 14th weeks of gestation, androgen exposure produces clitoromegaly alone.
- Komisaruk, Barry R.; Whipple, Beverly; Nasserzadeh, Sara; Beyer-Flores, Carlos (2009). The Orgasm Answer Guide. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-9396-4.
- Kotpal, R. L. (2010). Modern Text Book of Zoology: Vertebrates. Rastogi Publications. ISBN 978-81-7133-891-7.
- Krychman, Michael L. (2009). 100 Questions & Answers About Women's Sexual Wellness and Vitality: A Practical Guide for the Woman Seeking Sexual Fulfillment. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7637-8697-7. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Labuski, Christine (2015). It Hurts Down There: The Bodily Imaginaries of Female Genital Pain. SUNY Press. ISBN 978-1-4384-5885-4. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 7 June 2018.
- Lehmiller, Justin J. (2013). The Psychology of Human Sexuality. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-118-35129-1. Archived from the original on 18 December 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Libertino, John A. (1998). Reconstructive urologic surgery. Mosby. ISBN 978-0-8016-7802-8.
- Lief, Harold I. (1994). "Discussion of the Paper by Helen Singer Kalplan". In Berger, Milton Miles (ed.). Women Beyond Freud: New Concepts of Feminine Psychology. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-87630-709-0.
- Llord, J; Uchil, D (2011). "12: Reproduction: Ambiguous Genitalia". In Arulkumaran, Sabaratnam; Regan, Lesley; Papageorghiou, Aris; Monga, Ash; Farquharson, David (eds.). Oxford Desk Reference: Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-162087-4. Archived from the original on 2 May 2016. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Lloyd, Elisabeth Anne (2005). The Case of the Female Orgasm: Bias in the Science of Evolution. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01706-1. OCLC 432675780. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Merz, Eberhard; Bahlmann, F. (2004). Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Vol. 1. Thieme Medical Publishers. ISBN 978-1-58890-147-7.
- McAnulty, Richard D.; Burnette, M. Michele (2003). Exploring human sexuality: making healthy decisions. Allyn & Bacon. ISBN 978-0-205-38059-6.
- Miller, Geoffrey (2011). The Mating Mind: How Sexual Choice Shaped the Evolution of Human Nature. Random House Digital. ISBN 978-0-307-81374-9. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Momoh, Comfort (2005). "1: Female Genital Mutilation". In Momoh, Comfort (ed.). Female Genital Mutilation. Radcliffe Publishing. ISBN 978-1-85775-693-7. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Morris, Desmond (2007). The Naked Woman: A Study of the Female Body. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-312-33853-4. Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- Morganstern, Steven; Abrahams, Allen (1998). The Prostate Sourcebook. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-1-56565-871-4. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Neil, L.; Sigal, Pete; Chuchiak, IV, John F. (2007). Sexual Encounters/Sexual Collisions: Alternative Sexualities in Colonial Mesoamerica. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-6670-6. Archived from the original on 19 December 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- O'Connell, Helen E.; Sanjeevan, Kalavampara V (2006). Goldstein, Irwin Joseph (ed.). Women's Sexual Function and Dysfunction: Study, Diagnosis and Treatment. Taylor & Francis US. ISBN 978-1-84214-263-9. Archived from the original on 2 January 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Pitts-Taylor, Victoria (2008). Cultural Encyclopedia of the Body. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-313-34145-8. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- Pomeroy, Wardell Baxter (1982) [1972]. Dr. Kinsey and the Institute for Sex Research 1982. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-02916-1. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Porst, Hartmut; Buvat, Jacques (2008). Standard Practice in Sexual Medicine. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4051-7872-3. Archived from the original on 22 December 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Reinisch, June M; Beasley, Ruth (1991). The Kinsey Institute New Report on Sex. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-312-06386-3. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Roberts, Keath (2006). Lotus Illustrated Dictionary of Sex. Lotus Press. ISBN 978-81-89093-59-4. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Rodgers, Joann Ellison (2003). Sex: A Natural History. Henry Holt and Company. ISBN 978-0-8050-7281-5. Retrieved 29 September 2023.
- Rosenthal, Martha (2012). Human Sexuality: From Cells to Society. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0-618-75571-4. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Rosenzweig, Mark R.; Leiman, Arnold L.; Breedlove, Marc (1996). Biological psychology. Sinauer Associates. ISBN 978-0-87893-775-2.
- Rosevear, Donovan Reginald (1974). The carnivores of West Africa. London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). ISBN 978-0-565-00723-2.
- Roughgarden, Joan (2004). Evolution's Rainbow: Diversity, Gender, and Sexuality in Nature and People. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-24073-5.
- Saladin, Kenneth S. (2010). Human anatomy. McGraw-Hill Higher Education. ISBN 978-0-07-298636-5. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Seidman, Steven; Fischer, Nancy L.; Meeks, Chet (2006). Handbook of the New Sexuality Studies. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-415-38648-7. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Schatzberg, Alan F.; Cole, Jonathan O.; DeBattista, Charles (2010). Manual of Clinical Psychopharmacology. Vol. 1. American Psychiatric Pub. ISBN 978-1-58562-377-8. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Schünke, Michael; Schulte, Erik; Ross, Lawrence M.; Lamperti, Edward D.; Schumacher, Udo (2006). Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System. Vol. 1. Thieme Medical Publishers. ISBN 978-3-13-142081-7. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Schuenke, Michael; Schulte, Erik; Schumacher, Udo (2010). General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System. Thieme Medical Publishers. ISBN 978-1-60406-287-8. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Schwartz, Pepper; Kempner, Martha (2015). 50 Great Myths of Human Sexuality. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-67433-8. Archived from the original on 21 December 2019. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- Shrage, Laurie J.; Stewart, Robert Scott (2015). Philosophizing About Sex. Broadview Press. ISBN 978-1-77048-536-5. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 7 June 2018.
- Sloane, Ethel (2002). Biology of Women. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0-7668-1142-3. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Swancutt, Diana M (2007). "Still before sexuality: "Greek" androgyny, the Roman imperial politics of masculinity and the Roman invention of the Tribas". In Penner, Todd C.; Stichele, Caroline Vander (eds.). Mapping gender in ancient religious discourses. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-15447-6. Archived from the original on 13 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Taormino, Tristan (2009). The Big Book of Sex Toys. Quiver. ISBN 978-1-59233-355-4. Archived from the original on 30 April 2016. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Tavris, Carol; Wade, Carole; Offir, Carole (1984). The longest war: sex differences in perspective. University of Michigan. ISBN 978-0-15-551186-6.
- Weiten, Wayne; Dunn, Dana S.; Hammer, Elizabeth Yost (2011). Psychology Applied to Modern Life: Adjustment in the 21st century. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1-111-18663-0. Archived from the original on 2 January 2014. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Westheimer, Ruth (2000). Encyclopedia of sex. Continuum. ISBN 978-0-8264-1240-9.
- Wilkinson, Edward J. (2012). Wilkinson and Stone Atlas of Vulvar Disease. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-1-4511-7853-1. Archived from the original on 21 December 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Williams, Linda (2008). Screening Sex. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-4285-4. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Wingfield, John C (2006). "Communicative Behaviors Hormone–Behavior Interactions, and Reproduction in Vertebrates". In Neill, Jimmy D (ed.). Physiology of Reproduction. Vol. 2. Gulf Professional Publishing. ISBN 978-0-12-515402-4. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- Wood, Rachel (2017). Consumer Sexualities: Women and Sex Shopping. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-315-44750-6. Archived from the original on 20 December 2019. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
External links
 The dictionary definition of clitoris at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of clitoris at Wiktionary Media related to Clitoris at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Clitoris at Wikimedia Commons- "The Clitoris – Animated Documentary" by Lori-Malépart Traversy (Video), 2016.








