| A | |
|---|---|
| A a | |
 | |
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | Alphabetic |
| Language of origin | Latin language |
| Sound values | |
| In Unicode | U+0041, U+0061 |
| Alphabetical position | 1 |
| History | |
| Development | |
| Time period | c. 700 BCE – present |
| Descendants | |
| Sisters | |
| Other | |
| Associated graphs | a(x), ae, eau, au |
| Writing direction | Left-to-right |
| ISO basic Latin alphabet |
|---|
| AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz |
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet,[1][2] used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is a (pronounced /ˈeɪ/ AY), plural aes.[nb 1][2]
It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives.[3] The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey |a| and single-storey |ɑ|. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type.
In English, a is the indefinite article, with the alternative form an.
Name
In English, the name of the letter is the long A sound, pronounced /ˈeɪ/. Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables.
History
The earliest known ancestor of A is aleph—the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet[4]—where it represented a glottal stop [ʔ], as Phoenician only used consonantal letters. In turn, the ancestor of aleph may have been a pictogram of an ox head in proto-Sinaitic script[5] influenced by Egyptian hieroglyphs, styled as a triangular head with two horns extended.
When the ancient Greeks adopted the alphabet, they had no use for a letter representing a glottal stop—so they adapted sign to represent the vowel /a/, calling the letter by the similar name alpha. In the earliest Greek inscriptions dating to the 8th century BC following the Greek Dark Ages, the letter rests upon its side. However, in the later Greek alphabet it generally resembles the modern capital form—though many local varieties can be distinguished by the shortening of one leg, or by the angle at which the cross line is set.
The Etruscans brought the Greek alphabet to the Italian Peninsula, and left the form of alpha unchanged. When the Romans adopted the Etruscan alphabet to write Latin, the resulting form used in the Latin script would come to be used to write many other languages, including English.
| Egyptian | Proto-Sinaitic | Proto-Canaanite | Phoenician | Western Greek | Etruscan | Latin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Typographic variants


During Roman times, there were many variant forms of the letter A. First was the monumental or lapidary style, which was used when inscribing on stone or other more permanent media. There was also a cursive style used for everyday or utilitarian writing, which was done on more perishable surfaces. Due to the perishable nature of these surfaces, there are not as many examples of this style as there are of the monumental, but there are still many surviving examples of different types of cursive, such as majuscule cursive, minuscule cursive, and semi-cursive minuscule. Variants also existed that were intermediate between the monumental and cursive styles. The known variants include the early semi-uncial, the uncial, and the later semi-uncial.[6]
 Blackletter Blackletter
|
||
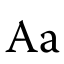 Roman Roman
|
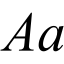 Italic Italic
|
 Script Script
|
At the end of the Roman Empire (5th century AD), several variants of the cursive minuscule developed through Western Europe. Among these were the semi-cursive minuscule of Italy, the Merovingian script in France, the Visigothic script in Spain, and the Insular or Anglo-Irish semi-uncial or Anglo-Saxon majuscule of Great Britain. By the ninth century, the Caroline script, which was very similar to the present-day form, was the principal form used in book-making, before the advent of the printing press. This form was derived through a combining of prior forms.[6]
15th-century Italy saw the formation of the two main variants that are known today. These variants, the Italic and Roman forms, were derived from the Caroline Script version. The Italic form ⟨ɑ⟩, also called script a, is often used in handwriting; it consists of a circle with a vertical stroke on its right. In the hands of medieval Irish and English writers, this form gradually developed from a 5th-century form resembling the Greek letter tau ⟨τ⟩.[4] The Roman form ⟨a⟩ is found in most printed material, and consists of a small loop with an arc over it.[6] Both derive from the majuscule form ⟨A⟩. In Greek handwriting, it was common to join the left leg and horizontal stroke into a single loop, as demonstrated by the uncial version shown. Many fonts then made the right leg vertical. In some of these, the serif that began the right leg stroke developed into an arc, resulting in the printed form, while in others it was dropped, resulting in the modern handwritten form. Graphic designers refer to the Italic and Roman forms as single-decker a and double decker a respectively.
Italic type is commonly used to mark emphasis or more generally to distinguish one part of a text from the rest set in Roman type. There are some other cases aside from italic type where script a ⟨ɑ⟩, also called Latin alpha, is used in contrast with Latin ⟨a⟩, such as in the International Phonetic Alphabet.
Use in writing systems
| Orthography | Phonemes |
|---|---|
| Standard Chinese (Pinyin) | /a/ |
| English | /æ/, /ɑː/, /ɒ/, /ɔː/, /ɛː/, /eɪ/, /ə/ |
| French | /a/, /ɑ/ |
| German | /a/, /aː/ |
| Portuguese | /a/, /ɐ/ |
| Saanich | /e/ |
| Spanish | /a/ |
| Turkish | /a/ |
English

In modern English orthography, the letter ⟨a⟩ represents at least seven different vowel sounds, here represented using the vowels of Received Pronunciation, with effects of ⟨r⟩ ignored and mergers in General American mentioned where relevant:
- the near-open front unrounded vowel /æ/ as in pad
- the open back unrounded vowel /ɑː/ as in father—merged with /ɒ/ as /ɑ/ in General American—which is closer to its original Latin and Greek sound[5]
- the open back rounded vowel /ɒ/ (merged with /ɑː/ as /ɑ/ in General American) in was and what[4]
- the open-mid back rounded vowel /ɔː/ in water
- the diphthong /eɪ/ as in ace and major, usually when ⟨a⟩ is followed by one, or occasionally two, consonants and then another vowel letter—this results from Middle English lengthening followed by the Great Vowel Shift
- a schwa /ə/ in many unstressed syllables, as in about, comma, solar
The double ⟨aa⟩ sequence does not occur in native English words, but is found in some words derived from foreign languages such as Aaron and aardvark.[8] However, ⟨a⟩ occurs in many common digraphs, all with their own sound or sounds, particularly ⟨ai⟩, ⟨au⟩, ⟨aw⟩, ⟨ay⟩, ⟨ea⟩ and ⟨oa⟩.
⟨a⟩ is the third-most-commonly used letter in English after ⟨e⟩ and ⟨t⟩, as well as in French; it is the second most common in Spanish, and the most common in Portuguese. ⟨a⟩ represents approximately 8.2% of letters as used in English texts;[9] the figure is around 7.6% in French[10] 11.5% in Spanish,[11] and 14.6% in Portuguese.[12]
Other languages
In most languages that use the Latin alphabet, ⟨a⟩ denotes an open unrounded vowel, such as /a/, /ä/, or /ɑ/. An exception is Saanich, in which ⟨a⟩—and the glyph ⟨Á⟩—stands for a close-mid front unrounded vowel /e/.
Other systems
- In the International Phonetic Alphabet, ⟨a⟩ is used for the open front unrounded vowel, ⟨ä⟩ is used for the open central unrounded vowel, and ⟨ɑ⟩ is used for the open back unrounded vowel.
- In X-SAMPA, ⟨a⟩ is used for the open front unrounded vowel and ⟨A⟩ is used for the open back unrounded vowel.
Other uses
- When using base-16 notation, A or a is the conventional numeral corresponding to the number 10.
- In algebra, the letter a along with various other letters of the alphabet is often used to denote a variable, with various conventional meanings in different areas of mathematics. In 1637, René Descartes "invented the convention of representing unknowns in equations by x, y, and z, and knowns by a, b, and c",[13] and this convention is still often followed, especially in elementary algebra.
- In geometry, capital Latin letters are used to denote objects including line segments, lines, and rays[6] A capital A is also typically used as one of the letters to represent an angle in a triangle, the lowercase a representing the side opposite angle A.[5]
- A is often used to denote something or someone of a better or more prestigious quality or status: A−, A or A+, the best grade that can be assigned by teachers for students' schoolwork; "A grade" for clean restaurants; A-list celebrities, A1 at Lloyd's for shipping, etc. Such associations can have a motivating effect, as exposure to the letter A has been found to improve performance, when compared with other letters.[14]
- A is used to denote size, as in a narrow size shoe,[5] or a small cup size in a brassiere.[15]
Related characters
Latin alphabet
- ⟨Æ æ⟩: a ligature of ⟨AE⟩ originally used in Latin
- ⟨A⟩ with diacritics: Å å Ǻ ǻ Ḁ ḁ ẚ Ă ă Ặ ặ Ắ ắ Ằ ằ Ẳ ẳ Ẵ ẵ Ȃ ȃ Â â Ậ ậ Ấ ấ Ầ ầ Ẫ ẫ Ẩ ẩ Ả ả Ǎ ǎ Ⱥ ⱥ Ȧ ȧ Ǡ ǡ Ạ ạ Ä ä Ǟ ǟ À à Ȁ ȁ Á á Ā ā Ā̀ ā̀ Ã ã Ą ą Ą́ ą́ Ą̃ ą̃ A̲ a̲ ᶏ[16]
- Phonetic alphabet symbols related to A—the International Phonetic Alphabet only uses lowercase, but uppercase forms are used in some other writing systems:
- ⟨Ɑ ɑ⟩: Latin alpha, represents an open back unrounded vowel in the IPA
- ⟨ᶐ⟩: Latin small alpha with a retroflex hook[16]
- ⟨Ɐ ɐ⟩: Turned A, represents a near-open central vowel in the IPA
- ⟨Λ ʌ⟩: Turned V, represents an open-mid back unrounded vowel in IPA
- ⟨Ɒ ɒ⟩: Turned alpha or script A, represents an open back rounded vowel in the IPA
- ⟨ᶛ⟩: Modifier letter small turned alpha[16]
- ⟨ᴀ⟩: Small capital A, an obsolete or non-standard symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet used to represent various sounds (mainly open vowels)
- ⟨A a ᵄ⟩: Modifier letters are used in the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet (UPA),[17] sometimes encoded with Unicode subscripts and superscripts
- ⟨a⟩: Subscript small a is used in Indo-European studies[18]
- ⟨ꬱ⟩: Small letter a reversed-schwa is used in the Teuthonista phonetic transcription system[19]
- ⟨Ꞻ ꞻ⟩: Glottal A, used in the transliteration of Ugaritic[20]
Derived signs, symbols and abbreviations
- ⟨ª⟩: ordinal indicator
- ⟨Å⟩: Ångström sign
- ⟨∀⟩: turned capital letter A, used in predicate logic to specify universal quantification ("for all")
- ⟨@⟩: At sign
- ⟨₳⟩: Argentine austral
- ⟨Ⓐ⟩: anarchy symbol
Ancestor and sibling letters
- ⟨𐤀⟩: Phoenician aleph, from which the following symbols originally derive:[21]
- ⟨Ա ա⟩: Armenian letter ayb
Other representations
Computing
The Latin letters ⟨A⟩ and ⟨a⟩ have Unicode encodings U+0041 A LATIN CAPITAL LETTER A and U+0061 a LATIN SMALL LETTER A. These are the same code points as those used in ASCII and ISO 8859. There are also precomposed character encodings for ⟨A⟩ and ⟨a⟩ with diacritics, for most of those listed above; the remainder are produced using combining diacritics.
Variant forms of the letter have unique code points for specialist use: the alphanumeric symbols set in mathematics and science, Latin alpha in linguistics, and halfwidth and fullwidth forms for legacy CJK font compatibility. The Cyrillic and Greek homoglyphs of the Latin ⟨A⟩ have separate encodings U+0410 А CYRILLIC CAPITAL LETTER A and U+0391 Α GREEK CAPITAL LETTER ALPHA.
Other
| NATO phonetic | Morse code |
| Alpha |
|

|

|

| |
| Signal flag | Flag semaphore | American manual alphabet (ASL fingerspelling) | British manual alphabet (BSL fingerspelling) | Braille dots-1 Unified English Braille |
Notes
- ^ Aes is the plural of the name of the letter. The plural of the letter itself is rendered As, A's, as, or a's.
References
- ^ "Latin alphabet". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ a b Simpson & Weiner 1989, p. 1.
- ^ McCarter 1974, p. 54.
- ^ a b c Hoiberg 2010, p. 1.
- ^ a b c d Hall-Quest 1997, p. 1.
- ^ a b c d Diringer 2000, p. 1.
- ^ Mankin, Jennifer; Simner, Julia (30 May 2017). "A Is for Apple: the Role of Letter-Word Associations in the Development of Grapheme-Colour Synaesthesia" (PDF). Multisensory Research. 30 (3–5): 409–446. doi:10.1163/22134808-00002554. ISSN 2213-4794. PMID 31287075. Retrieved 16 December 2023.
- ^ Gelb & Whiting 1998, p. 45
- ^ "Letter frequency (English)". Archived from the original on 4 March 2021. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ^ "Corpus de Thomas Tempé" (in French). Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 15 June 2007.
- ^ Pratt, Fletcher (1942). Secret and Urgent: The story of codes and ciphers. Garden City, NY: Blue Ribbon. pp. 254–5. OCLC 795065.
- ^ "Frequência da ocorrência de letras no Português" (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 3 August 2009. Retrieved 16 June 2009.
- ^ Tom Sorell, Descartes: A Very Short Introduction, (2000). New York: Oxford University Press. p. 19.
- ^ Ciani & Sheldon 2010, pp. 99–100.
- ^ Luciani, Jené (2009). The Bra Book: The Fashion Formula to Finding the Perfect Bra. Dallas: Benbella. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-933771-94-6.
- ^ a b c Constable, Peter (19 April 2004), L2/04-132 Proposal to Add Additional Phonetic Characters to the UCS (PDF), archived (PDF) from the original on 11 October 2017, retrieved 24 March 2018 – via www.unicode.org
- ^ Everson, Michael; et al. (20 March 2002), L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet Characters for the UCS (PDF), archived (PDF) from the original on 19 February 2018, retrieved 24 March 2018 – via www.unicode.org
- ^ Anderson, Deborah; Everson, Michael (7 June 2004), L2/04-191: Proposal to Encode Six Indo-Europeanist Phonetic Characters in the UCS (PDF), archived (PDF) from the original on 11 October 2017, retrieved 24 March 2018 – via www.unicode.org
- ^ Everson, Michael; Dicklberger, Alois; Pentzlin, Karl; Wandl-Vogt, Eveline (2 June 2011), L2/11-202: Revised Proposal to Encode "Teuthonista" Phonetic Characters in the UCS (PDF), archived (PDF) from the original on 11 October 2017, retrieved 24 March 2018 – via www.unicode.org
- ^ Suignard, Michel (9 May 2017), L2/17-076R2: Revised Proposal for the Encoding of an Egyptological YOD and Ugaritic Characters (PDF), archived (PDF) from the original on 30 March 2019, retrieved 8 March 2019 – via www.unicode.org
- ^ Jensen, Hans (1969). Sign, Symbol, and Script. New York: G. P. Putman's Sons.
- ^ "Hebrew Lesson of the Week: The Letter Aleph". 17 February 2013. Archived from the original on 26 May 2018. Retrieved 25 May 2018 – via The Times of Israel.
- ^ "Cyrillic Alphabet". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 26 May 2018. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ Silvestre, M. J. B. (1850). Universal Palaeography. Translated by Madden, Frederic. London: Henry G. Bohn. Retrieved 27 October 2020.
- ^ Frothingham, A. L. Jr. (1891). "Italic Studies". Archaeological News. American Journal of Archaeology. 7 (4): 534. JSTOR 496497. Retrieved 27 October 2020.
- ^ Steele, Philippa M., ed. (2017). Understanding Relations Between Scripts: The Aegean Writing Systems. Oxford: Oxbow. ISBN 978-1-78570-647-9. Retrieved 27 October 2020.
- ^ Fortson, Benjamin W. (2010). Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction (2nd ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-1-4443-5968-8. Retrieved 27 October 2020.
Bibliography
- "English Letter Frequency". Math Explorer's Club. Cornell University. 2004. Archived from the original on 22 April 2014. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- "Percentages of Letter Frequencies per Thousand Words". Trinity College. 2006. Archived from the original on 25 January 2007. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
- Ciani, Keith D.; Sheldon, Kennon M. (2010). "A Versus F: The Effects of Implicit Letter Priming on Cognitive Performance". British Journal of Educational Psychology. 80 (1): 99–119. doi:10.1348/000709909X466479. PMID 19622200.
- Diringer, David (2000). "A". In Bayer, Patricia (ed.). Encyclopedia Americana. Vol. I. Danbury, CT: Grolier. ISBN 978-0-717-20133-4.
- Gelb, I. J.; Whiting, R. M. (1998). "A". In Ranson, K. Anne (ed.). Academic American Encyclopedia. Vol. I. Danbury, CT: Grolier. ISBN 978-0-7172-2068-7.
- Hall-Quest, Olga Wilbourne (1997). "A". In Johnston, Bernard (ed.). Collier's Encyclopedia. Vol. I. New York: P. F. Collier.
- Hoiberg, Dale H., ed. (2010). "A". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 1. Chicago. ISBN 978-1-59339-837-8.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - McCarter, P. Kyle (1974). "The Early Diffusion of the Alphabet". The Biblical Archaeologist. 37 (3): 54–68. JSTOR 3210965. S2CID 126182369.
- Simpson, J. A.; Weiner, E. S. C., eds. (1989). "A". Oxford English Dictionary. Vol. I (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-861213-1.
External links
- History of the Alphabet Archived 10 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine
 Texts on Wikisource:
Texts on Wikisource:
- "A" in A Dictionary of the English Language by Samuel Johnson
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. I (9th ed.). 1878. p. 1.
- "A". The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
- "A". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. I (11th ed.). 1911. p. 1.
- "A". The New Student's Reference Work. 1914.
- "A". Collier's New Encyclopedia. 1921.










