This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2012) |
Thừa Thiên Huế | |
|---|---|
 Location of Thừa Thiên Huế within Vietnam | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 16°20′N 107°35′E / 16.333°N 107.583°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | North Central Coast |
| Capital | Huế |
| Government | |
| • People's Council Chair | Lê Trường Lưu |
| • People's Committee Chair | Nguyễn Văn Phương |
| Area | |
• Province | 4,947.11 km2 (1,910.09 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Province | 1,366,500 |
| • Density | 280/km2 (720/sq mi) |
| • Urban [2]: 115 | 819,100 |
| • Rural [2]: 117 | 547,400 |
| Demographics | |
| • Ethnicities | Vietnamese, Chăm, Tà Ôi, Cơ Tu, Bru, Thai |
| GDP[3] | |
| • Total | VND 47.428 trillion US$ 2.060 billion |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 49xxx |
| Area codes | 234 |
| ISO 3166 code | VN-26 |
| HDI (2020) | (34th) |
| Website | thuathienhue |
Thừa Thiên Huế is a southernmost coastal province in the North Central Coast region, the Central of Vietnam, approximately in the center of the country. It borders Quảng Trị to the north, Quảng Nam and Đà Nẵng to the south, Salavan of Laos to the west and the South China Sea to the east.
Thừa Thiên Huế has 128 km of coastline, 22,000 ha of lagoons and over 200,000 ha of forest. The province is located in the middle of thr North Central and South Central regions (including the South Central Coast and Central Highlands), and is transitional in many aspects: geology, climate, administrative division and local culture.
The province is widely known as Xứ Huế (the Land of Huế), after its provincial capital and largest city of Huế. The former imperial capital of the Nguyễn dynasty, Huế is today a popular tourist destination thanks to its extensive complex of imperial palaces, tombs and temples.
In recognition of Huế's rapid development, it is due to become Vietnam's sixth centrally-governed municipality in 2025. As part of this process, Huế will annex the rest of Thừa Thiên Huế province to streamline administration.[5]
History
The region's history dates back some 20,800 years according to archaeological findings from the Sa Huynh culture, as well as from relics in the region. Đại Việt became an independent nation around 938 AD of which territorial conflict lasts for about four centuries between the Đại Việt and the Champa. The two provinces then changed their names to Thanh and Hóa. In 1307, Đoàn Nhữ Hài was appointed by the emperor, Trần Anh Tông, to administer the area. Settlers from the north (Thanh Hóa) migrated south and integrated with the people of the Kingdom of Champa. During this time, the settlement of Hoa Chau province began, which included the area of present-day Thừa Thiên.
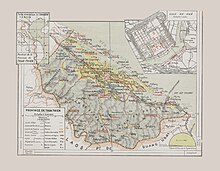
Between the settlement of Thuận Hóa (1306) to the founding of Phú Xuân (1687), there were conflicts and uncertainties for the local people, which including the fall of the Trần Dynasty to the renaissance of the Hồ dynasty. Thuận Hóa and Phú Xuân became the location of the Đại Việt kingdom once Nguyễn Hoàng was appointed head of Thuận Hóa (1511–1558). Lord Nguyễn Hoàng (1558–1613) established bases at Ai Tu, Tra Bat and Dinh Cat, while his lords moved palaces to Kim Long (1636), where they would eventually base their operations in Phú Xuân (1687). The Nguyễn lords ruled the area until the Trinh clan conquered it in 1775. The farmers' movement led by the Tây Sơn brothers gained momentum in 1771. The Tây Sơn insurgent army conquered the Nguyễn capital after winning the battle of Phú Xuân in 1786, where they continued north and overthrew the Trinh Dynasty. In Phú Xuân, Nguyễn Huệ appointed himself king; with internal strife within the Tây Sơn Movement and the death of Nguyễn Huệ (1792), Nguyễn Ánh took advantage of the situation and conquered Gia Định with the support of foreign forces. He became attached to the Tây Sơn movement and took over Phú Xuân and the throne, thereby choosing the dynasty title of Gia Long (1802).
After the French conquest of Vietnam, Phú Xuân was officially renamed to Huế in 1899. It remained the capital of Annam, one of French Indochina's six constituent regions, until the State of Vietnam was established in 1949.[6] Prior to 1975, the province was known simply as Thừa Thiên.
The province suffered from heavy fighting during the Vietnam War, as it was the second-most northerly province of the South Vietnam, close to the North Vietnamese border (DMZ) at the 17th parallel. 2,893 U.S. soldiers died in Thừa Thiên, more than in any other Vietnamese province.[7] The Massacre at Huế occurred here; an estimated 2,800 to 6,000 civilians and South Vietnamese army prisoners of war were slaughtered by the Việt Cộng during the Tet Offensive of 1968. The province saw a large influx of northern settlers soon after the Vietnam War ended, as with the rest of the former South. Thừa Thiên Huế and neighboring Quảng Nam province suffered greatly from severe flooding in 1999.
Geography
The Perfume River (called Sông Hương or Hương Giang in Vietnamese) passes through the center of province. The province also accommodates the Tam Giang–Cau Hai lagoon, the largest lagoon in Southeast Asia, which is 68 kilometres (42 mi) long with a surface area of 220 square kilometres (85 sq mi). The province comprises four different zones: a mountainous area, hills, plains and lagoons separated from the sea by sandbanks. It has 128 kilometres (80 mi) of beaches. The mountains, covering more than half the total surface of the province, are along the west and southwest border of the province, their height varying from 500 metres (1,600 ft) to 1,480 metres (4,860 ft). The hills are lower, between 20 metres (66 ft) and 200 metres (660 ft), with some points at 400 metres (1,300 ft), and occupy about a third of the province's area, between the mountains and the plains. The plains account for about a tenth of the surface area, with a height of only up to 20 metres (66 ft) above sea level. Between the hills are the lagoons which occupy the remaining 5% of the province's surface area.[8]
Bạch Mã National Park is a protected area near the city of Hué. It covers 220 square kilometres (85 sq mi) and comprises three zones: a strictly protected core area, an administrative area and a buffer zone. The climate is similar to central Vietnam in general: a tropical monsoon climate. In the plains and in the hills, the average annual temperature is 25 °C (77 °F), but in the mountains only 21 °C (70 °F) (statistical yearbook 2004). The cool season is from November to March with cold northeasterly winds. The lowest average monthly temperature is in January: 20 °C (68 °F). In the cool season temperatures can fall to 12 °C (54 °F) in the plains and the relative humidity is high, between 85% and 95%. Then follows a warmer period from April to September with average monthly temperatures up to 29 °C (84 °F) in July, reaching up to 41 °C (106 °F) at times. It is very humid in July but relative humidity is lower, sometimes down to 50%.[9]
The annual precipitation in the province is 3,200 millimetres (130 in), but there are important variations. Depending on the year, the annual average may be 2,500 millimetres (98 in) to 3,500 millimetres (140 in) in the plains and 3,000 millimetres (120 in) to 4,500 millimetres (180 in) in the mountains. In some years the rainfall may be much higher and reach more than 5,000 millimetres (200 in) in the mountains.[8] The rainy season is from September to December—about 70% of the precipitation occurring in those months. Rainfall often occurs in short heavy bursts which can cause flooding and erosion, with serious social, economic and environmental consequences. The historic floods of November 1999 led to 600 deaths and affected 600,000 homes.[10][11]
Flora and fauna
A remote region known as the "Green Corridor" is home to many rare species. New species of snake, butterfly, and orchid have been found there in 2005 and 2006, as stated by Chris Dickinson of the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) on 26 September 2007.[12][13] The scientists discovered 11 new species of plants and animals, including a snake, two butterflies and five leafless orchid varieties. The new snake species is a white-lipped keelback (Hebius leucomystax). The new butterfly species are a skipper from the genus Zela, and the other from Satyrinae. The new plant species also include one in the genus Aspidistra, and a poisonous Arum perennial.[14]
Administrative divisions
Thừa Thiên Huế is subdivided into 9 district-level sub-divisions:[15]
- 6 districts:
- 2 district-level towns:
- 1 provincial city:
- Huế (capital)
They are further subdivided into 8 commune-level towns (or townlets), 105 communes, and 39 wards.
Demographics
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
The average population of the province is 1.143.572, which consist of approximately 567.253 males and 576.319 females. The rural population is approximately 587.516 while the urban population is 556.056 (2015).[16]
| Largest cities or townships in Thừa Thiên Huế province (2015) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Type | District | Population |
| 1 | Huế | City | 354,124 | |
| 2 | Hương Trà | Town | 116,147 | |
| 3 | Hương Thủy | Town | 101,353 | |
| 4 | Thuận An | Township | Phú Vang district | 21,220 |
| 5 | Phú Đa | Township | Phú Vang district | 12,381 |
| 6 | Lăng Cô | Township | Phú Lộc district | 12,177 |
| 7 | Phú Lộc | Township | Phú Lộc district | 10,613 |
| 8 | Sịa | Township | Quảng Điền district | 10,583 |
| 9 | A Lưới | Township | A Lưới district | 7,393 |
| 10 | Phong Điền | Township | Phong Điền district | 6,743 |
| 11 | Khe Tre | Township | Nam Đông district | 3,818 |
Economy
The retail sales of goods and services (trade, hotel, restaurant, tourism) in the province is 10,960.6 billion đồng, or 0.9 percent of national GDP. This is compared with 12.7 percent for Hanoi and 23.5 percent for Ho Chi Minh City (2009).[17] The province has more than 120 km of coastline, which provides for a seafood industry that produces over 40,000 tonnes per year, consisting of over 500 species of fish.[18]
There are more than 100 mines for minerals and non-mineral resources with the majority consisting of limestone, granite and kaolin.[19] Arts and crafts (wood works, fabrics, furnitures, paper arts, pottery, etc.), literature (textbooks), and spicy cuisines (includes dry goods and vegetarian fare) are the main exports of this region. Exquisite custom-made áo dài (Vietnamese long dress) and nón lá (conical hat) are popular souvenirs for foreign visitors and overseas Vietnamese. Toy-making, lantern design, paper flower crafting, and figurine-making are traditional local crafts. Fruits such as rambutan, jackfruit, lychee, durian, dao, dragon fruit, star fruit, mangosteen, coconut, and kumquat are grown in this area, thanks to substantial rainfall received each year.
Huế is home to a vast number of historically significant buildings, largely a legacy from its time as a capital of the Nguyễn dynasty (1802–1945), including the Imperial Citadel, the Flag Tower, the Royal Palace, and the Royal Tombs. Huế's Forbidden Purple City was once reserved solely for the royal family's use; it was severely damaged during the Vietnam War. Outside the city is the religious site known as Nam Giao Hill ("Heaven's Altar"). Hue Brewery Ltd is located on the Hương Giang river, a popular brand widely known across Vietnam. The Brewery is a joint state-private partnership founded in 1990, with an initial investment of US$2.4 million and a capacity of 3 million liters per year, which has since grown to a capacity of 100 million liters per year in 2007.[20]
Transportation
Vietnam's National Route 1, which runs the entire length of the nation from north to south, passes through Huế. Huế and Đà Nẵng are the main intermediate stops on the railway line from Hanoi to Ho Chi Minh City. This province is served by two sea ports, Thuận An Port and Chân Mây Port.
Phu Bai International Airport, the province's sole airport, is situated 15 km south of Huế; it ranks fourth in passenger numbers among Vietnam's airports. While a new terminal was completed in 2023 to receive international flights, Phu Bai currently still only has direct flights to domestic destinations; the first international routes to Kunming, Taipei and Seoul are planned to be inaugurated in 2025.[21]
Education
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
This province is home to Huế University (e.g.: Huế Economic University, Huế Medicine University, Huế Pedagogical University, Huế Forestry and Agriculture University, Huế University of Sciences, Huế University of Arts, Huế Conservatory of Music and Huế College of Foreign Languages). As of 2009 the province had 190 schools, 1302 classrooms, 2184 teachers and 36,200 pupils.[22]
The most famous high school in Thua Thien Hue province is Quốc Học – Huế High School for the Gifted. It is well known for its high quality of education and French heritage.
International relations
Sister cities
 Namur, Belgium
Namur, Belgium Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Yogyakarta, Indonesia Gyeongju, South Korea
Gyeongju, South Korea Honolulu, United States
Honolulu, United States New Haven, United States
New Haven, United States
Notable residents
- Thích Nhất Hạnh, Buddhist monk
- Trịnh Công Sơn, composer
- Ngô Viết Thụ, architect
- Ho Ngoc Ha, singer and actress
Etymology
The province's name derives from the Sino-Vietnamese 承天順化.[citation needed]
References
- ^ Biểu số 4.3: Hiện trạng sử dụng đất vùng Bắc Trung Bộ và Duyên hải miền Trung năm 2022 [Table 4.3: Current land use status in the North Central and South Central Coast regions in 2022] (PDF) (Decision 3048/QĐ-BTNMT) (in Vietnamese). Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (Vietnam). 18 October 2023. – the data in the report are in hectares, rounded to integers
- ^ a b c General Statistics Office of Vietnam (2023). Statistical Yearbook of Vietnam 2022 (PDF). Statistical Publishing House (Vietnam). ISBN 978-604-75-2429-7.
- ^ "Tình hình kinh tế, xã hội Thừa Thiên - Huế năm 2018". Cổng thông tin điện tử tỉnh Thừa Thiên - Huế. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ "Human Development Index by province(*) by Cities, provincies and Year". General Statistics Office of Vietnam. Retrieved September 28, 2024.
- ^ Đăng, Hiếu; Võ, Thạnh (2 November 2024). "Hình hài TP Huế trực thuộc trung ương năm 2025". VnExpress. Retrieved 12 November 2024.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Thua Thien Hue some facts on historical establishment and development". Thừa Thiên Huế province government website. Archived from the original on 3 October 2011. Retrieved 26 September 2011.
- ^ http://www.rjsmith.com/kia_tbl.html" Archived 2010-04-15 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Atlas des lagunes de Thừa Thiên Huế, 2003
- ^ Villegas 2004
- ^ Villegas, Piero (2004). "Flood modelling in Perfume river basin, Hue province, Vietnam" (PDF).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Integrated Management of Lagoon Activities Project - an FAO sustainable lagoon management project in the province.
- ^ Recent news release by WWF
- ^ The Green Corridor Project Archived 2007-09-15 at the Wayback Machine - a WWF conservation endeavor located in the province.
- ^ "Yahoo.com, Scientists find new species in Vietnam".
- ^ "Districts & Hue City". About Government / Administrative system. ThuaThienHue province. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ^ "Population and Employment". Monthly Statistical Information. General Statistics Office of Vietnam. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ^ "Retail sales of goods and services at current prices by province". Statistical Data. General Statistics Office of Vietnam. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ^ "Potentials and perspective". About Thừa Thiên Huế Province. Thừa Thiên Huế Portal. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ^ "Geographical conditions and natural resources". About Thừa Thiên Huế Province. Thừa Thiên Huế Portal. Archived from the original on 31 March 2012. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ^ "About Us". Hue Brewery Ltd. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ^ "Thừa Thiên-Huế: Tăng cường thu hút du khách qua đường hàng không". VietnamPlus. 5 September 2024. Retrieved 12 November 2024.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "General Statistics Office Of Vietnam". Gso.gov.vn. 13 August 2010. Retrieved 13 August 2012.




























